Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 16, 2023; 11(8): 1837-1846
Published online Mar 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1837
Published online Mar 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1837
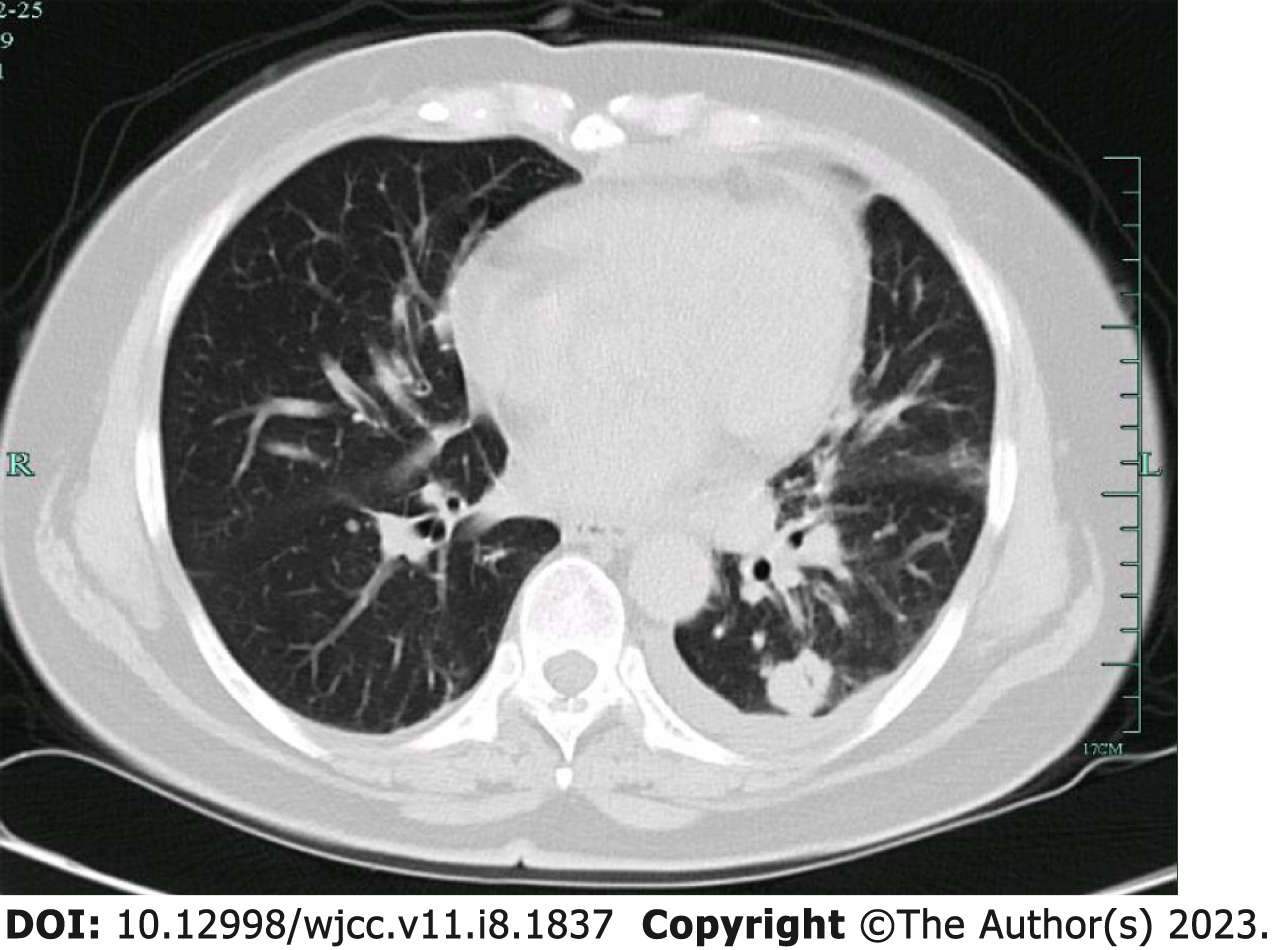
Figure 1 High resolution computed tomography examination.
A: High resolution computed tomography (CT) examination of the patient indicated multiple nodules in inferior lobe of left lung, one with a thick-walled cavity and one with nodules, suggesting granulomatous inflammation and the possibility of Cryptococcus; B: The lesions were enlarged, and internal cavity was narrowed compared to old CT photos; C: Tissue culture suggested Aspergillus spp.; D: The three times of chest CT reexamination after the treatment, all of which indicated that the infection lesions in inferior lobe of left lung were shrinking, suggesting that the treatment was effective.
Figure 2 Multiple mediastinal lymph node metastasis, and pleural effusion with a small amount of pericardial effusion.
Figure 3 High resolution computed tomography reexamination.
A: The chest high resolution computed tomography reexamination of the patient suggested nodules in the right middle lobe and bilateral lower lobe and proliferative lesions were considered; B: the detection of serum cryptococcal antigen showed a negative result, suggesting that the treatment was effective.
- Citation: Chen WY, Zhong C, Zhou JY, Zhou H. False positive detection of serum cryptococcal antigens due to insufficient sample dilution: A case series. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(8): 1837-1846
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i8/1837.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1837