Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 26, 2023; 11(3): 655-661
Published online Jan 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.655
Published online Jan 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.655
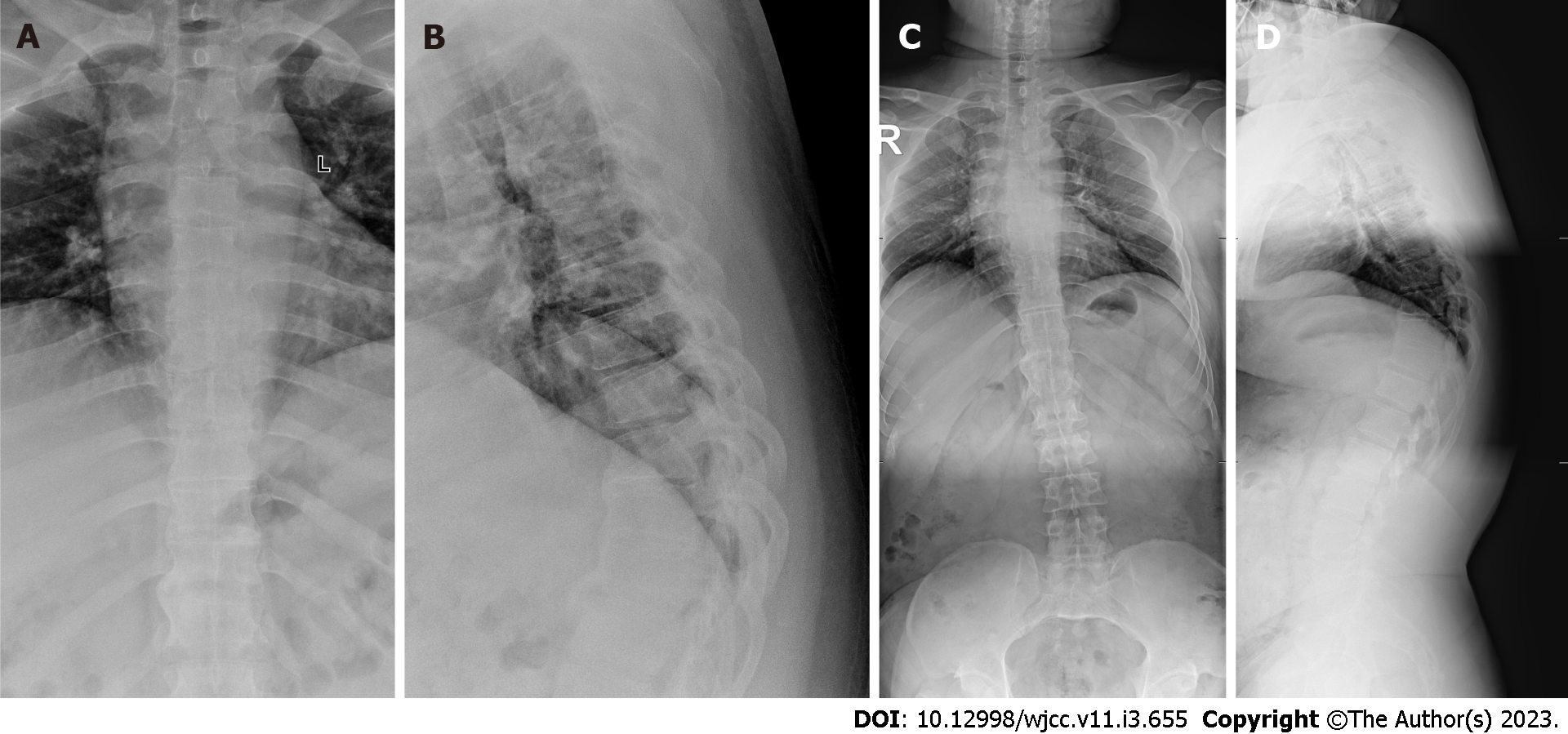
Figure 1 X-ray before treatment.
