Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2023; 11(30): 7432-7439
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7432
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7432
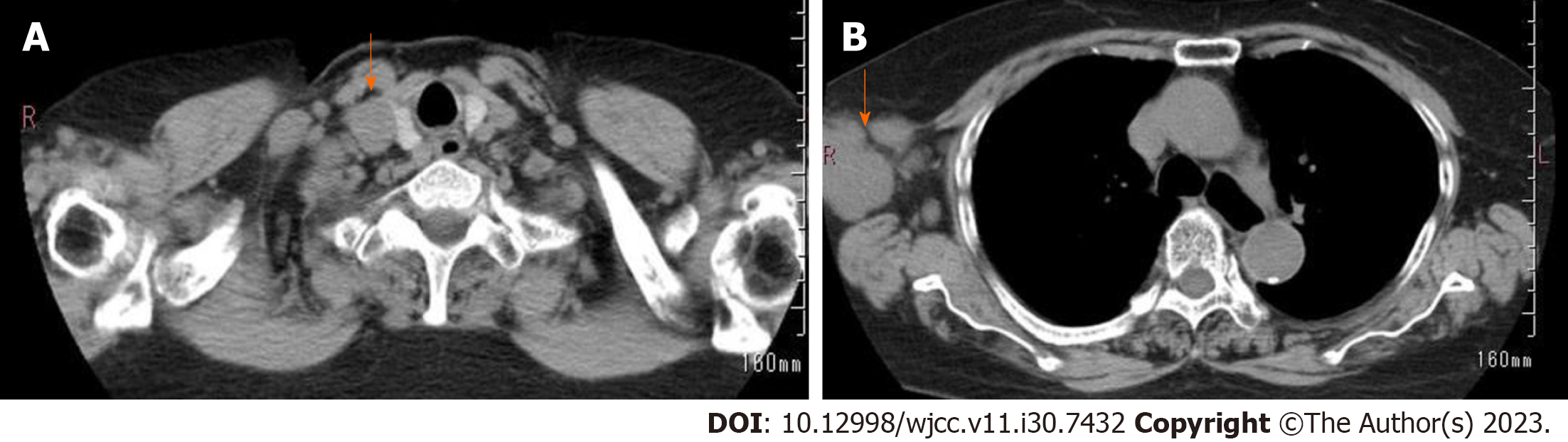
Figure 1 Imaging findings at diagnosis.
A: Subclavian lymph node enlargement; B: Right axillary lymph node enlargement.
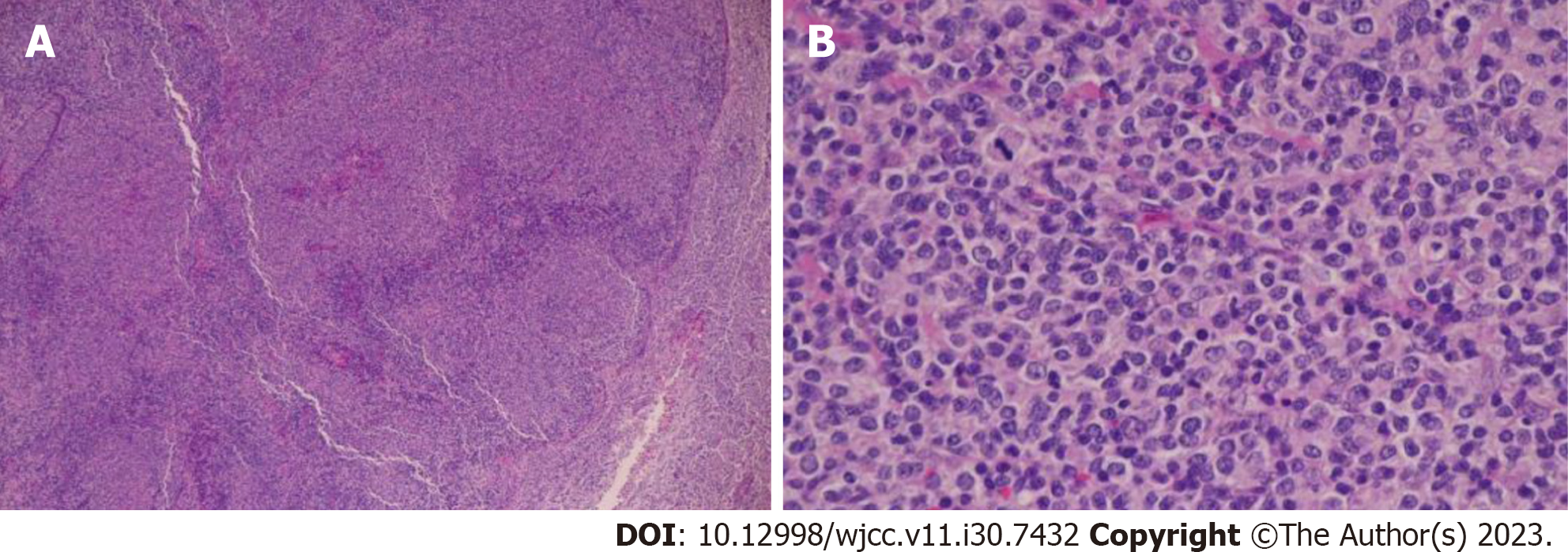
Figure 2 Pathological findings at diagnosis.
