Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2024; 12(12): 2109-2115
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i12.2109
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i12.2109
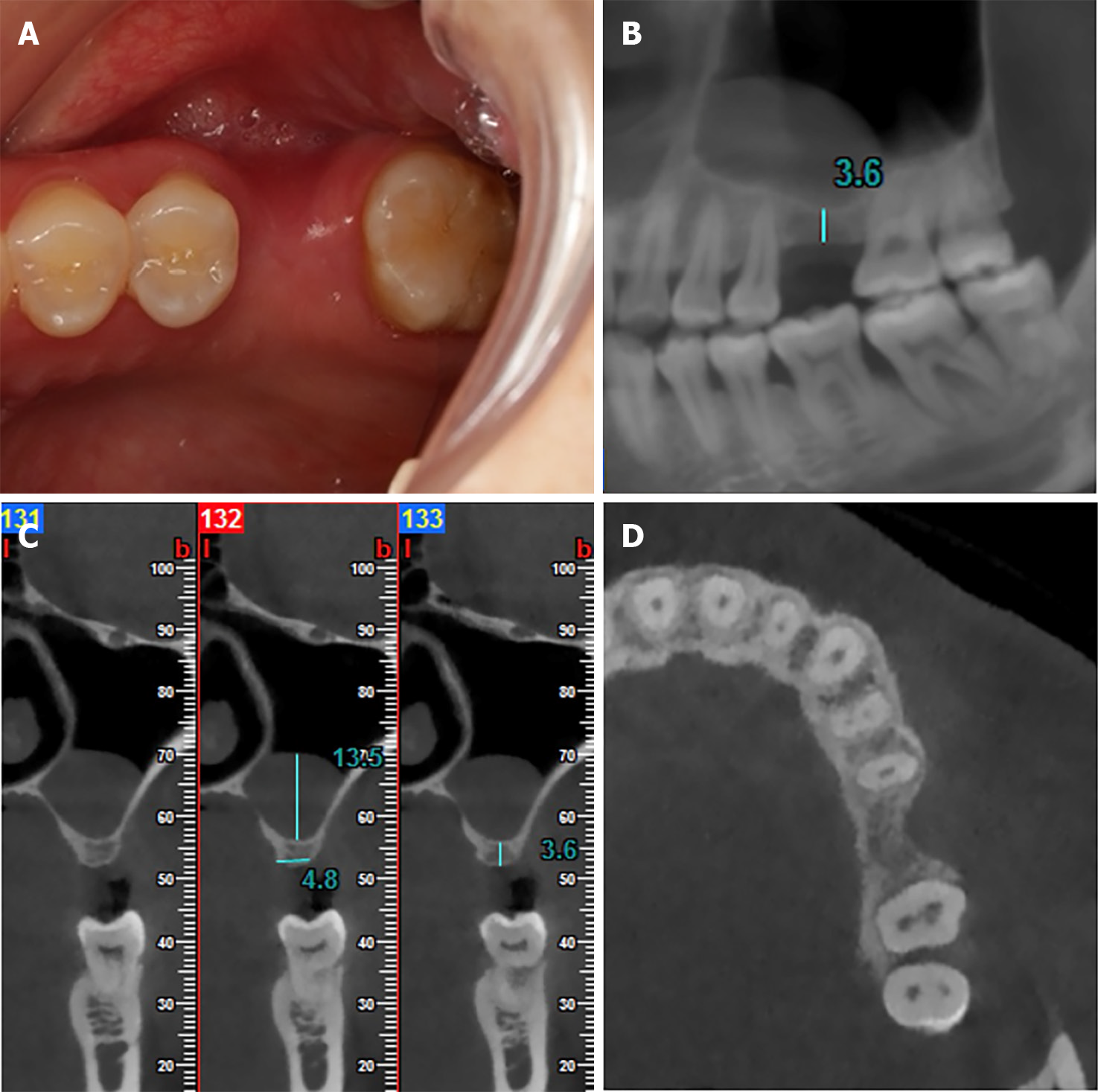
Figure 1 Preoperative occlusal view and cone beam computed tomography images of tooth 26.
A: Occlusal view of tooth 26 with the horizontal bone deficiency; B: Coronal cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) image showed the mesio-distal dimensions and the region of pseudocyst; C: Sagittal CBCT image showed the available bone heights of tooth 26 and the height of pseudocyst; D: Horizontal CBCT image showed horizontal bone deficiency of tooth 26.