A: An anterior X-ray of the thoracic vertebra before operation; B: A lateral X-ray of the thoracic vertebra before operation; C: An anterior X-ray of the full-length of the spine before operation; D: A lateral X-ray of the full-length of the spine before operation.
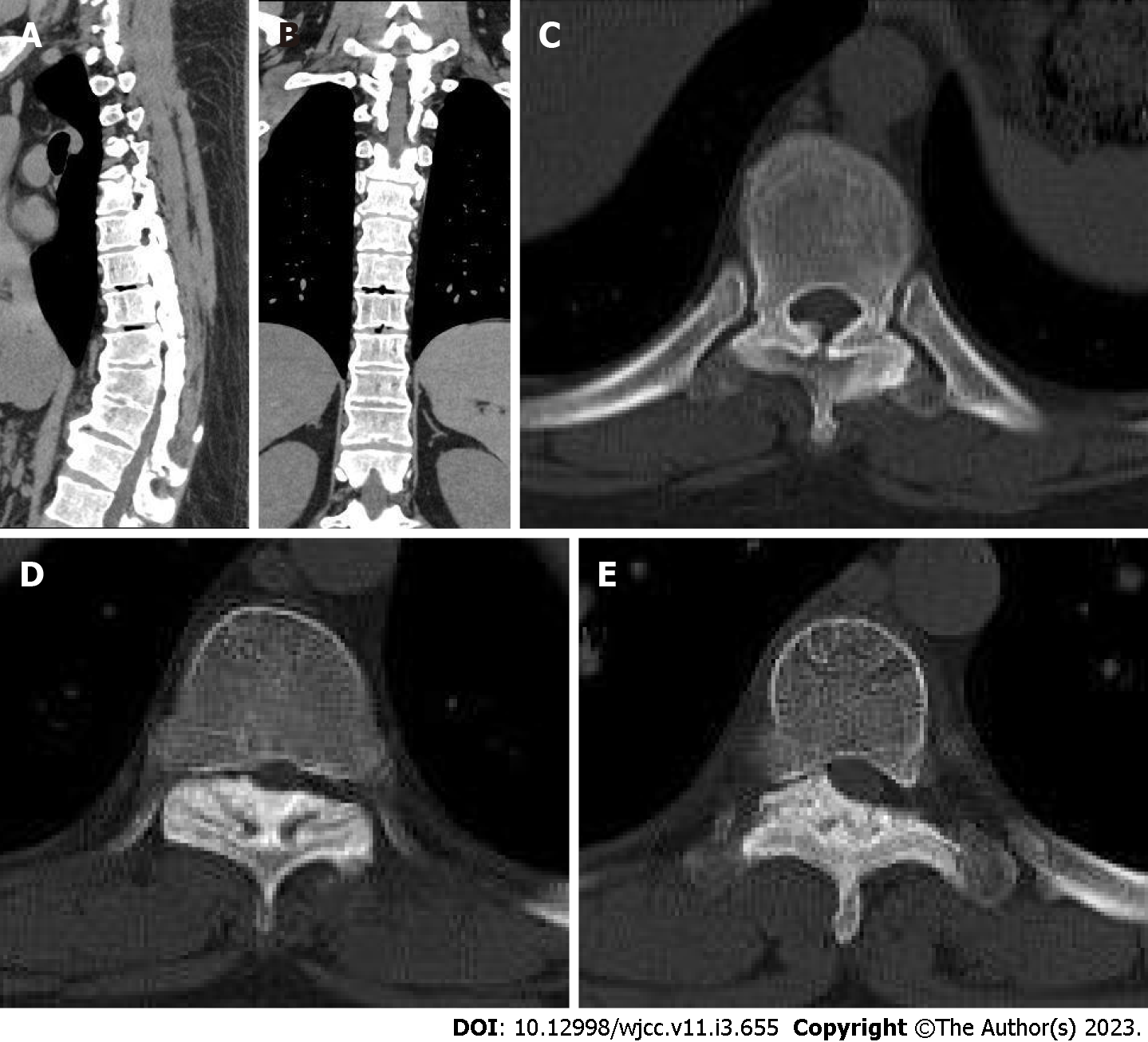
Figure 2 Thoracic computed tomography before treatment.