A: HE ×10; B: HE ×40.
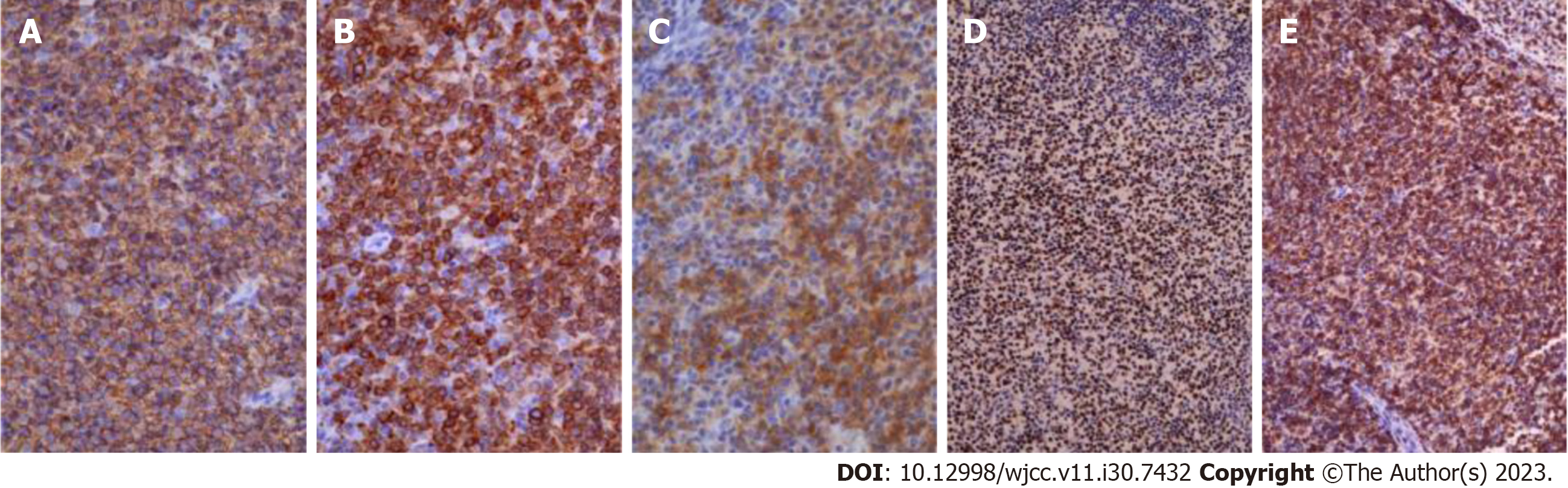
Figure 3 Immunostaining at diagnosis.
A: CD20 ×40(+); B: CD79a ×40(+); C: CD10 ×40(+); D: bcl6 ×20(+); E: bcl2 ×20(+).
