Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2023; 11(30): 7329-7336
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7329
Published online Oct 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7329
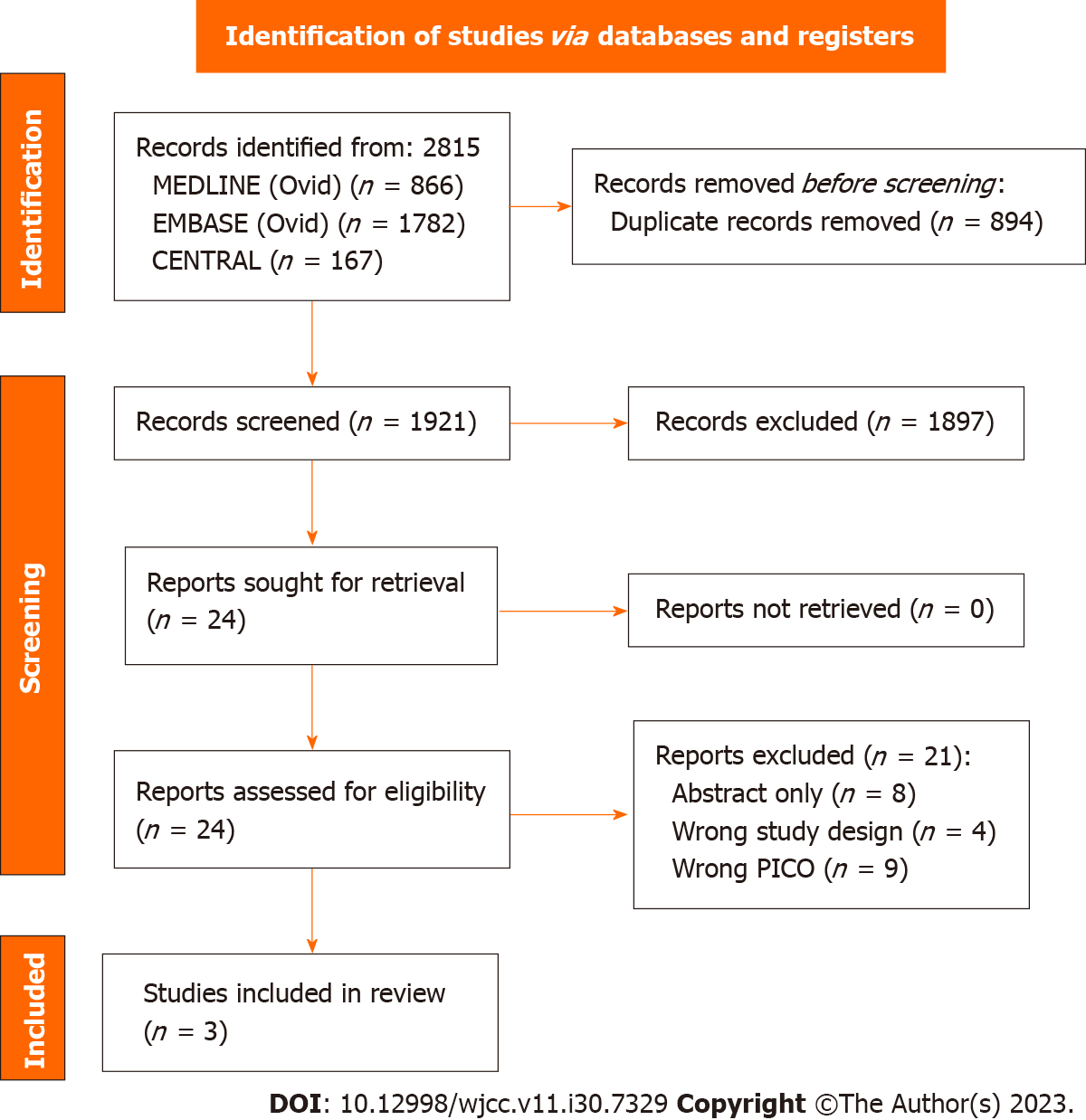
Figure 1 PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for study selection.
