Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 6, 2023; 11(28): 6806-6811
Published online Oct 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i28.6806
Published online Oct 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i28.6806
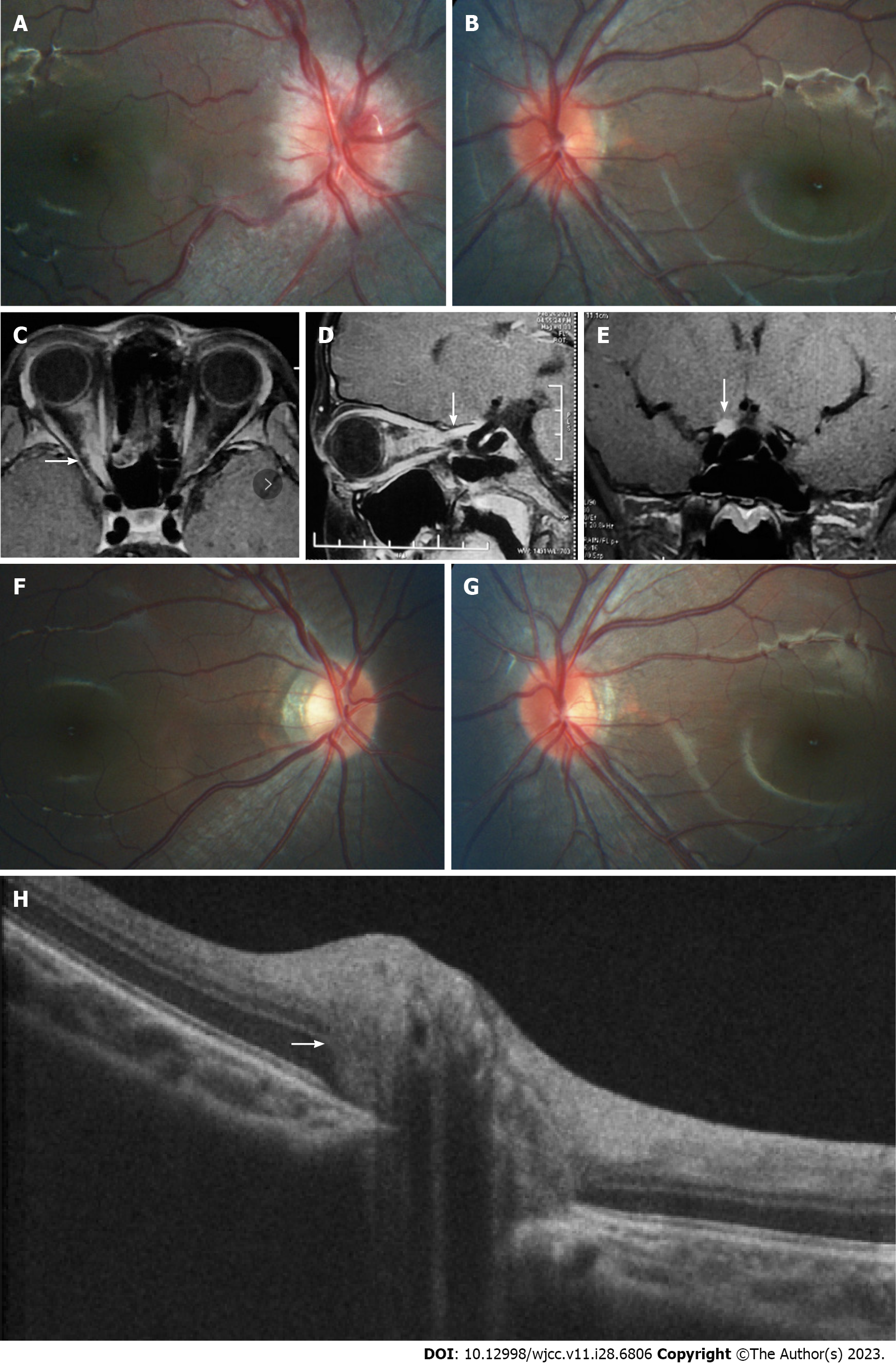
Figure 1 Morphology of optic nerve segments and changes before and after treatment.
A and B: Fundus photography prior to treatment; C-E: Pre-treatment magnetic resonance imaging demonstrating enhancement and enlargement in the intraorbital, intracanal, and intracranial segments of the right optic nerve (white arrows); F and G: Fundus photography post-treatment; H: Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography revealing the presence of a peripapillary hyperreflective ovoid mass-like structure on the left optic disc (white arrow).
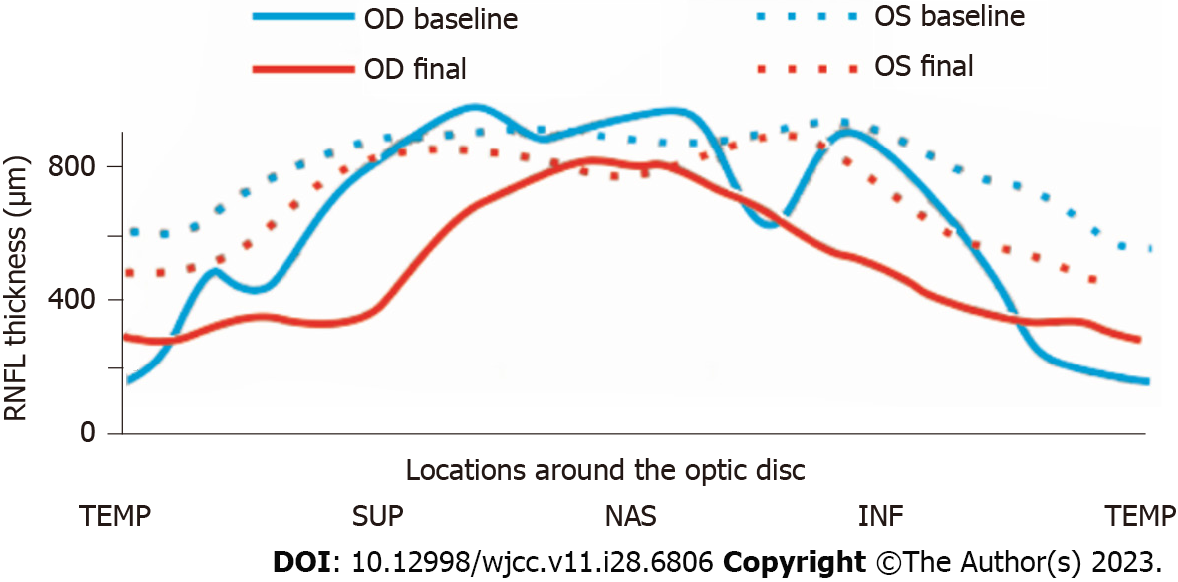
Figure 2 Changes in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness before and after treatment.
TEMP: Temporal; SUP: Superior; NAS: Nasal; INF: Inferior; RNFL: Retinal nerve fiber layer; OD: Optical density; OS: Overall survival.
- Citation: Zhao FF, Yao SQ, Wang Y, Li TP, Yang JF, Pang CP, Cen LP. Bilateral retinal nerve fiber layer thickness reduction in a 9-year-old myopic boy suffering from unilateral optic neuritis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(28): 6806-6811
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i28/6806.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i28.6806