Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2023; 11(22): 5398-5406
Published online Aug 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5398
Published online Aug 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5398
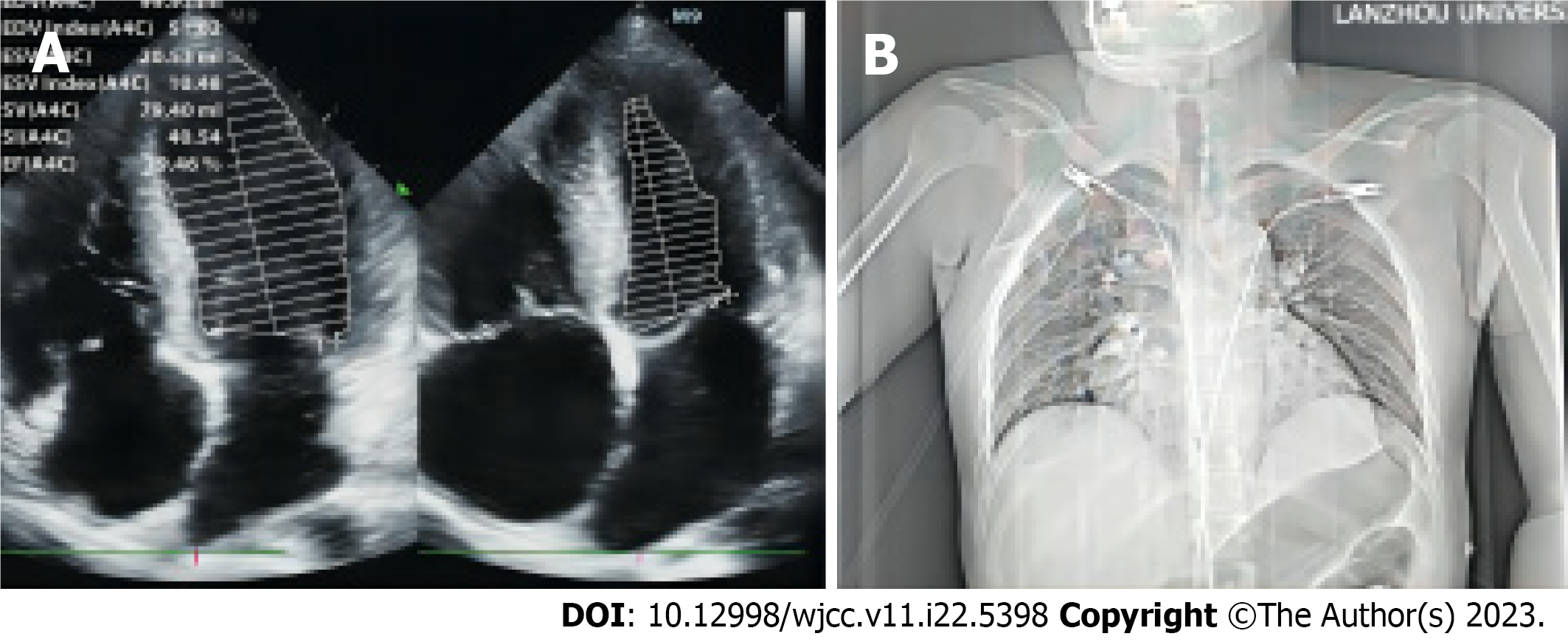
Figure 1 Echocardiographic and chest X-ray images.
A: Echocardiographic image. Mild enlargement of the whole heart, particularly the right heart, mild mitral and tricuspid valve regurgitation, moderate pulmonary hypertension, and small amounts of pericardial effusion were observed; B: Chest radiograph suggesting enlarged cardiac shadow.