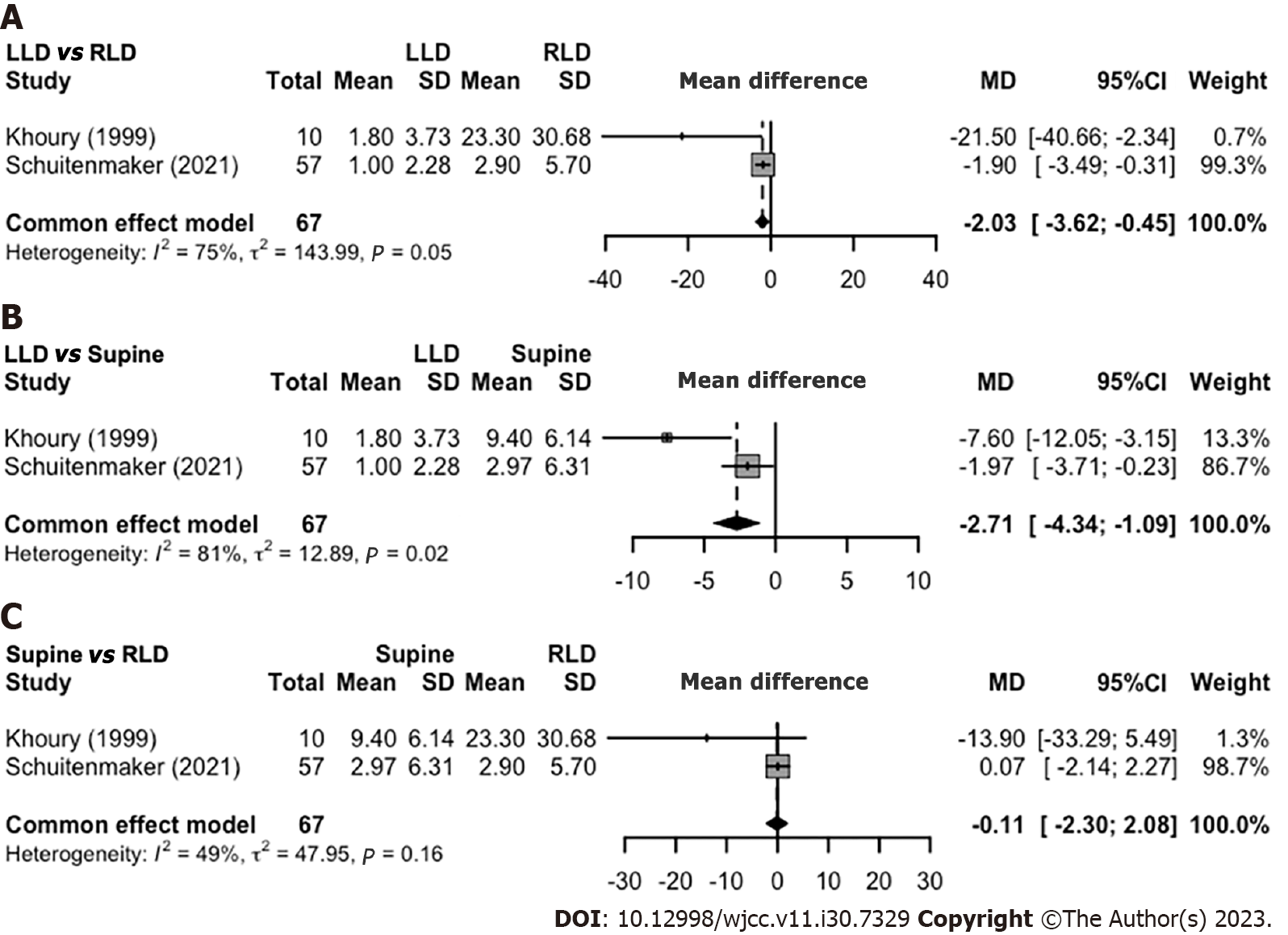
Figure 2 Spontaneous sleep position and nocturnal reflux symptoms.
A: Acid exposure time (% time pH<4) in left lateral decubitus (LLD) vs right lateral decubitus (RLD); B: LLD vs supine; C: Supine vs RLD. LLD: Left lateral decubitus; MD: Mean difference; RLD: Right lateral decubitus; SD: Standard deviation; 95%-CI: 95% confidence interval.
