Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 6, 2024; 12(16): 2847-2855
Published online Jun 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i16.2847
Published online Jun 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i16.2847
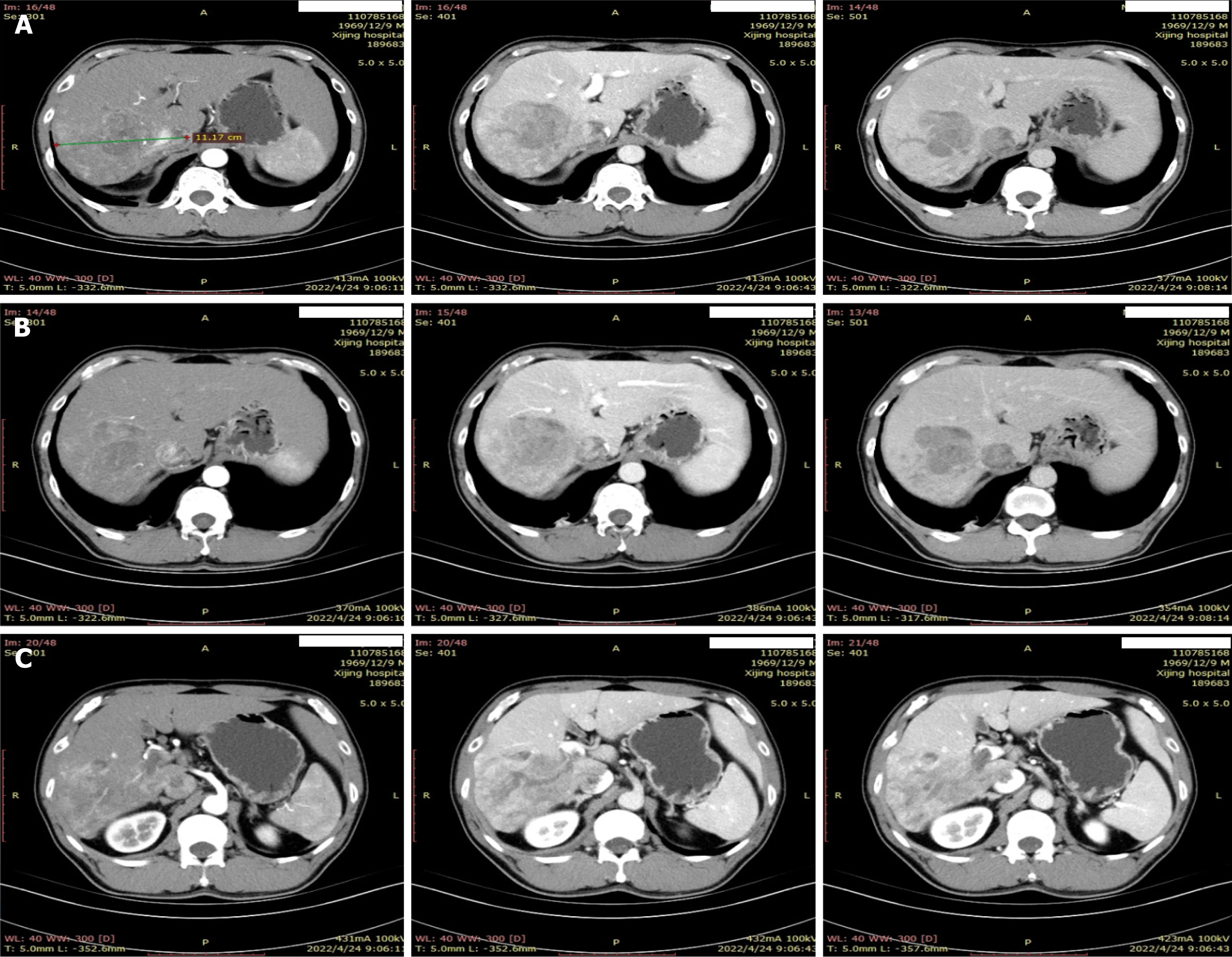
Figure 1 Radiological assessment of primary nodule at diagnosis.
A: Primary tumor; B: Portal vein tumor thrombus; C: Inferior vena cava thrombosis.
