Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2024; 12(16): 2887-2893
Published online Jun 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i16.2887
Published online Jun 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i16.2887
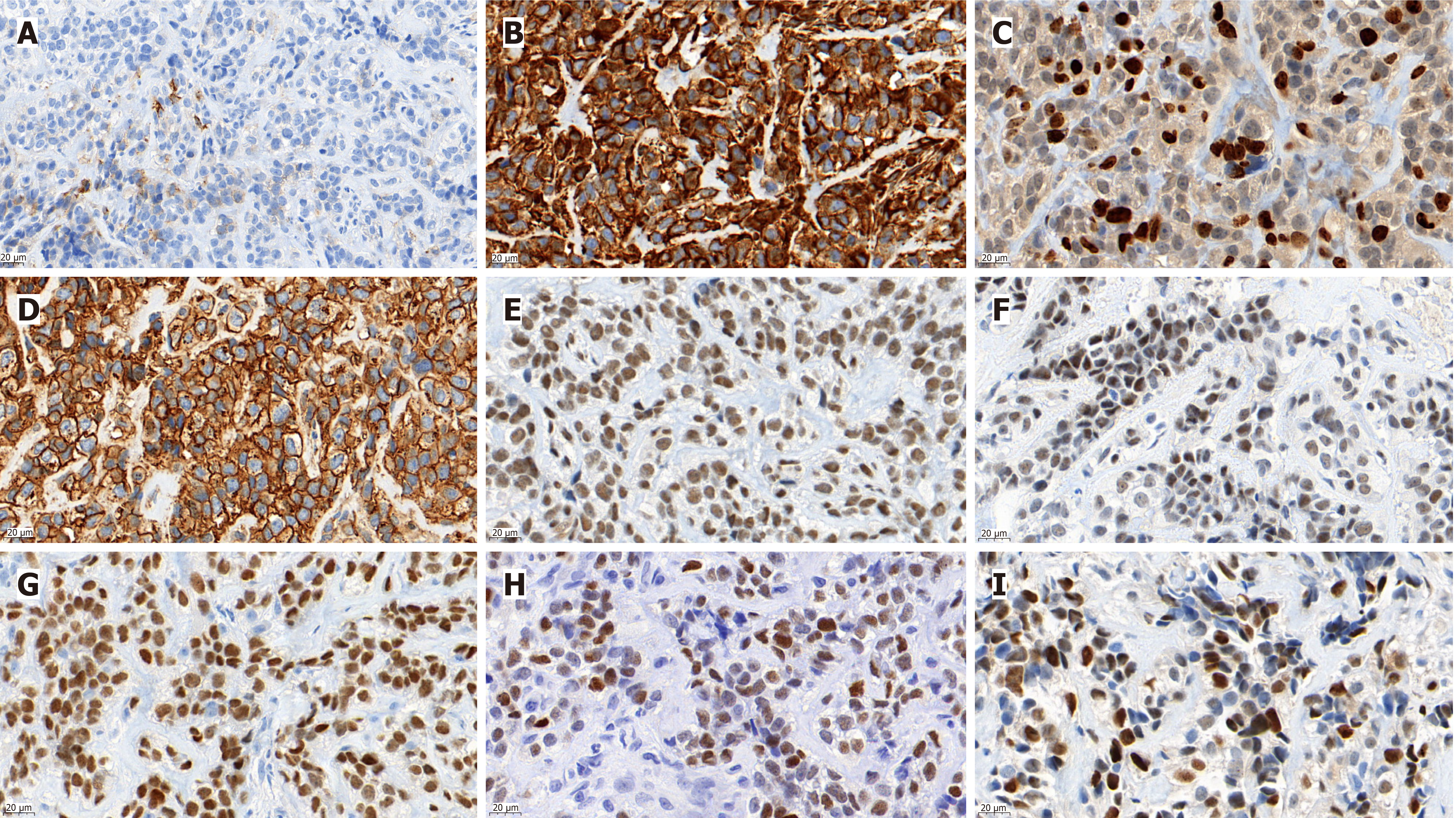
Figure 1 Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were positive for Vimentin, CD99, NKX2.
2, NKX3.1, INI-1, CyclinD1 and FLI1, and focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen. A: Immunohistochemistry showed a small number of epithelial membrane antigen positives in tumor cells; B: The tumor cells were diffusely positive for Vimentin; C: About 25% of the tumor cells were positive for Ki67; D: Tumor cells were also permeated with CD99 positivity; E-I: Positive for INI1, FLI1, NKX2.2, NKX3.1, and CyclinD1, respectively. Scale bars are in the lower left corner of each image (original magnification, 630 ×).