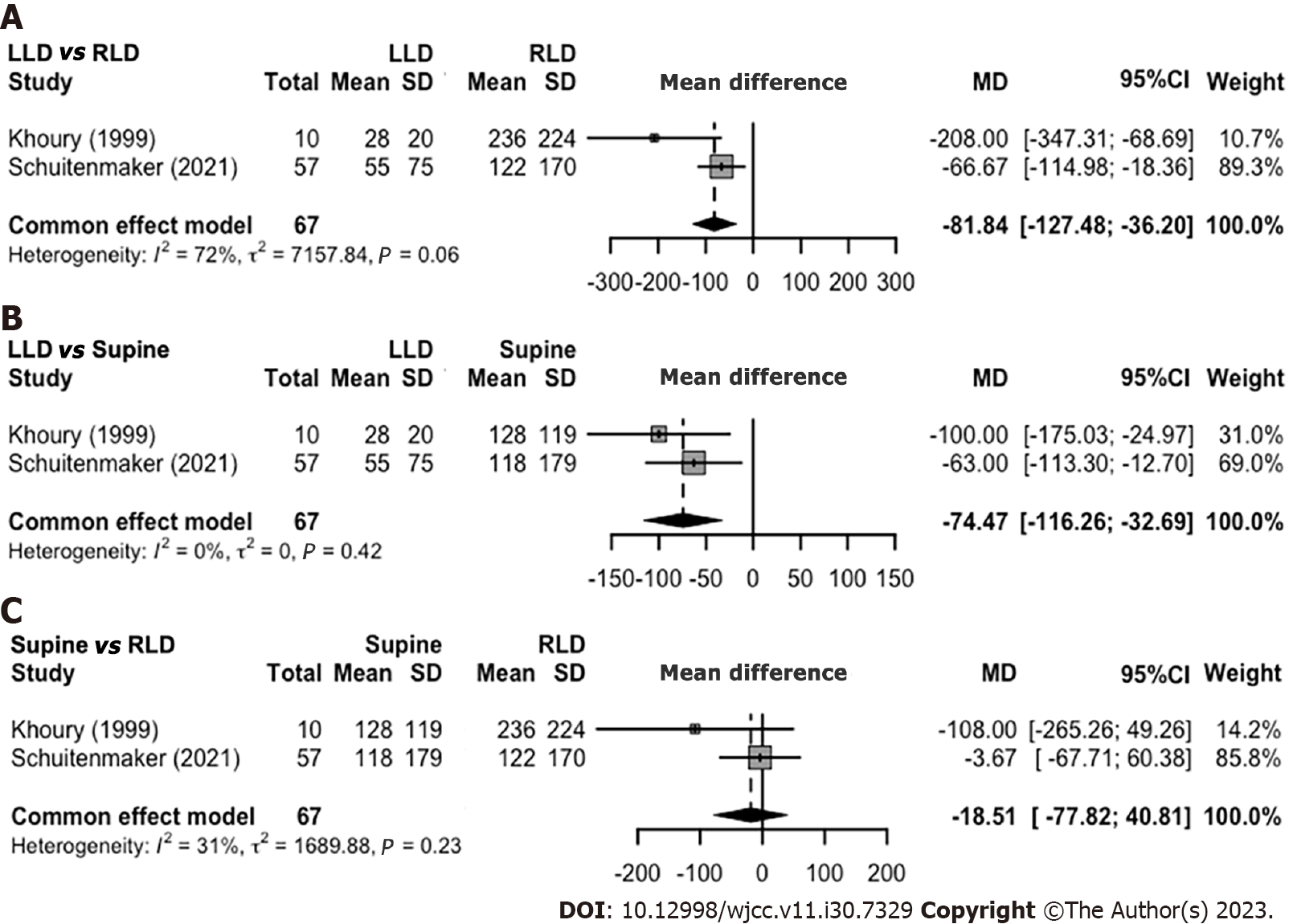
Figure 3 Spontaneous sleep position and nocturnal reflux symptoms.
A: Acid clearance time (sec/episode) in left lateral decubitus (LLD) vs right lateral decubitus (RLD); B: LLD vs Supine; C: Supine vs RLD. LLD: Left lateral decubitus; MD: Mean difference; RLD: Right lateral decubitus; SD: Standard deviation; 95%-CI: 95% confidence interval.
- Citation: Simadibrata DM, Lesmana E, Amangku BR, Wardoyo MP, Simadibrata M. Left lateral decubitus sleeping position is associated with improved gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(30): 7329-7336
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i30/7329.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7329