Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2023; 11(6): 1403-1409
Published online Feb 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i6.1403
Published online Feb 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i6.1403
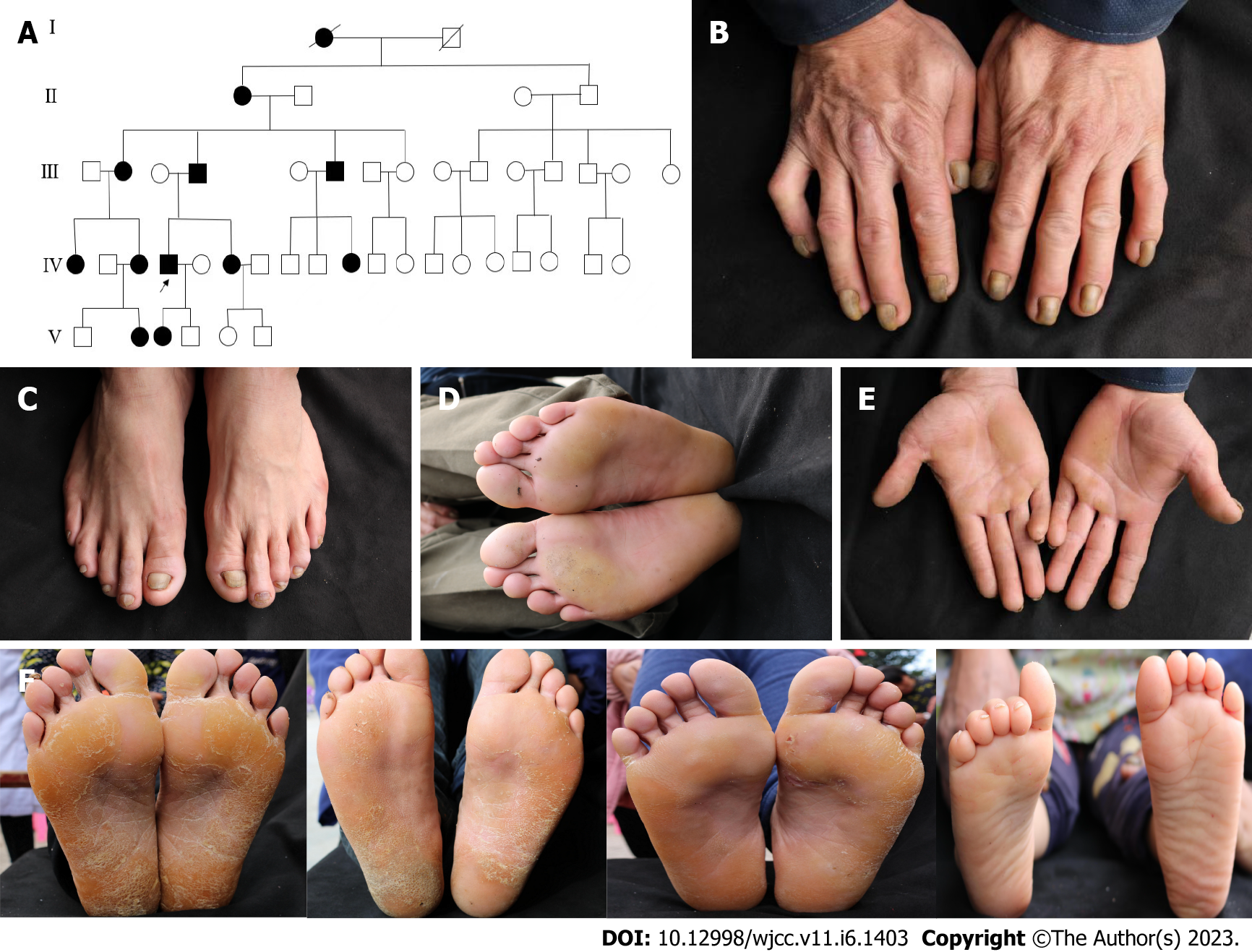
Figure 1 The proband.
A: Genealogical analysis of a Chinese family with hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Normal individuals are shown as clear circles (females) or squares (males), and affected individuals are shown as solid symbols. Deceased individuals are shown with a slash. The arrow indicates the proband; B: The proband (IV4) had thickening and yellowing of all fingernails; C: The proband had thickening and yellowing of all toenails; D: The proband had yellow patches visible on the soles of the feet; E: The proband had mild keratinization visible on the palm of the hand; F: The degree of palmar toe keratinization decreased in severity in the subsequent generations.