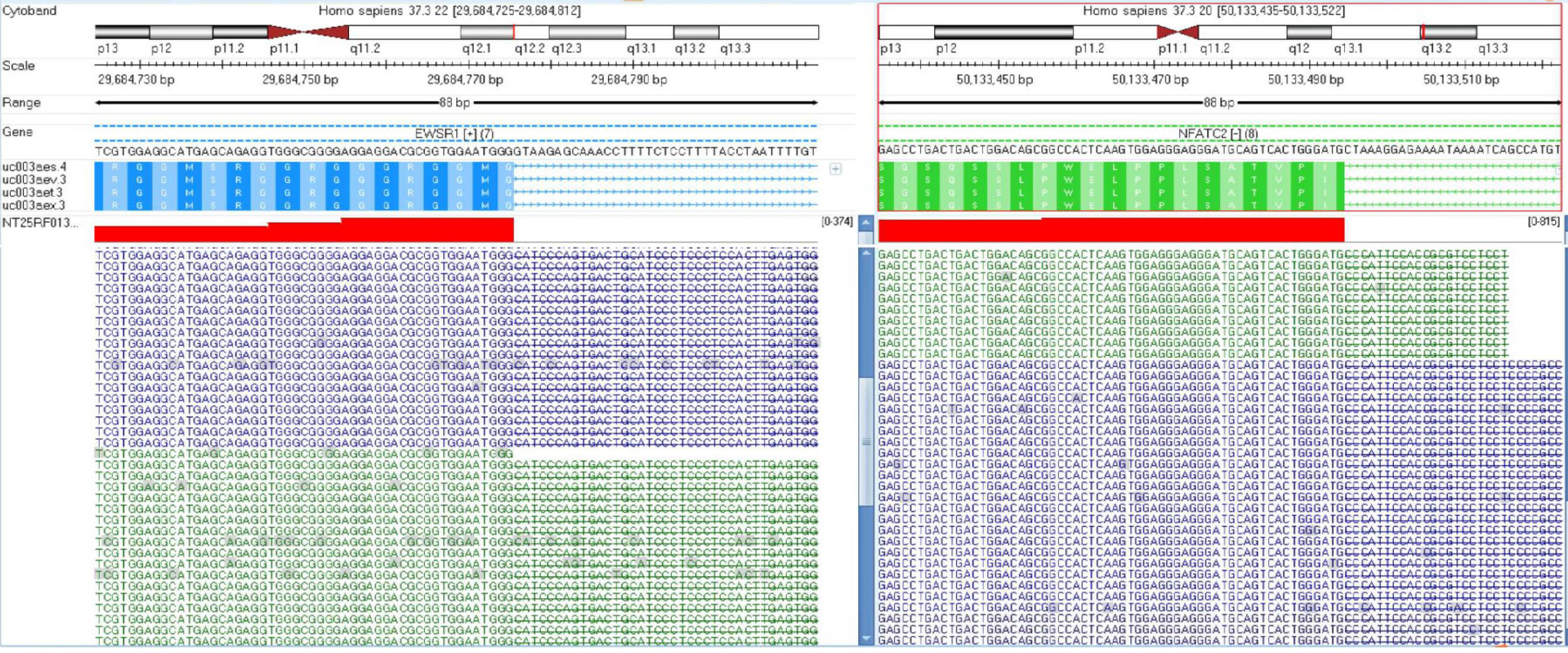
Figure 2 Next-generation sequencing revealed t(20;22)(q13.
2;q12.2) EWSR1-NFATC2 gene fusion.
