Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 26, 2024; 12(12): 2099-2108
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i12.2099
Published online Apr 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i12.2099
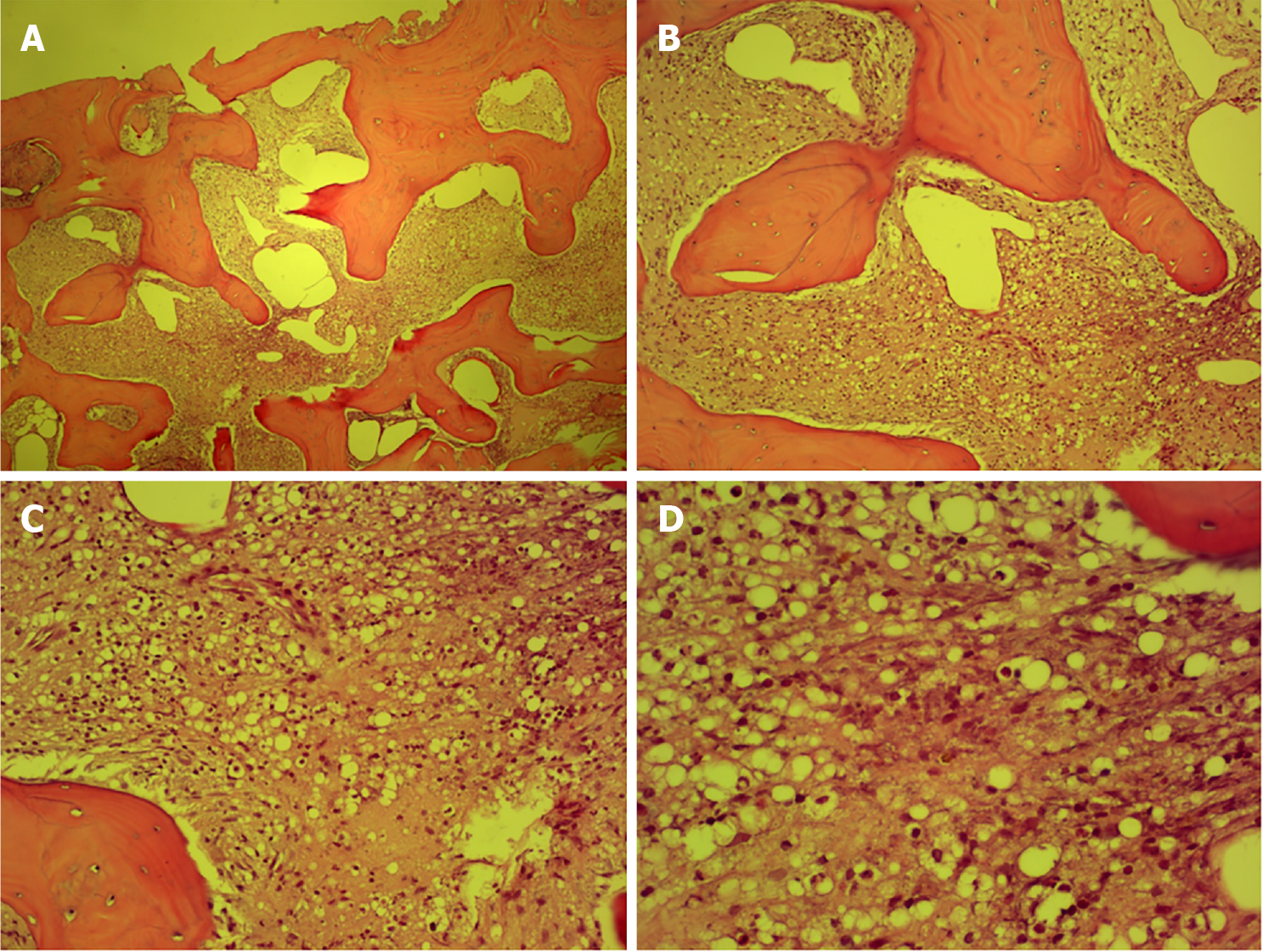
Figure 1 Pathology of the local puncture biopsy in Zibo Central Hospital.