A and B: A computed tomography scan of the anterior thorax has revealed calcification of the anterior longitudinal ligament in multiple vertebral bodies; C-E: They were the T5/6, T7/8, and T8/9 intervertebral spaces. The T5/6, T7/8, and T8/9 intervertebral discs protrude backward, and the corresponding horizontal segment of the dural sac is compressed.
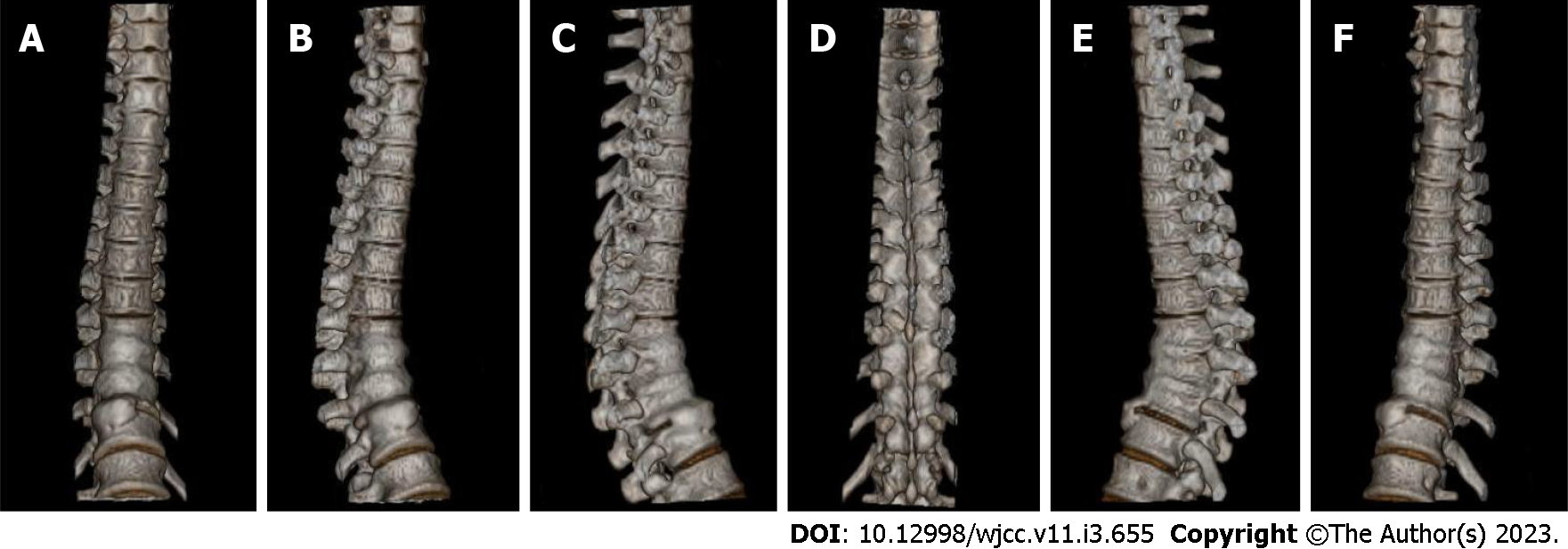
Figure 3 Three-dimensional reconstruction before treatment.
A-F: Three-dimensional reconstruction.