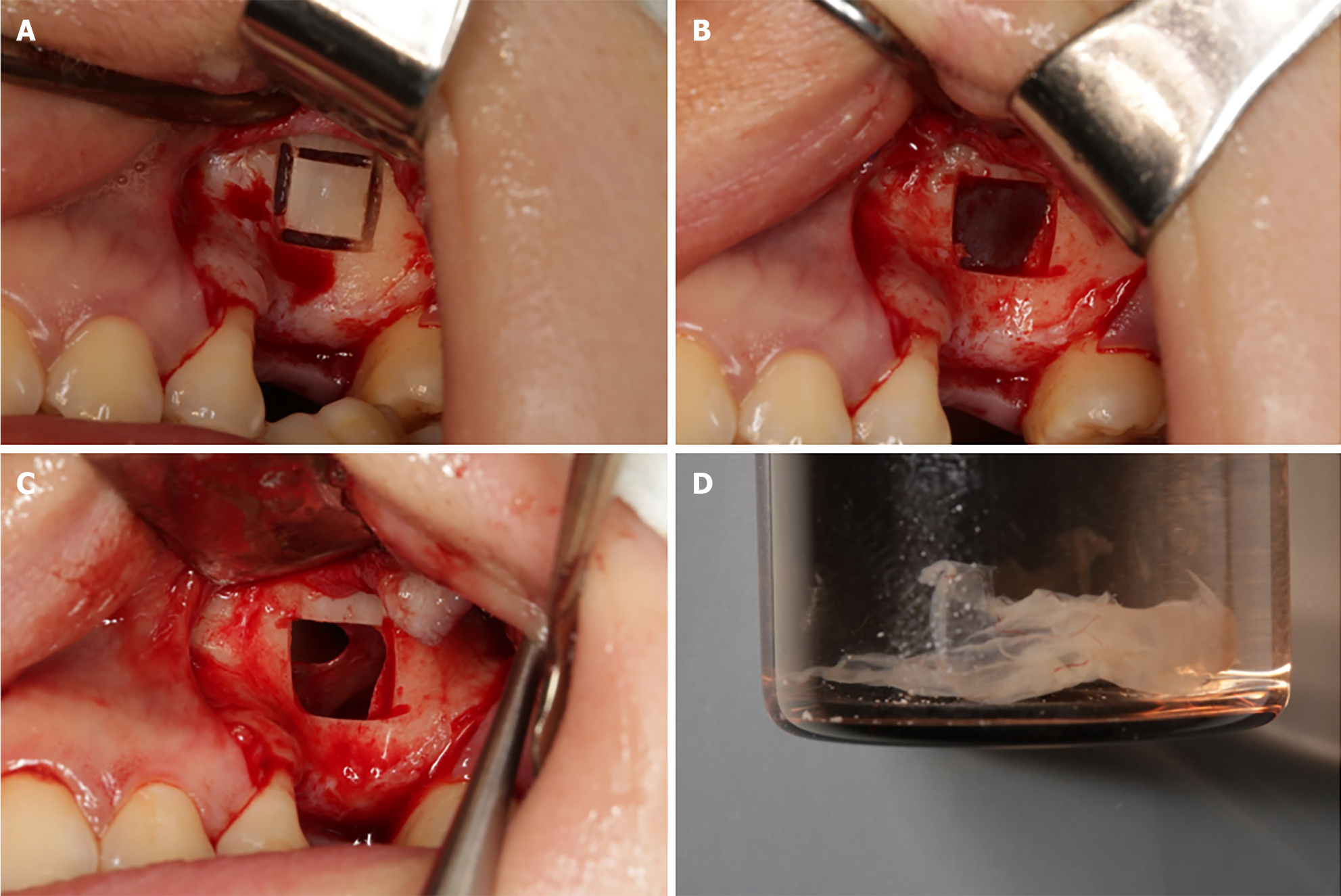
Figure 2 The surgical procedure.
A: Ultrasonic bone scalpel delineating the bone window; B: Lifting the bone window to expose the maxillary sinus mucosa; C: Intentionally rupturing the maxillary sinus floor mucosa, revealing a perforation; D: Removed maxillary sinus pseudocyst.