A: 4 × 10 times; B: 10 × 10 times; C: 20 × 10 times; D: 40 × 10 times.
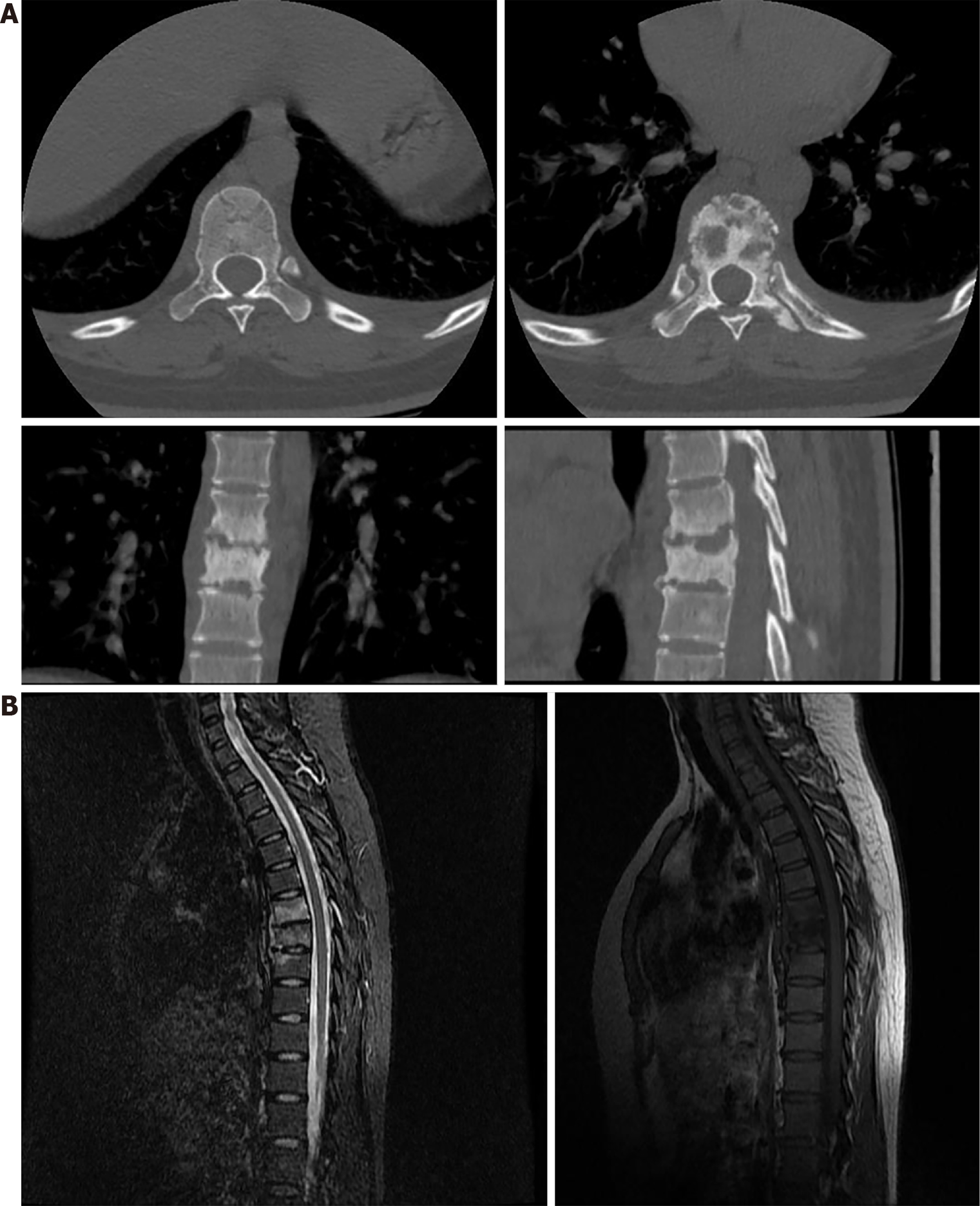
Figure 2 Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the thoracic spine.