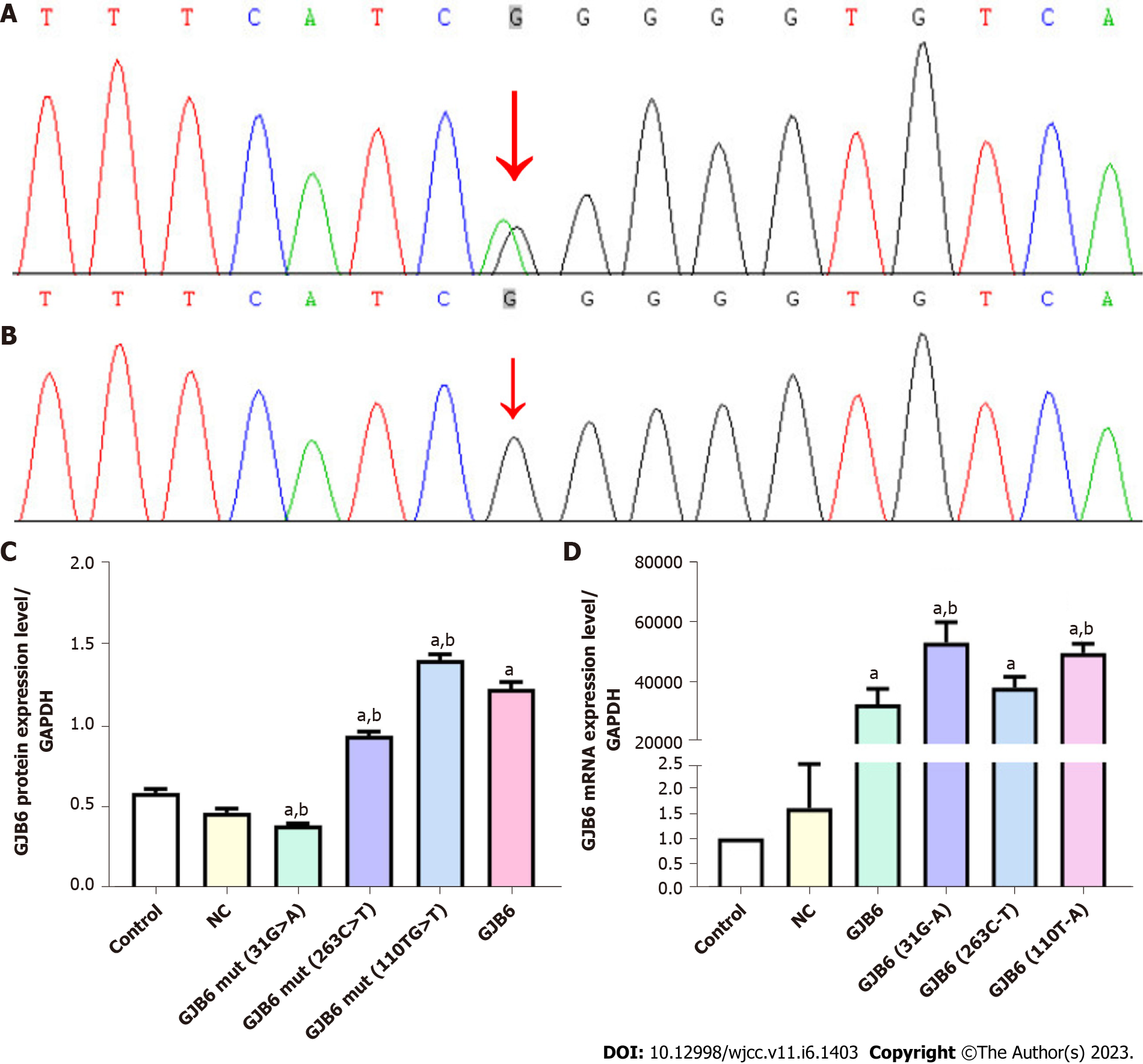
Figure 2 Region of GJB6.
A: Region of GJB6 derived from the proband showing a heterozygous missense mutation 263G→A (arrow) in GJB6; B: Sequence analysis of the same region of GJB6 from a normal individual; C: Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction results of the expression level of GJB6 mRNA (aP < 0.01 compared with the blank control and NC control groups; bP < 0.01 compared with the GJB6 overexpression group); D: Western blot results of the protein expression level of GJB6 (aP < 0.01 compared with the blank control and NC control groups; bP < 0.01 compared with the GJB6 overexpression group).
- Citation: Liao MY, Peng H, Li LN, Yang T, Xiong SY, Ye XY. Hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in a Chinese pedigree: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(6): 1403-1409
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i6/1403.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i6.1403