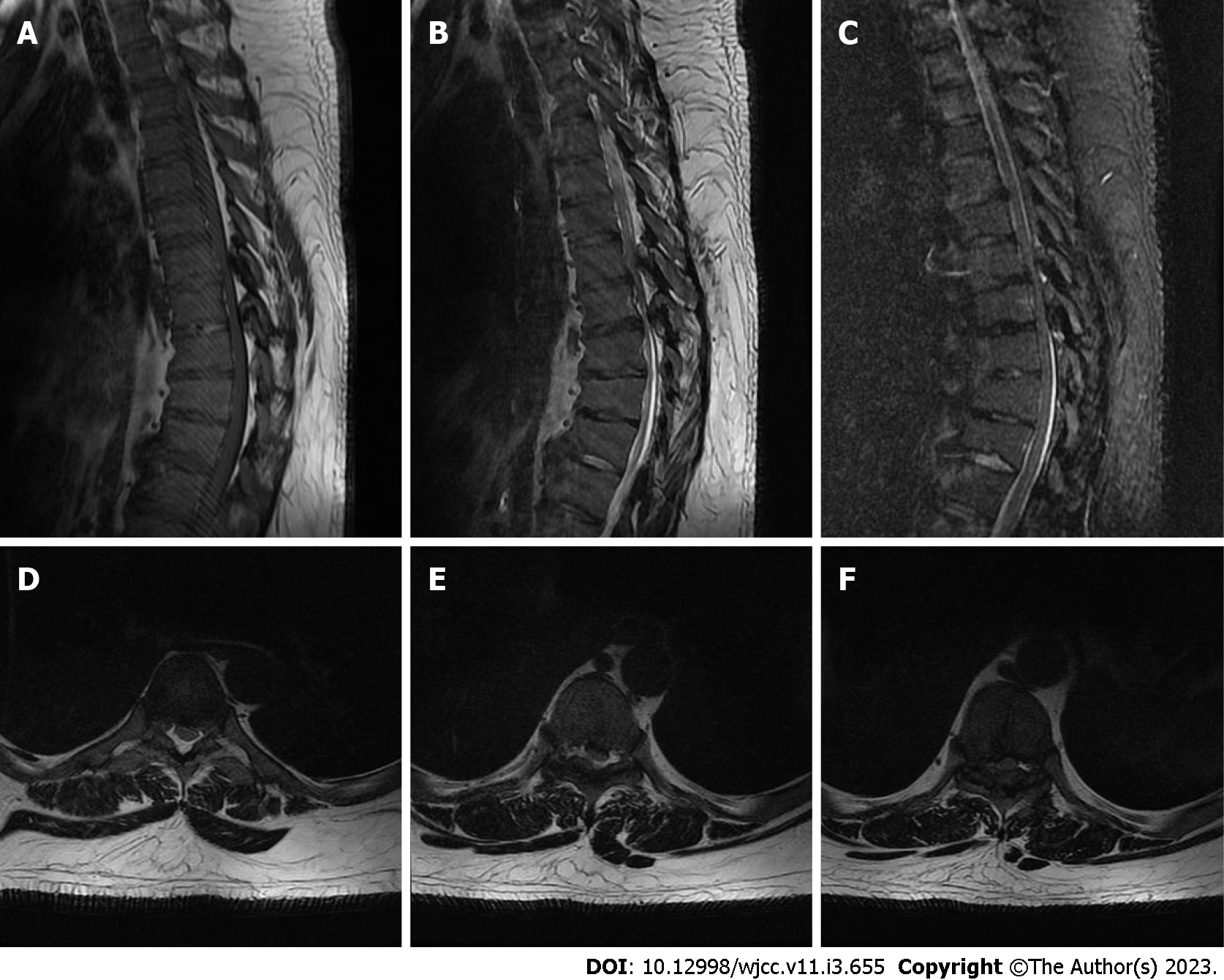
Figure 4 Thoracic magnetic resonance imaging before treatment.
A-C: An magnetic resonance imaging of the thoracic spine revealed a kyphosis in the local thoracic region. The T8-12 vertebral bodies were observed to have a wedge-like shape, with a narrow front and a wide back; D-F: They were the T5/6, T7/8, and T8/9 intervertebral spaces. The T5/6, T7/8, and T8/9 intervertebral discs protrude backward, and the corresponding horizontal segment of the dural sac is compressed.
