Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 6, 2023; 11(25): 5941-5946
Published online Sep 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5941
Published online Sep 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5941
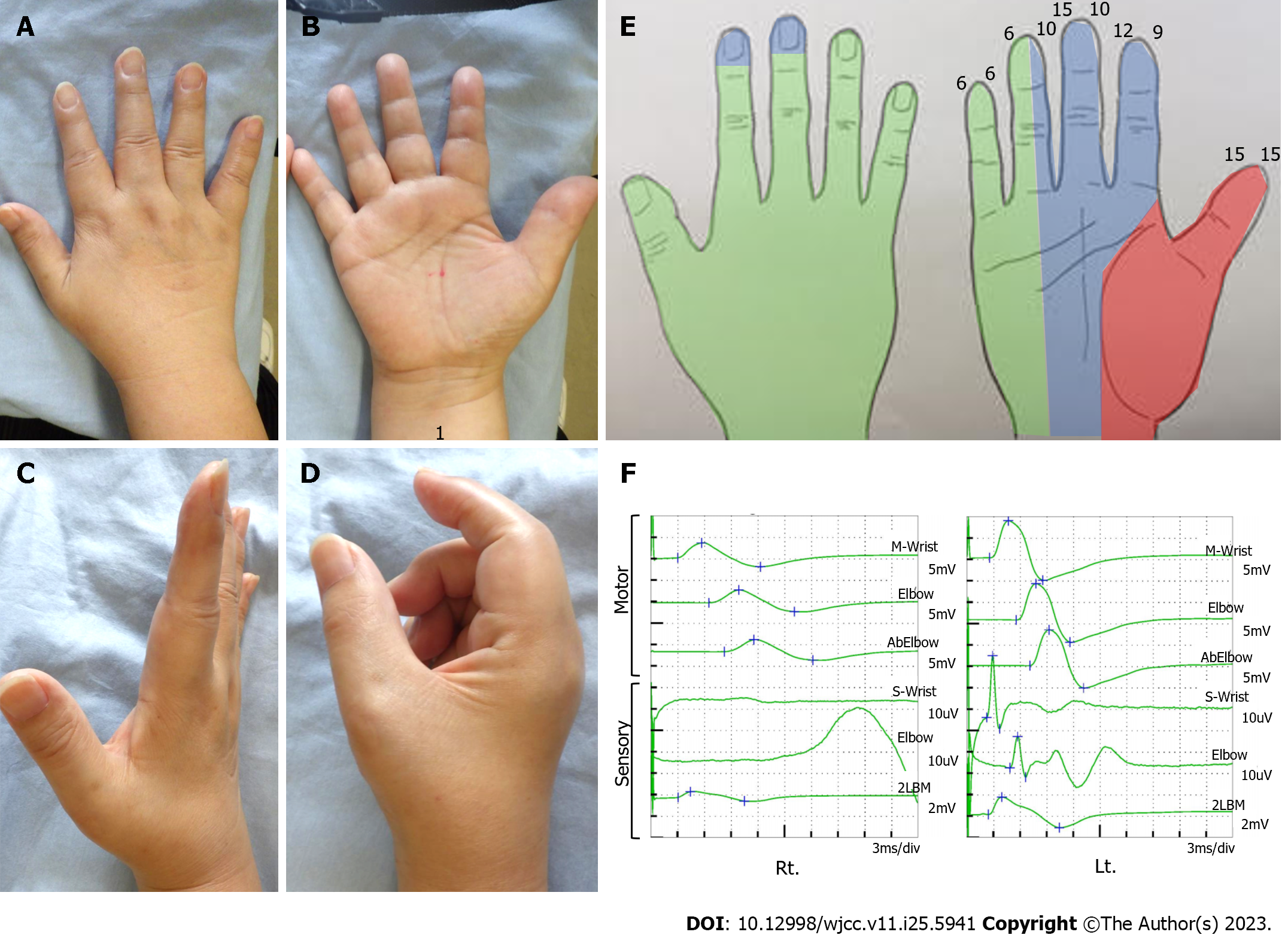
Figure 1 Preoperative physical examination.
A and B: Inspection of the right hand. The Tinel like sign was positive at the 2 proximal lateral digits from the wrist crease (1); C: Finger extension. Allowable without restriction; D: Finger flexion. Restriction of the index and middle fingers prevents full grip; E: Right hand perception. Numbers represent two-point discrimination test, colors represent semmes weinstein test results. There is a decreased perception in the median nerve area; F: Nerve conduction studies results of the median nerve. Compound muscle action potential was reduced and sensory nerve action potential showed no waveform appearance.
Figure 2 Intraoperative photographs.
A: The median nerve (1) is adherent to a fatty tissue (white arrow head) and flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) for the second digit (white arrow); B: The median nerve was dissected circumferentially, and FDS muscle belly was resected; C: Microscopic findings. There was mild erythema of the neuroepithelium, but no obvious injury or defect.
Figure 3 Postoperative physical examination.
A and B: Inspection of the right hand. An operation scar is present on the proximal median of the palm to the distal median of the forearm; C: Finger extension. Allowable without restriction; D: Finger flexion. Full grip is available; E: Decreased perception is localized to the phalanges of the index and middle fingers; F: Nerve conduction studies results of the median nerve at 6 mo postoperatively. The waveform of sensory nerve action potential can be confirmed.
- Citation: Suzuki T, Matsui Y, Momma D, Endo T, Iwasaki N. Median neuropathy after multiple punctures of the forearm for catheterization: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(25): 5941-5946
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i25/5941.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i25.5941