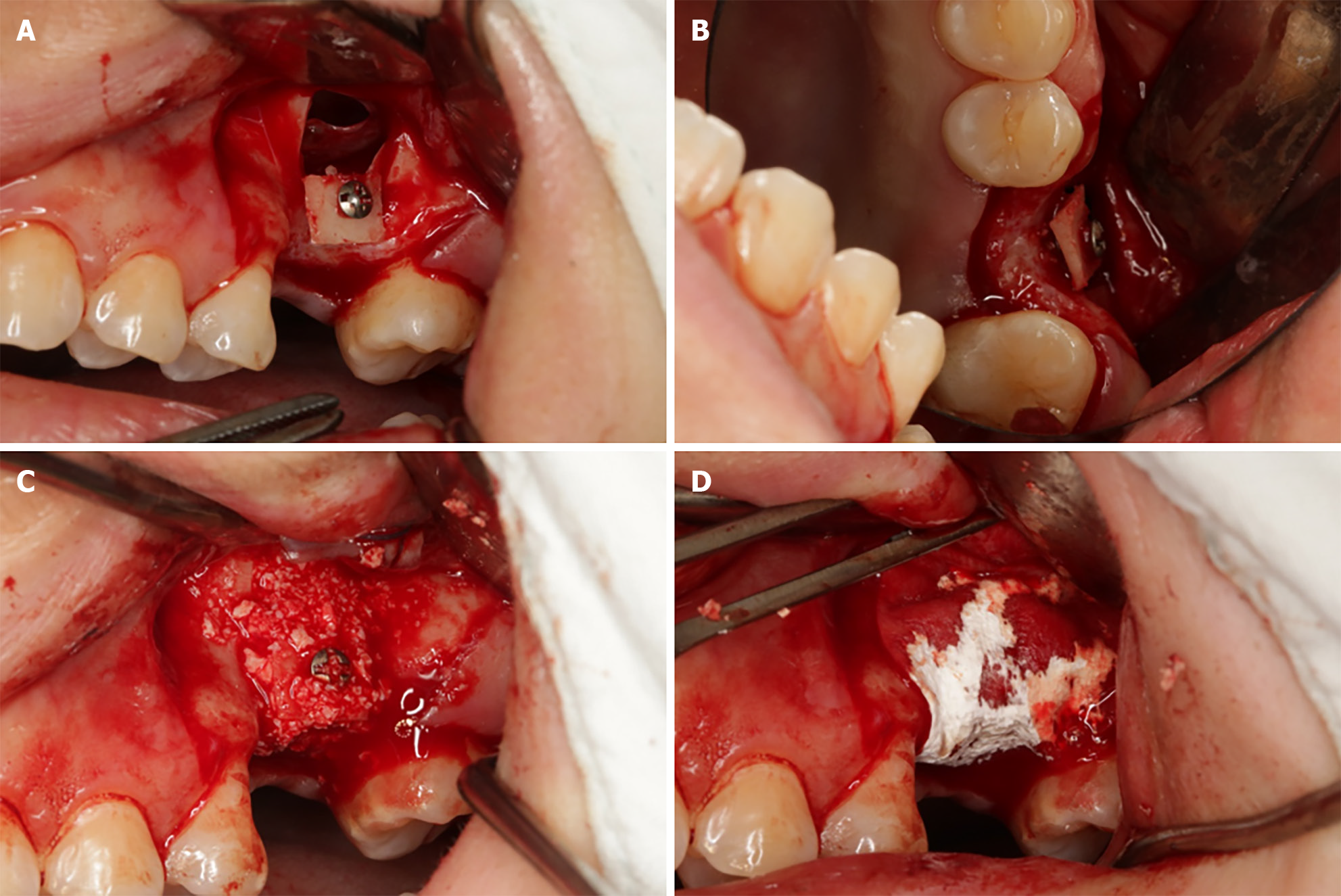
Figure 3 Intraoral photo demonstrating horizontal bone augmentation using cortical bone tenting technique.
A: Fixation of the bone window with titanium screw; B: Maintaining a certain distance between the bone window and the buccal aspect of the alveolar ridge; C: Filling the gap with DBBM; D: Covering the defect area with a collagen membrane.