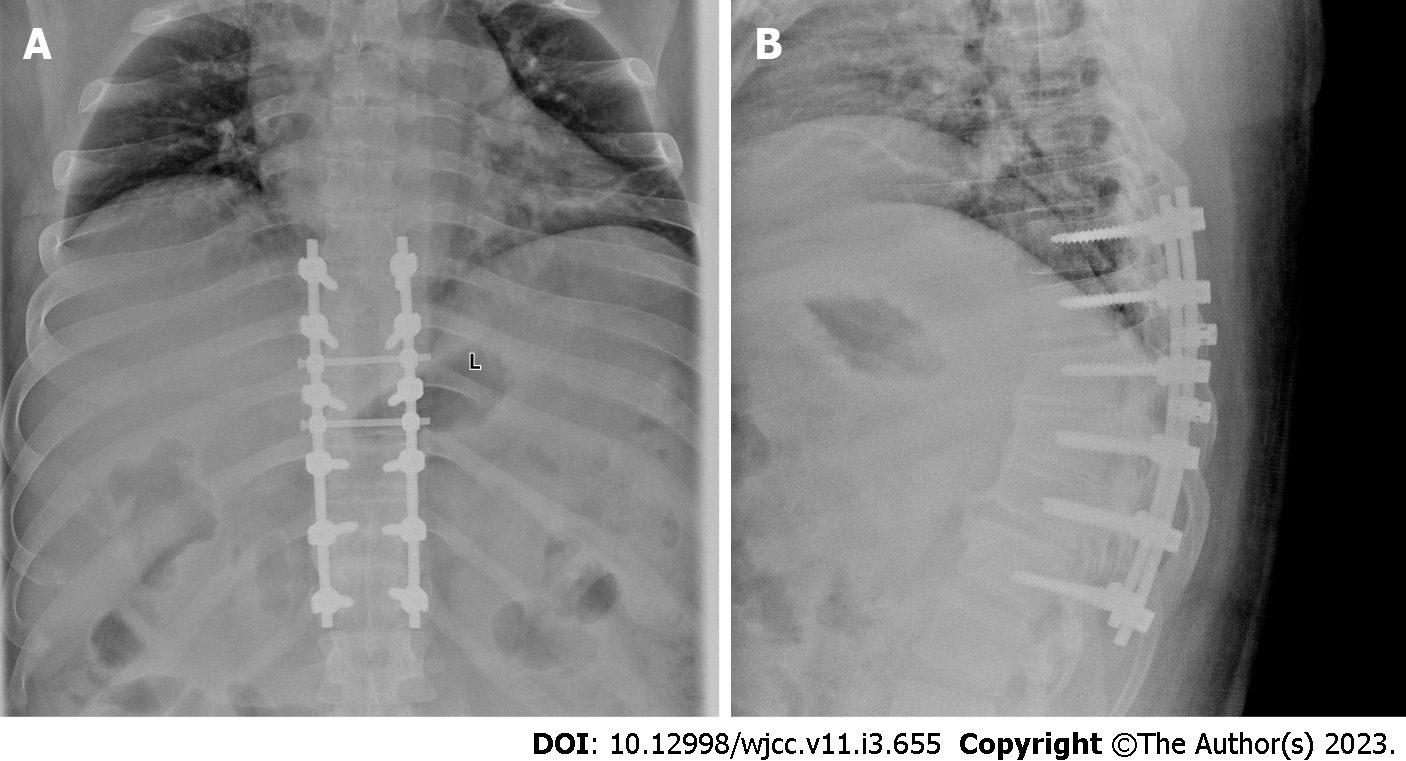
Figure 5 X-ray after treatment.
A and B: Anterior X-ray of thoracic vertebra before operation. They showed that the internal fixation position was suitable.
- Citation: Liu WZ, Chang ZQ, Bao ZM. Young thoracic vertebra diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis with Scheuermann disease: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(3): 655-661
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i3/655.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i3.655