Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2023; 11(31): 7562-7569
Published online Nov 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i31.7562
Published online Nov 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i31.7562
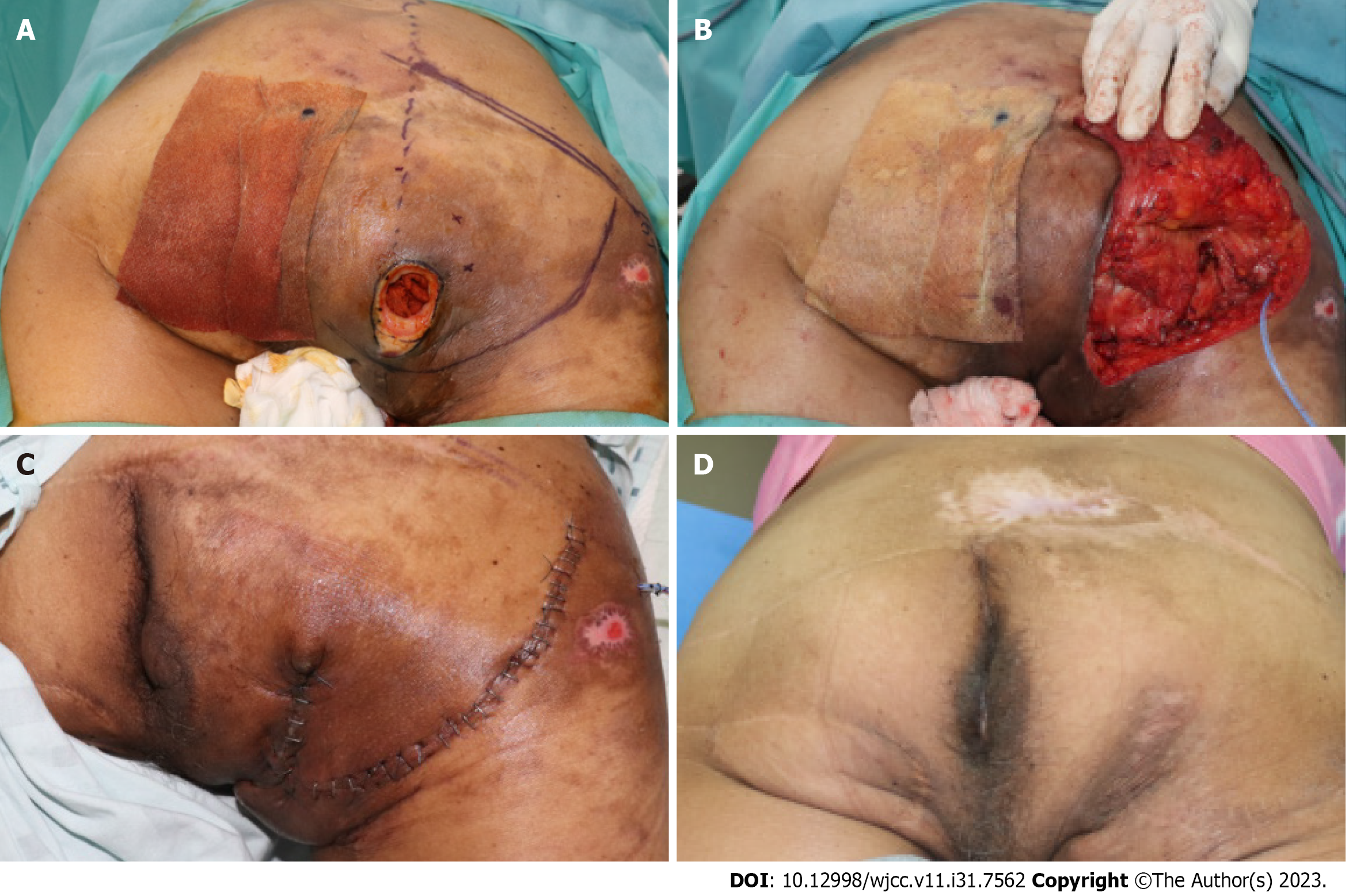
Figure 1 A 58 years old male patient with grade IV decubitus ulcer on ischial region.