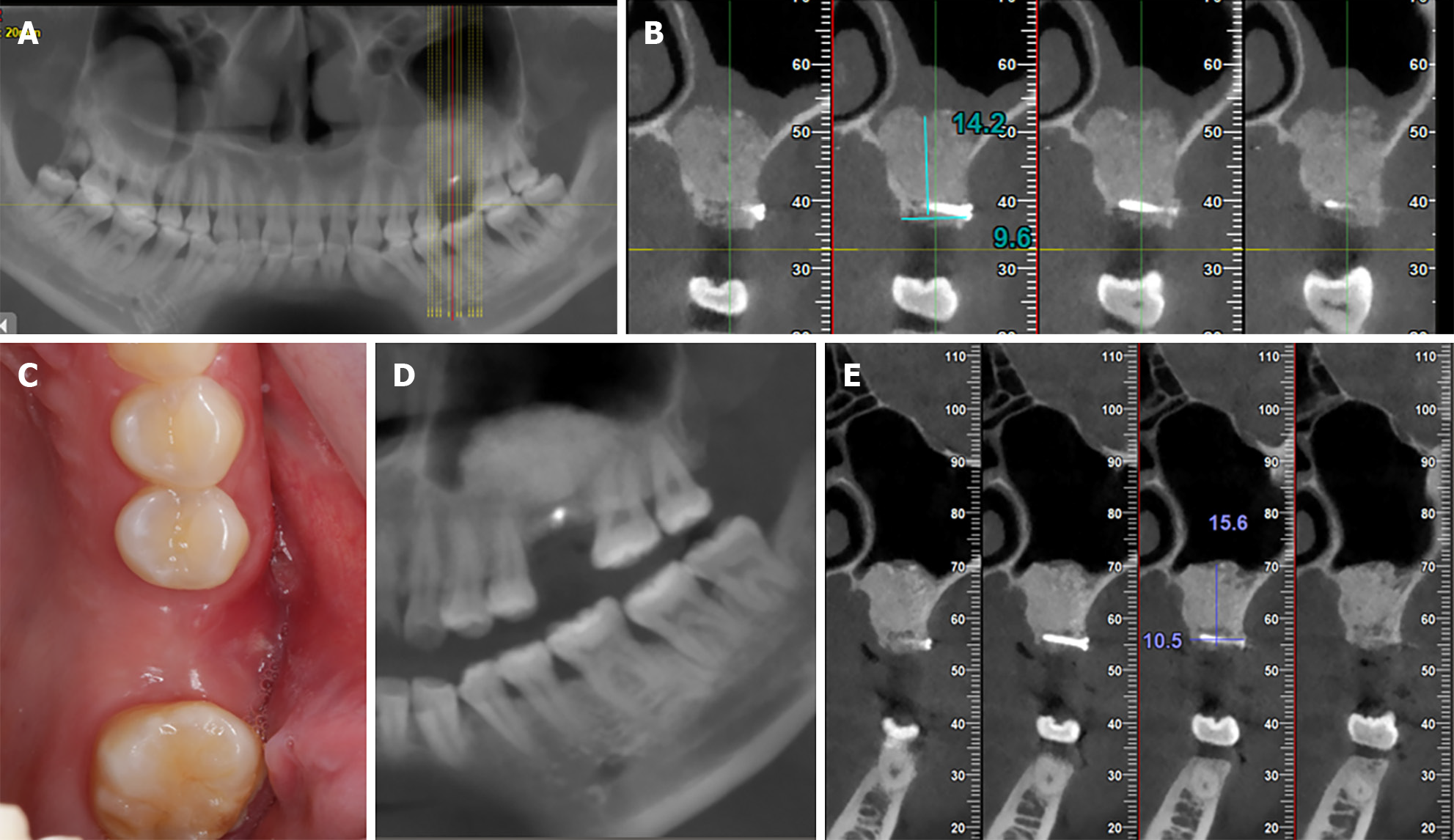
Figure 4 Immediate postoperative and 6-month follow-up.
A: Immediate postoperative sagittal cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) image showing the overall condition of the maxillary sinus; B: Immediate postoperative Coronal CBCT image showing the disappearance of the maxillary sinus floor mucosal pseudocyst, with a bone height of 15.8 mm and a bone width of 10.8 mm; C: At 9 months postoperative, adequate alveolar bone width can be observed intraorally; D: A: At 9 months postoperative, sagittal CBCT image showing the overall condition of the maxillary sinus; E: At 9 months postoperative, Coronal CBCT image showing the disappearance of the immediate postoperative maxillary sinus floor mucosal pseudocyst, with a bone height of 15.6 mm and a bone width of 10.5 mm.