A: Thoracic vertebral computed tomography shows bone destruction in T7-9, with T8 being the most significant; B: Magnetic resonance imaging of the thoracic vertebra showed signs of bone abnormalities in T7-9, with T7 and T8 being the most significant.
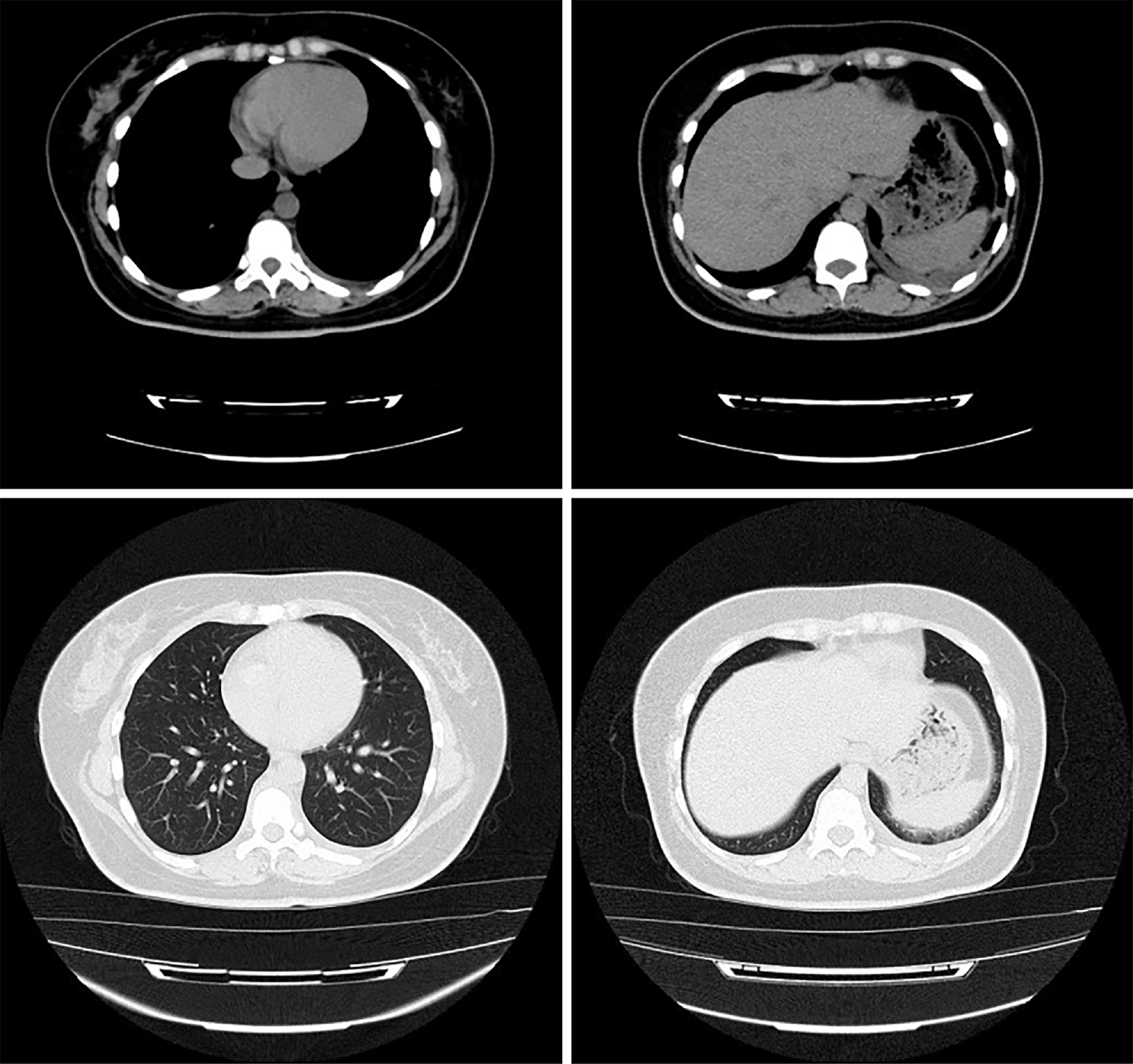
Figure 3 Computed tomography of the lungs.