A: Intraoperaetive findings: Discrepancy between opening (3 cm2 × 3 cm2) and soft tissue defect (7 cm2 × 3 cm2); B: Is observed. Design of Inferior gluteal artery based fasciocutaneous flap, inferior 1/3 portion of gluteus maximus muscle is splitted and transpositionted to cover exposed ischial tuberosity; C: Immediate postoperative findings; D: Postopertive phogograph at 6 mo follow up: No concavity is observed on the flap.
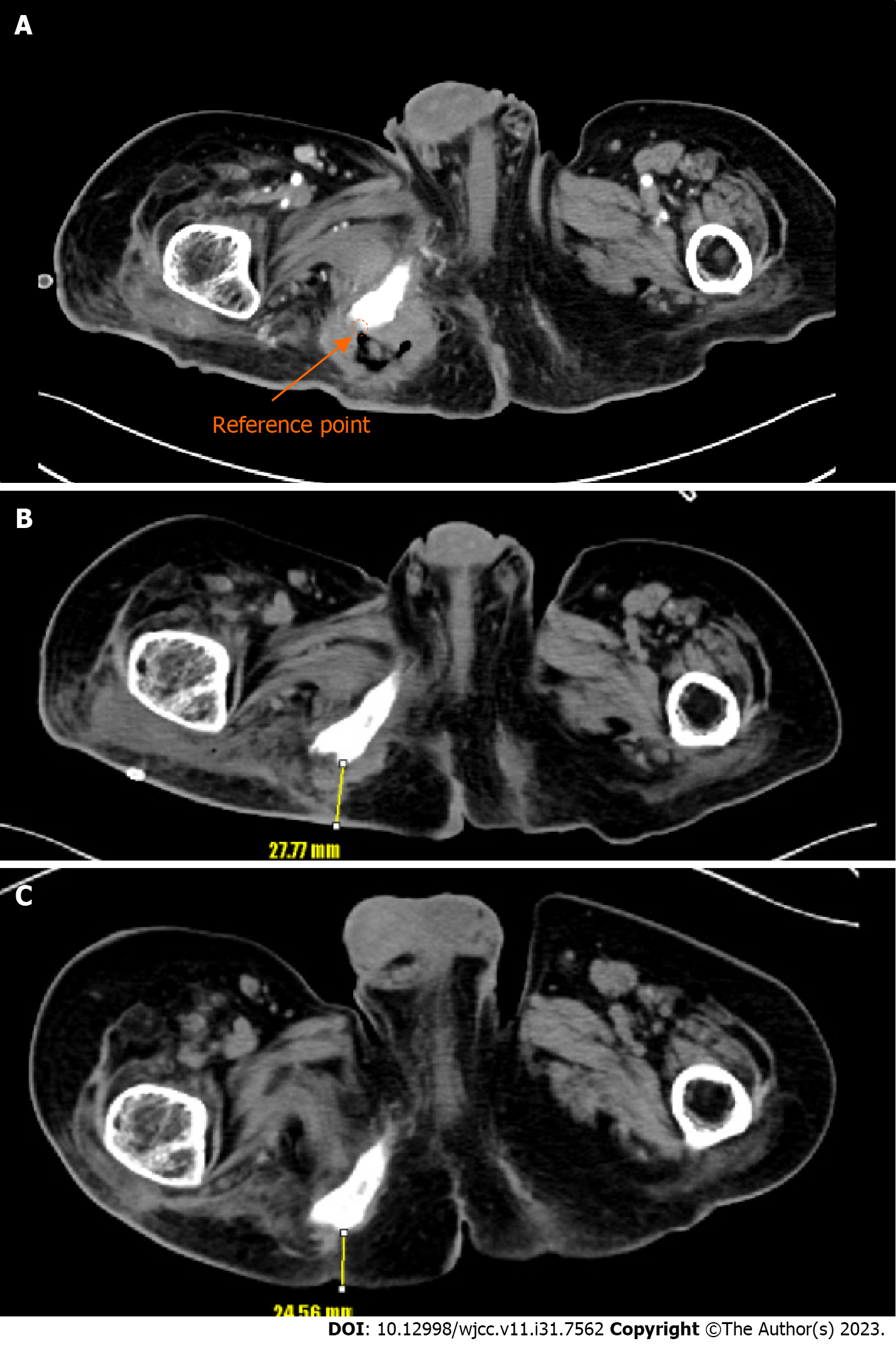
Figure 2 Computed tomography findings.