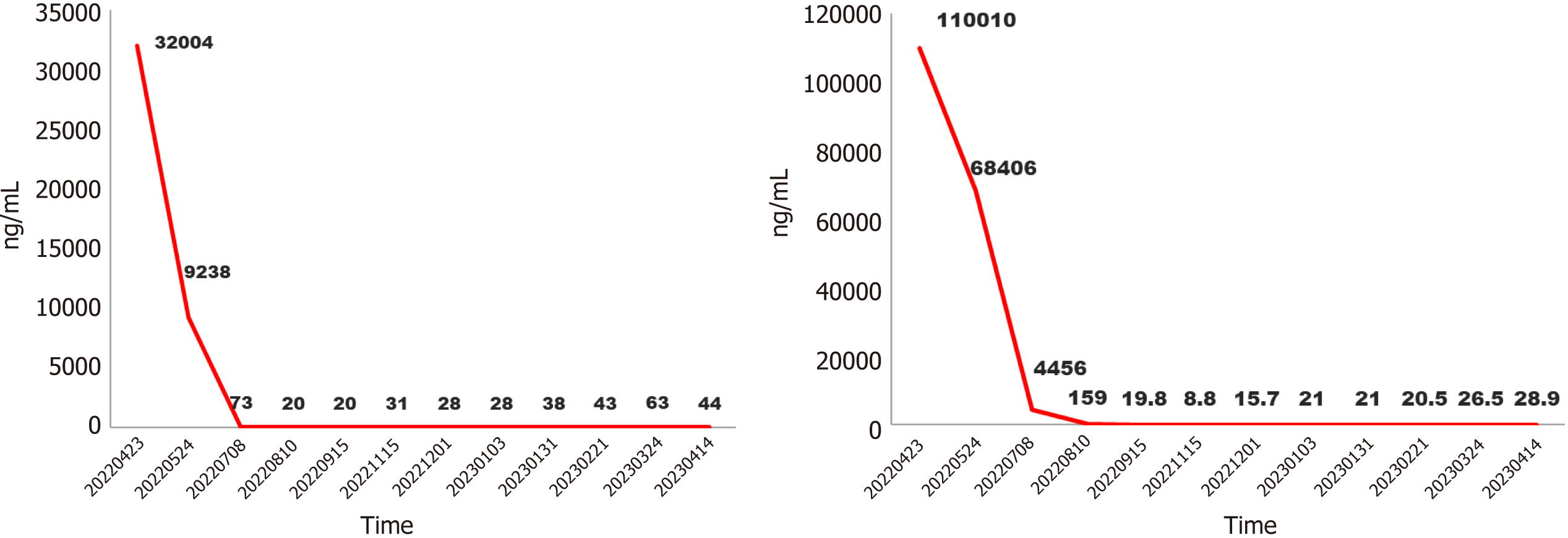
Figure 2 Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II and alpha fetoprotein level during treatment.
PIVKA-II: Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