Chest computed tomography shows mild inflammation in the middle and lower lobe of the right lung and a small amount of pleural effusion on both sides.
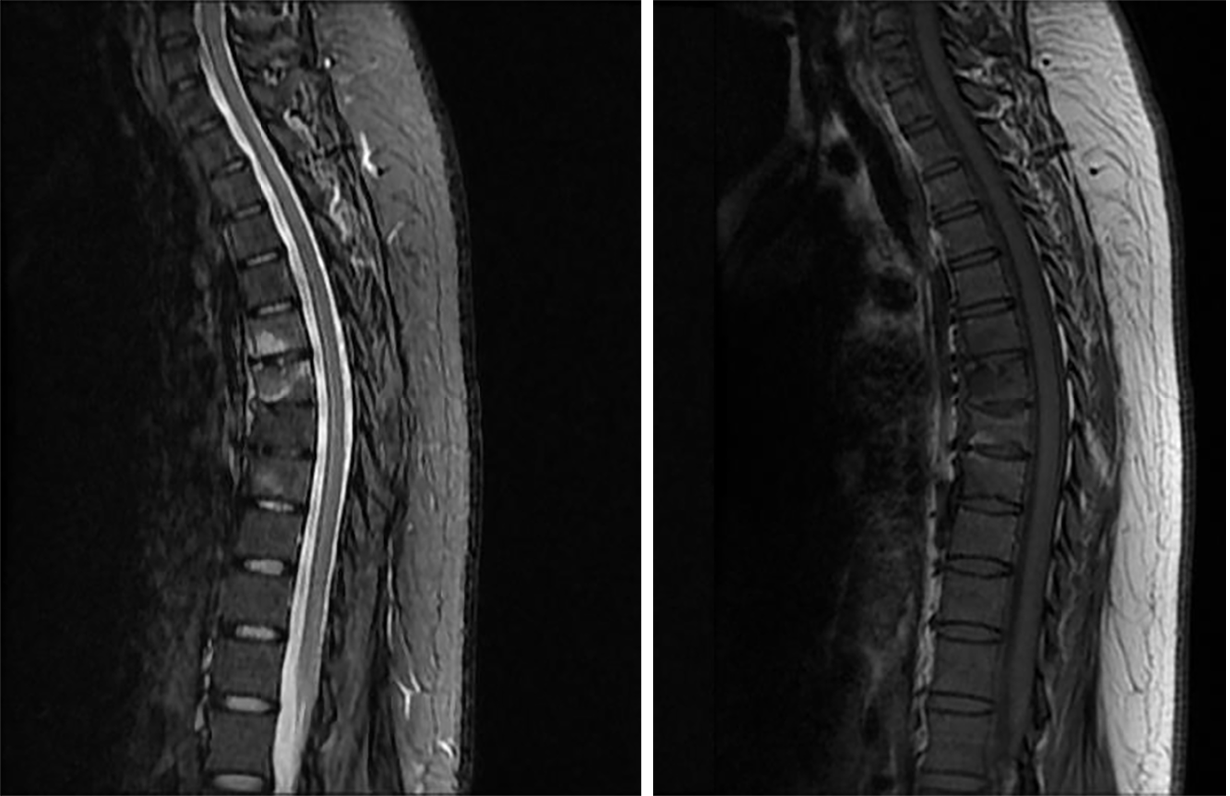
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging showed that the lesions of the T7-9 vertebrae were significantly reduced after treatment.
- Citation: Li L, Zhang BH, Cao JF, Zhang LJ, Guo LL. Thoracic spine infection caused by Pseudomonas fluorescens: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(12): 2099-2108
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i12/2099.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i12.2099