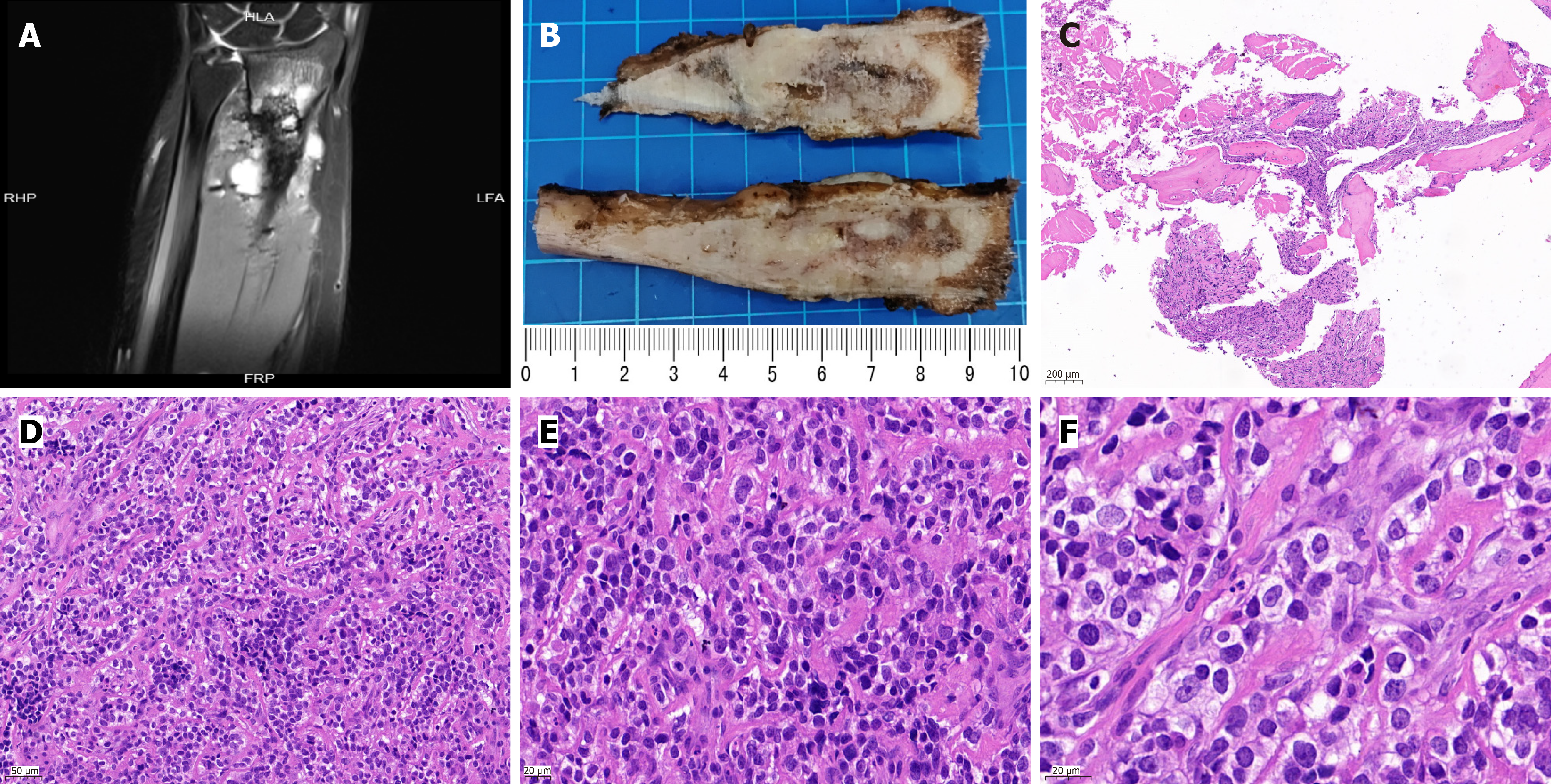
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance imaging plain scan + enhancement (3.
0T) indicated the location of the lesion. We could observe the tumor section in the surgical specimen, and the structure and morphology of tumor cells under the microscope. A: Multiple oval and patchy abnormal signals were found in the original surgical area of the left forearm and multiple abnormal signals were found in and around the distal bone on the plain and enhanced (3.0T) magnetic resonance imaging of the unilateral upper limb; B: The tumor involved the medullary cavity, and the texture of the cut surface was uneven and fishy; C: Tumor cells were seen in the mature bone tissue, original magnification, 50 ×; D: Tumor cells were of medium size and arranged in small nests with fibrous septa between the nests, original magnification, 200 ×; E and F: The tumor cells had clear cytoplasm, uniform nuclear morphology, dense chromatin, visible nucleoli, and rare mitotic figures. original magnification, 400 × (E), 630 × (F). Scale bars are in the lower left corner of each image.
- Citation: Hu QL, Zeng C. Clinicopathological analysis of EWSR1/FUS::NFATC2 rearranged sarcoma in the left forearm: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(16): 2887-2893
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i16/2887.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i16.2887