II; AFP: Alpha fetoprotein.
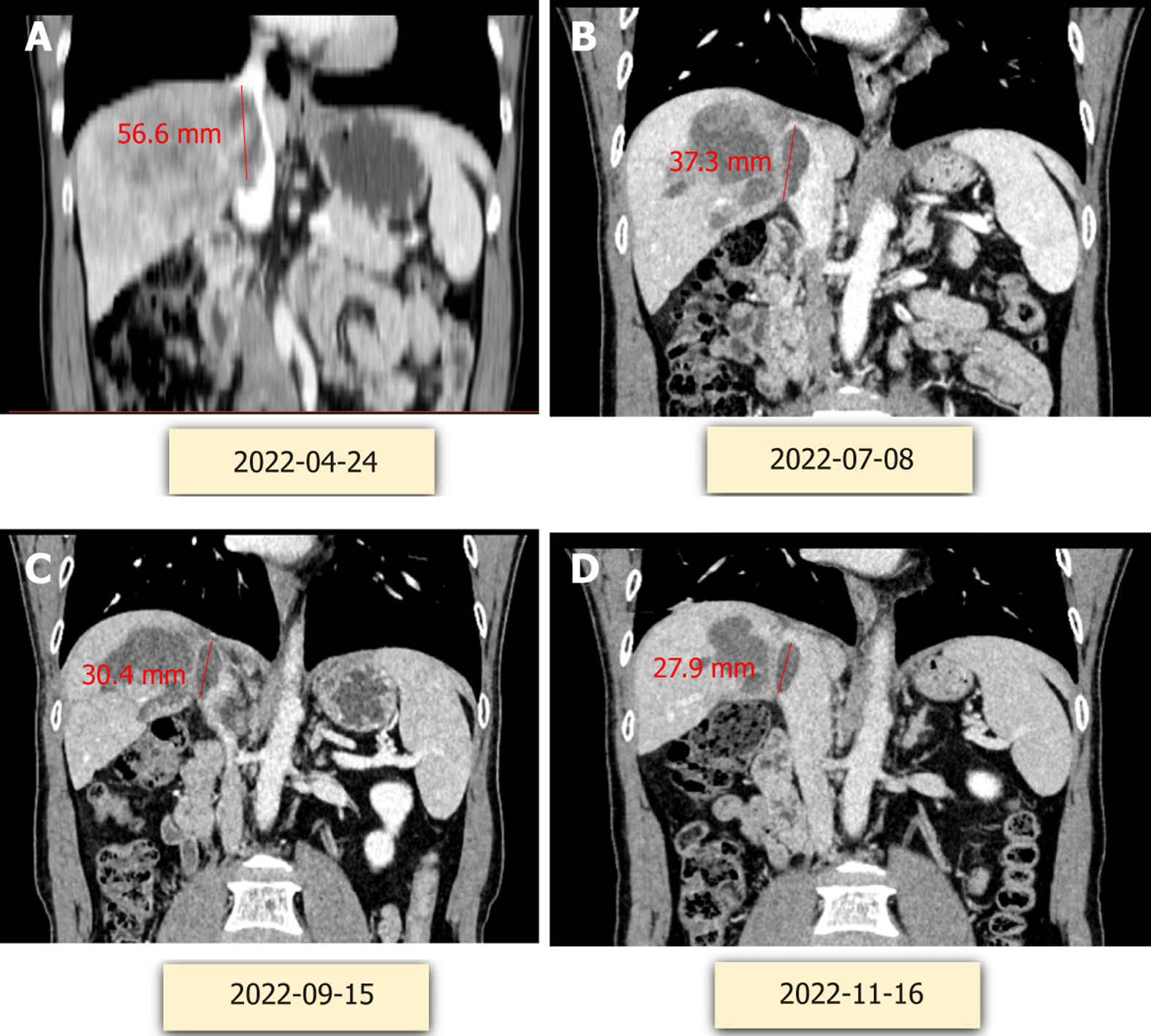
Figure 3 Tumor changes during treatment.
A: April 24, 2022; B: July 28, 2022; C: September 15, 2022; D: November 16, 2022.