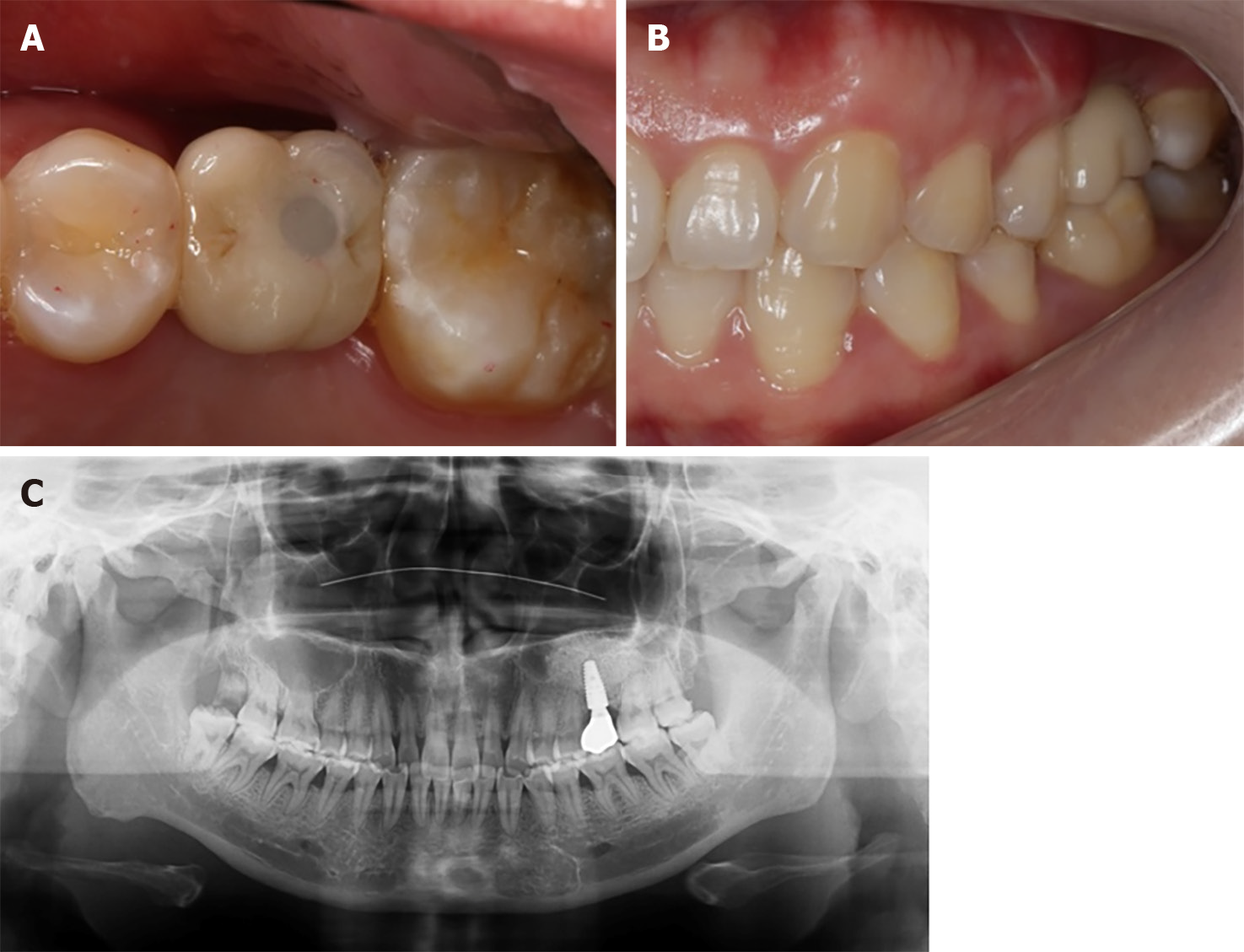
Figure 5 Clinical photos and imaging with final restoration.
A: Occlusal view of screw retained all-ceramic restoration; B: Proper occlusion after all-ceramic restoration; C: Panoramic view after restoration showed sufficient bone volume around dental implant.
- Citation: Wang YL, Shao WJ, Wang M. Bone block from lateral window - correcting vertical and horizontal bone deficiency in maxilla posterior site: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(12): 2109-2115
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i12/2109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i12.2109