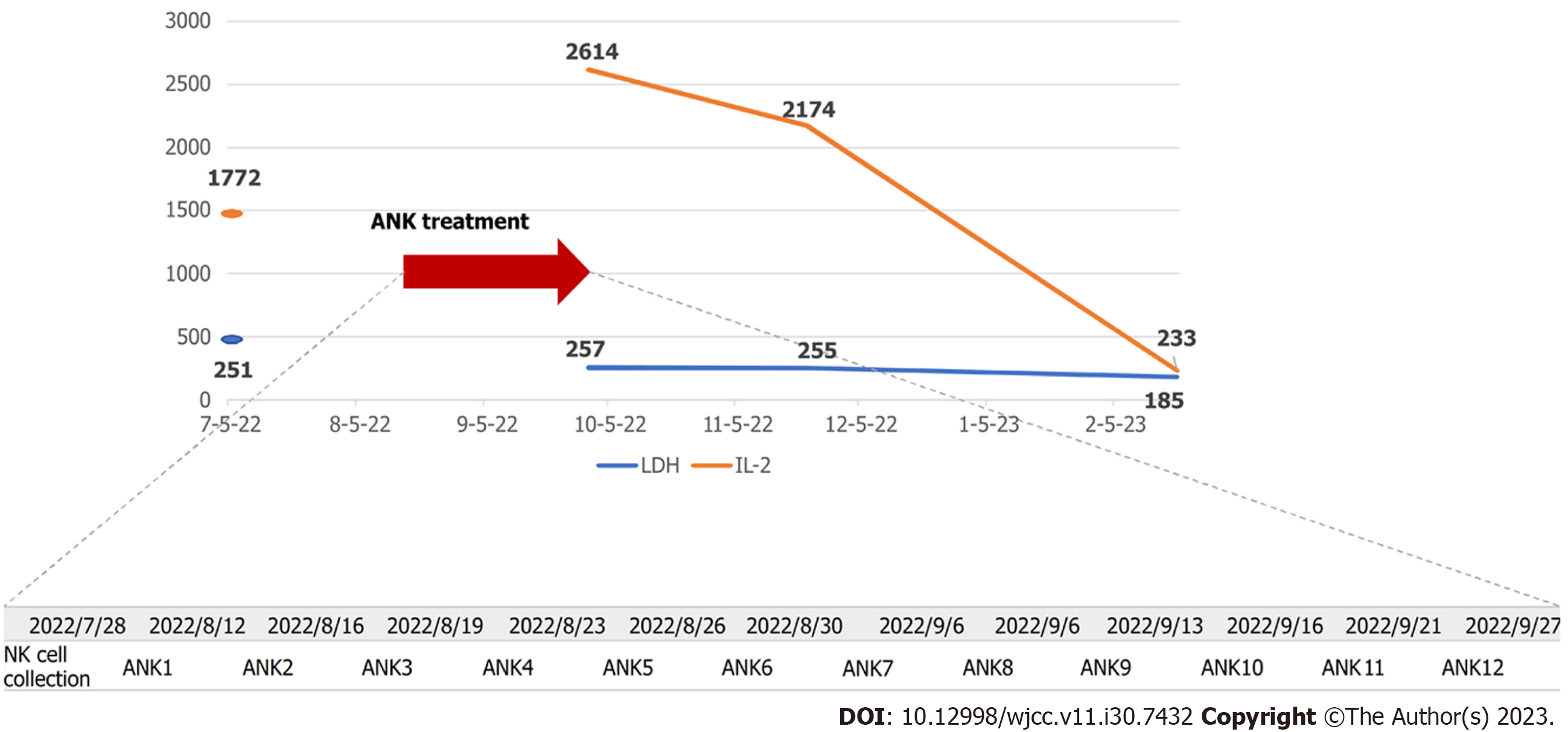
Figure 4 Course of lactate dehydrogenase, interleukin-2, and amplified natural killer treatment schedule.
ANK: Amplified natural killer; IL-2: Interleukin-2; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; NK: Natural killer.
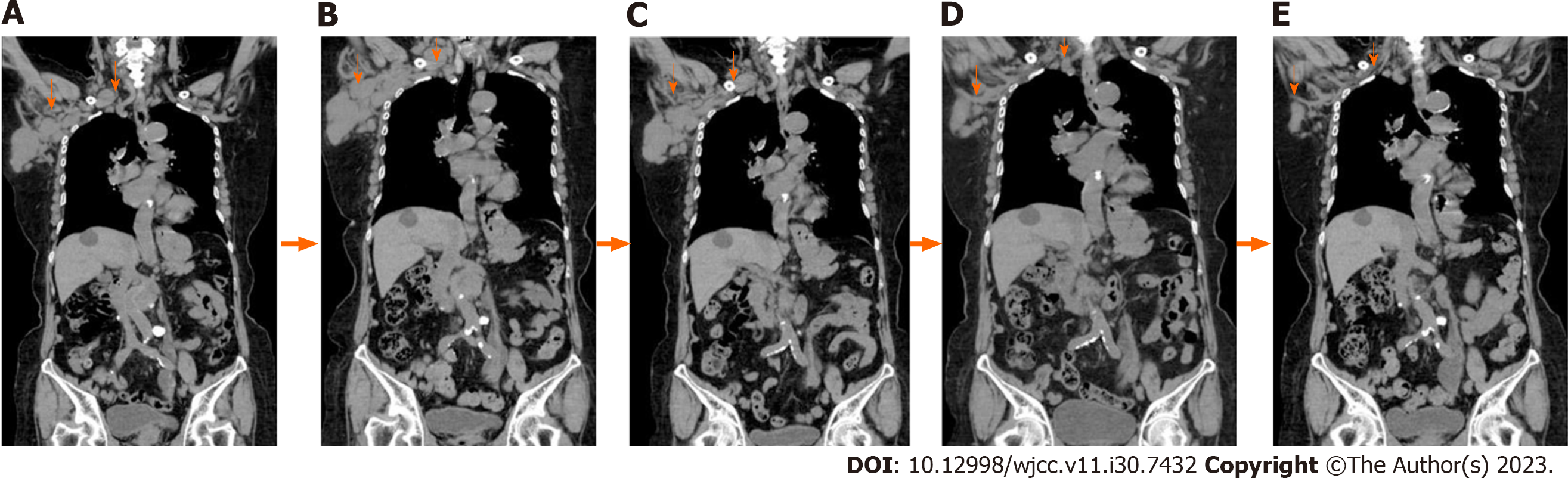
Figure 5 Post-treatment course of computed tomography imaging.