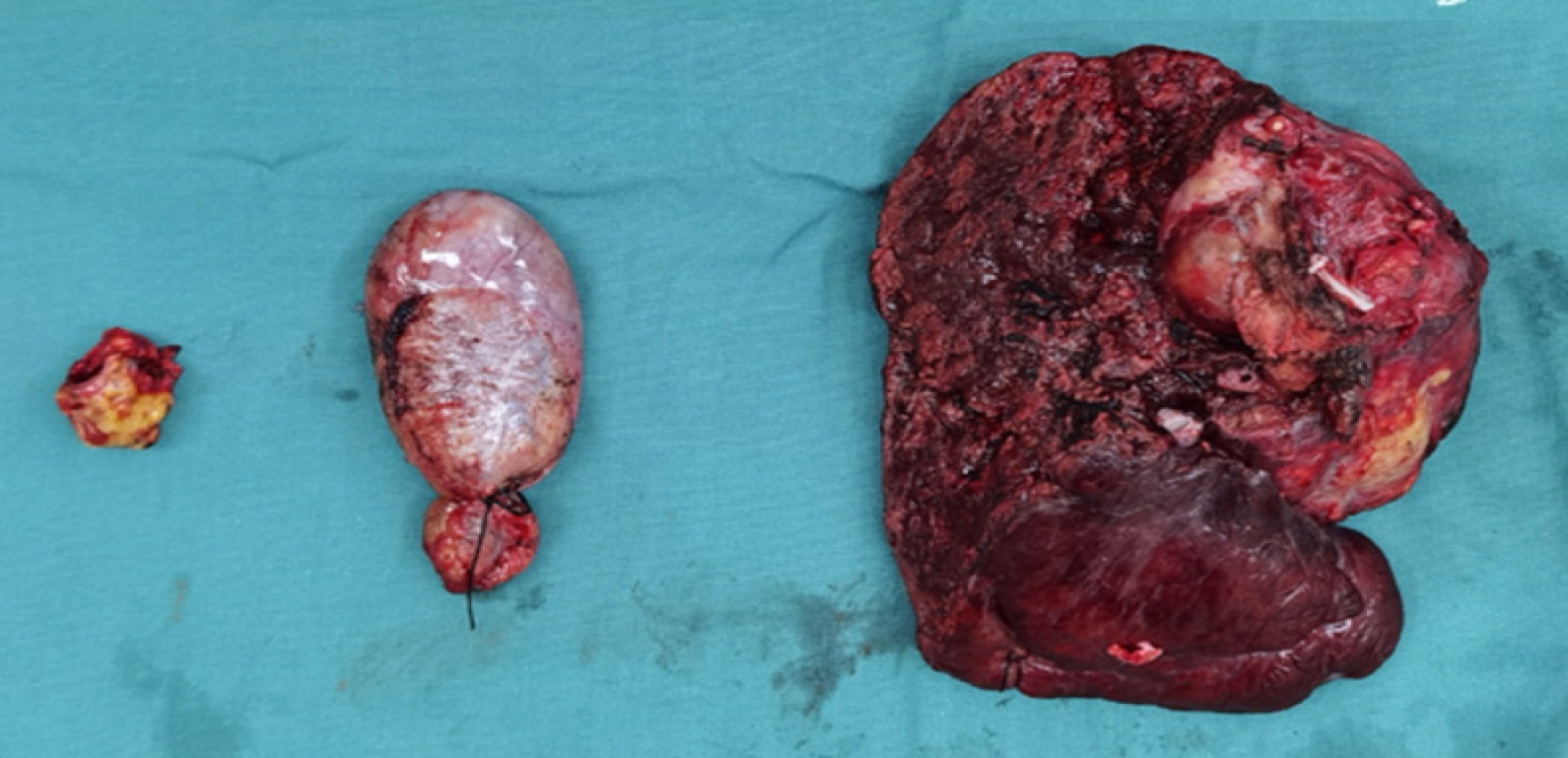
Figure 4 Tumour tissue removed by surgery.
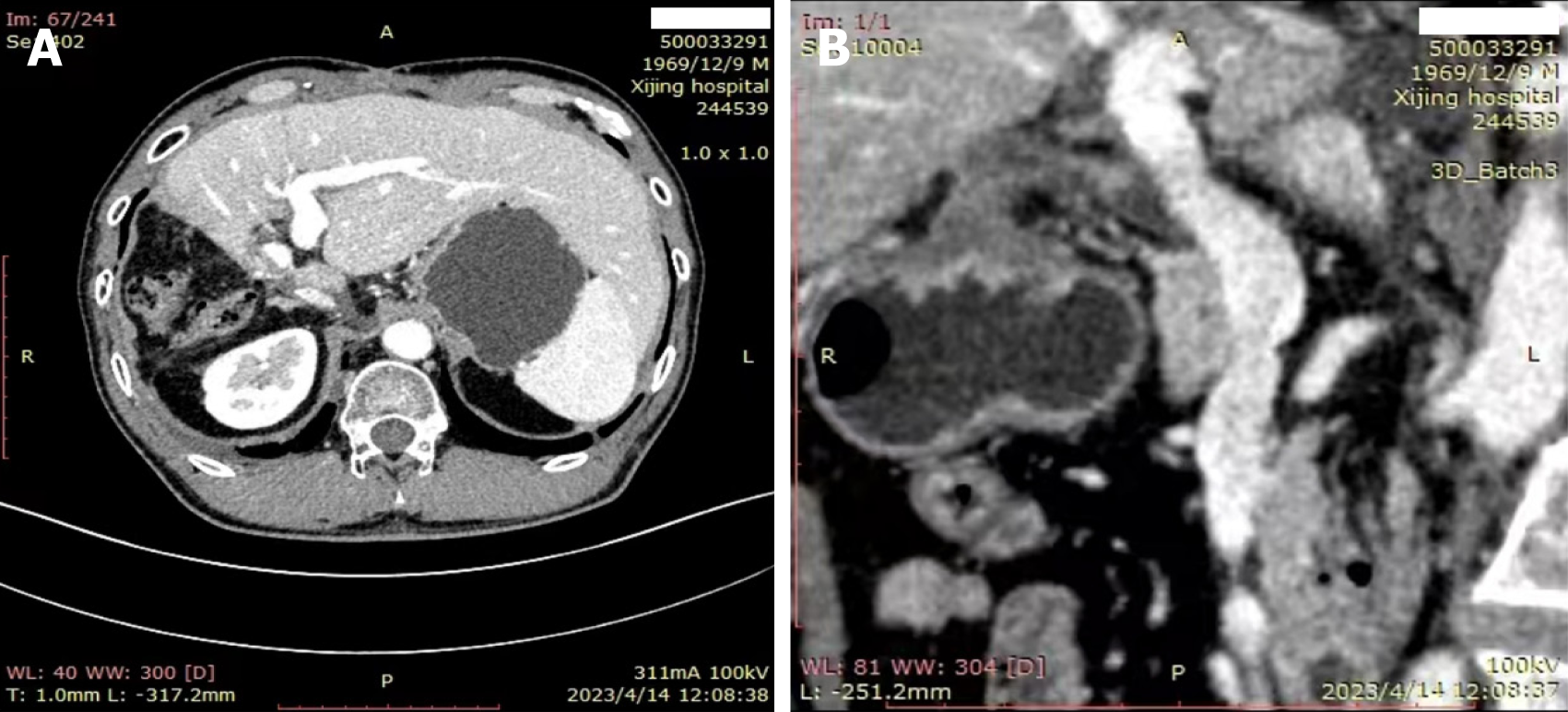
Figure 5 Radiological assessment after surgery.