A: Preoperative computed tomography (CT) findings: Reference point (orange arrow); B: Postoperative CT findings after 3 wk from reconstruction: Distance between reference point and skin is measured 27.77 mm (yellow arrow); C: Postoperative CT findings after 6 mo from reconstruction: Distance between reference point and skin is measured 24.56 mm (yellow arrow).
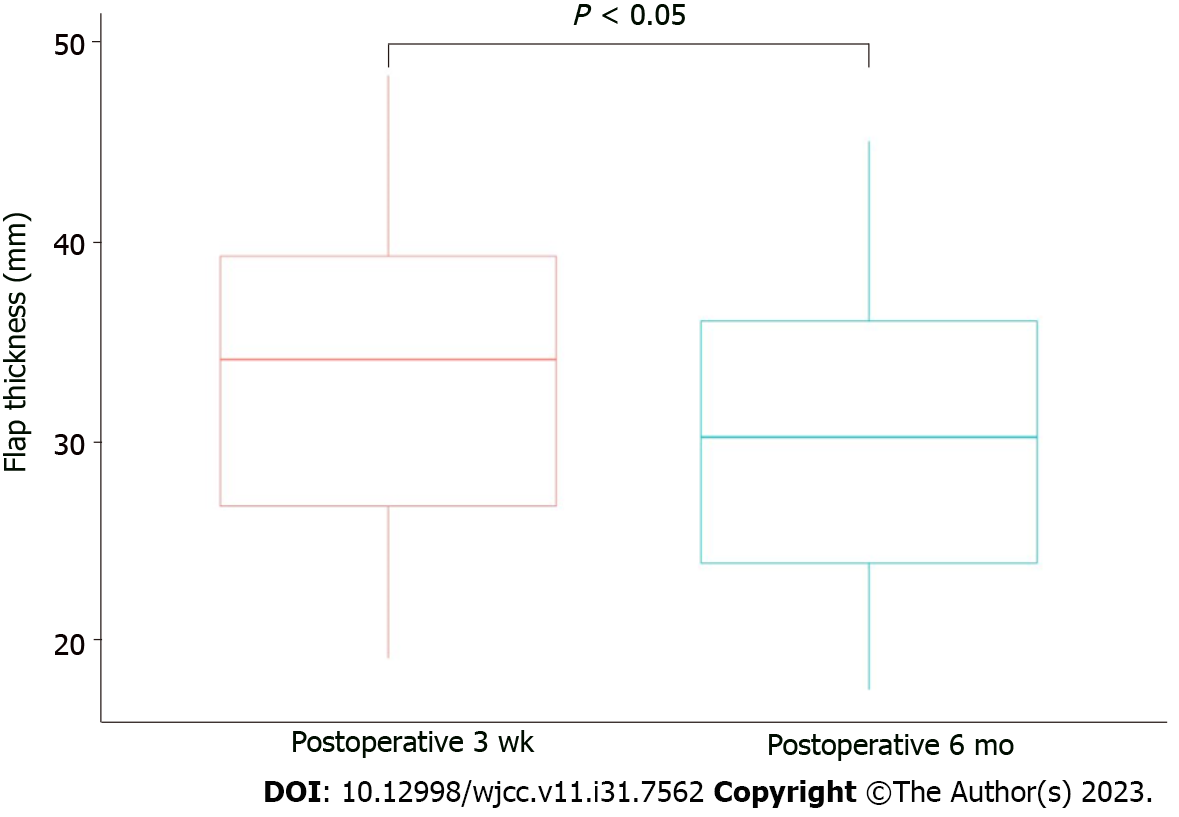
Figure 3 Evaluation of combined flap thickness.
The mean flap thickness of 3 wk postoperative computed tomography (CT) image was 32.85 ± 8.89 mm. The mean flap thickness of 6 mo postoperative CT image was 29.27 ± 8.22 mm (P value < 0.05).
- Citation: Kim EC, Park JD, Wee SY, Kim SY. Measurement of combined flap thickness for reconstruction of decubitus ulcer using computed tomography. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(31): 7562-7569
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i31/7562.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i31.7562