Three months after treatment, the size of the right axillary and subclavian lymph nodes appears to be gradually reduced; five months later, a marked reduction can be observed. A: July 2022; B: October 2022; C: December 2022; D: February 2023; E: March 2023.
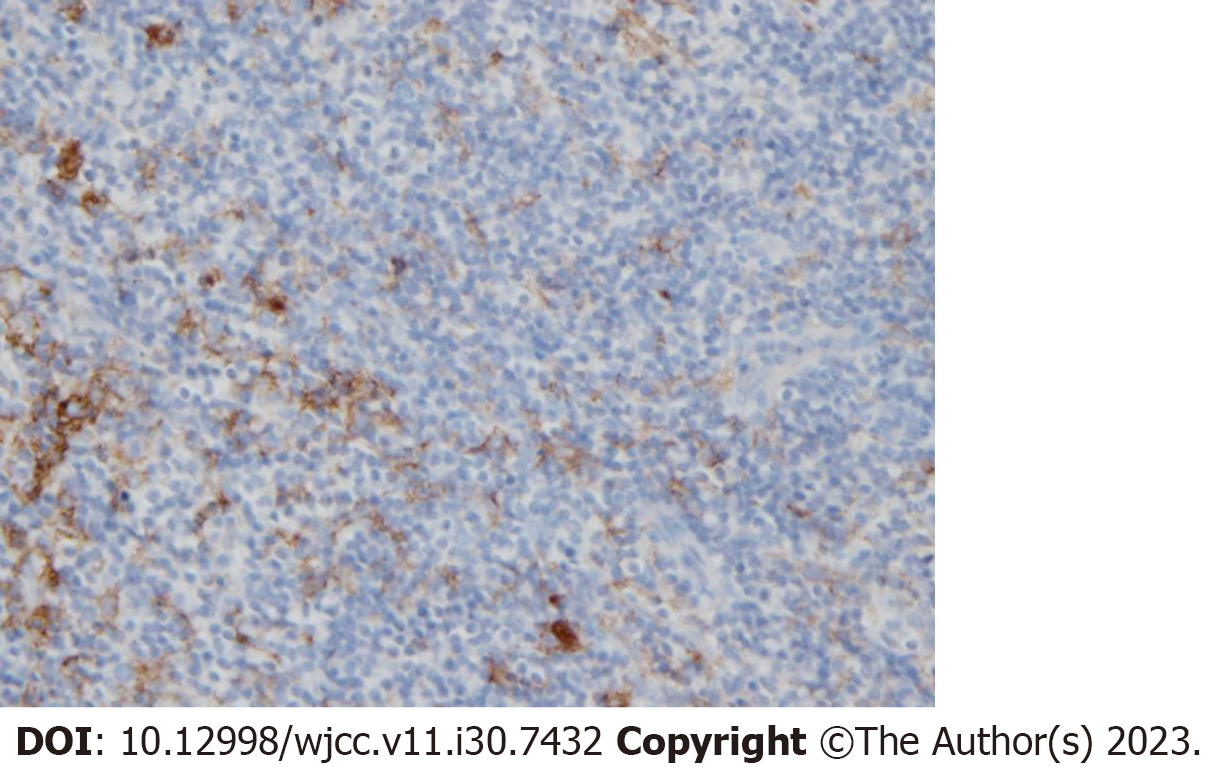
Figure 6 Pathological tissues derived from the patient were subjected to programmed death ligand 1 immunostaining, revealing positive immunostaining.
Programmed death ligand 1 × 40.
- Citation: Nagai K, Nagai S, Okubo Y, Teshigawara K. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma successfully treated with amplified natural killer therapy alone: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(30): 7432-7439
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i30/7432.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7432