A: Abdominal computed tomography (CT); B: Abdominal CT.
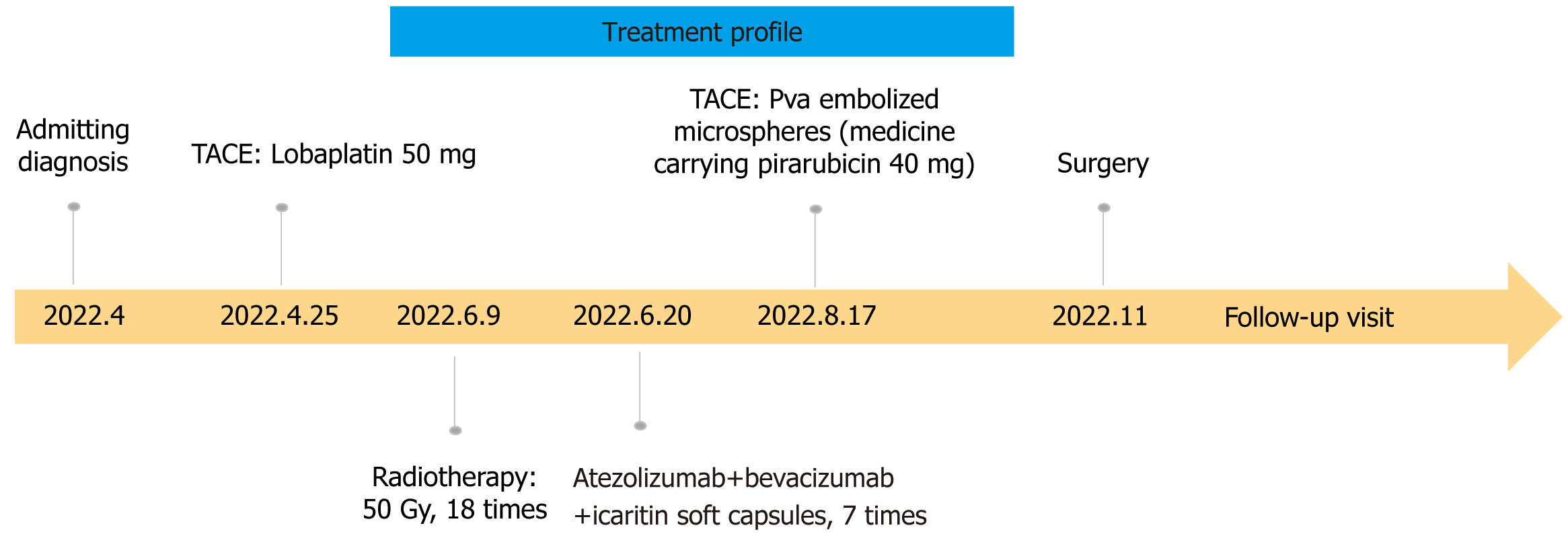
Figure 6 Treatment profile.
TACE: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
- Citation: Song WJ, Xu J, Nie Y, Li WM, Li JP, Yang L, Wei MQ, Tao KS. Conversion therapy of a giant hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombus and inferior vena cava thrombus: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(16): 2847-2855
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i16/2847.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i16.2847