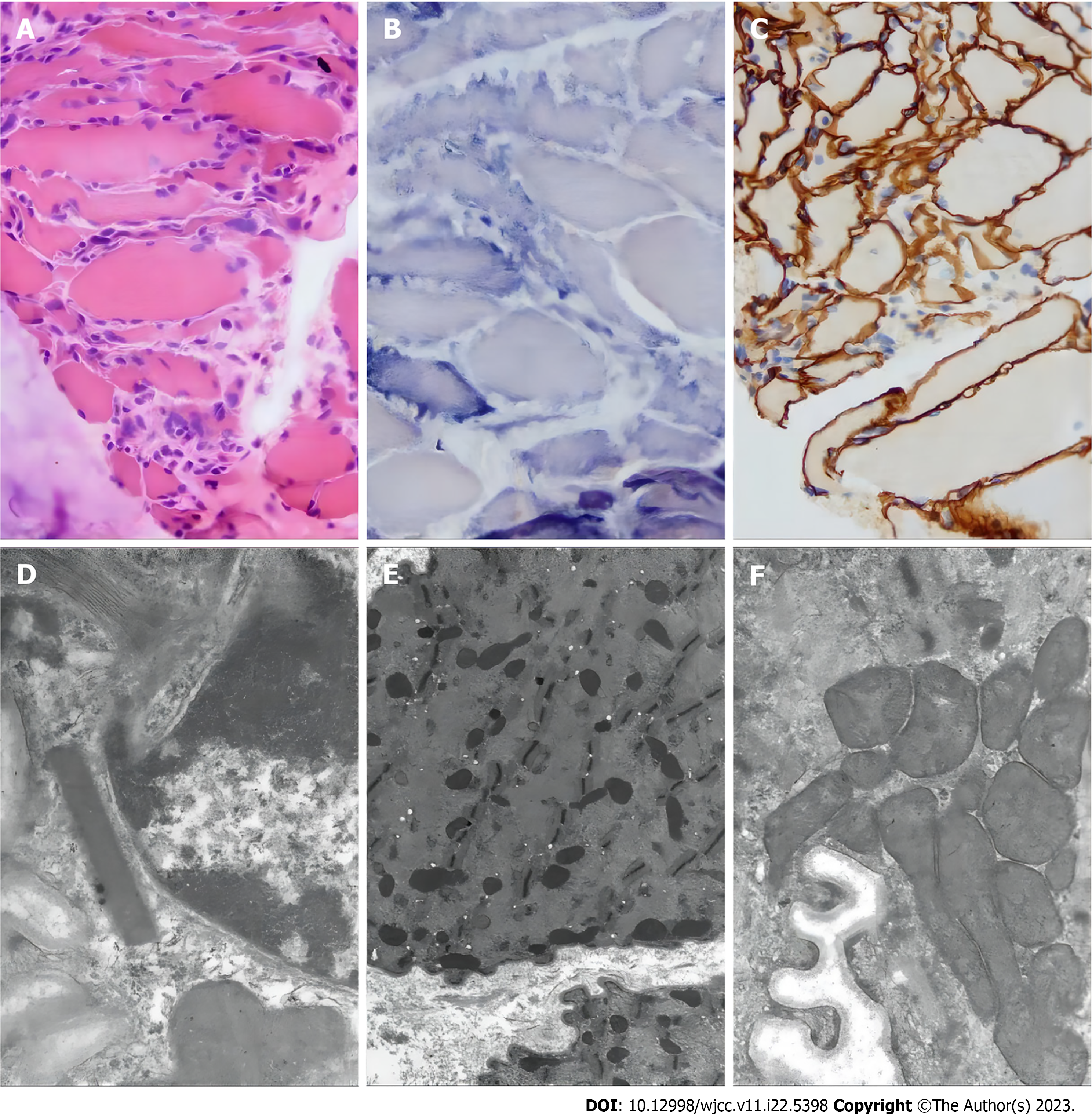
Figure 2 Optical and electron microscopy of the muscle biopsy of the left calf muscle.
The possibility of mitochondrial myopathy should be considered. A: Muscle biopsy with hematoxylin-eosin staining. The size of muscle fibers varies, some muscle fibers show atrophy, a few muscle fibers’ nuclei move inward, individual nuclei gather, muscle fissure is not obvious, and muscle fibers shrink. There is no obvious degeneration and necrosis, no lipid droplets and glycogen vacuoles in the cytoplasm of muscle fibers, no broken red fibers or rimmed vacuoles, no small keratinized muscle fibers or group atrophy, and no bundles. Fibrous tissue hyperplasia of muscle fascicular membrane and myo-intima is not obvious, and inflammatory cells are not obvious; B: Muscle biopsy with succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) staining. Muscle biopsy showed no ragged-blue fiber and strongly SDH reactive blood vessel; C: Muscle biopsy with dystrophin staining. Dystrophin expression was detected at the myosepta uniformly and continuously; D-F: Electron microscopy of muscle biopsy. Mitochondria under the sarcolemma and between myofibrils increase and accumulate, part of their volume increases, and individual mitochondria have suspected formation of lattice-like inclusion bodies.
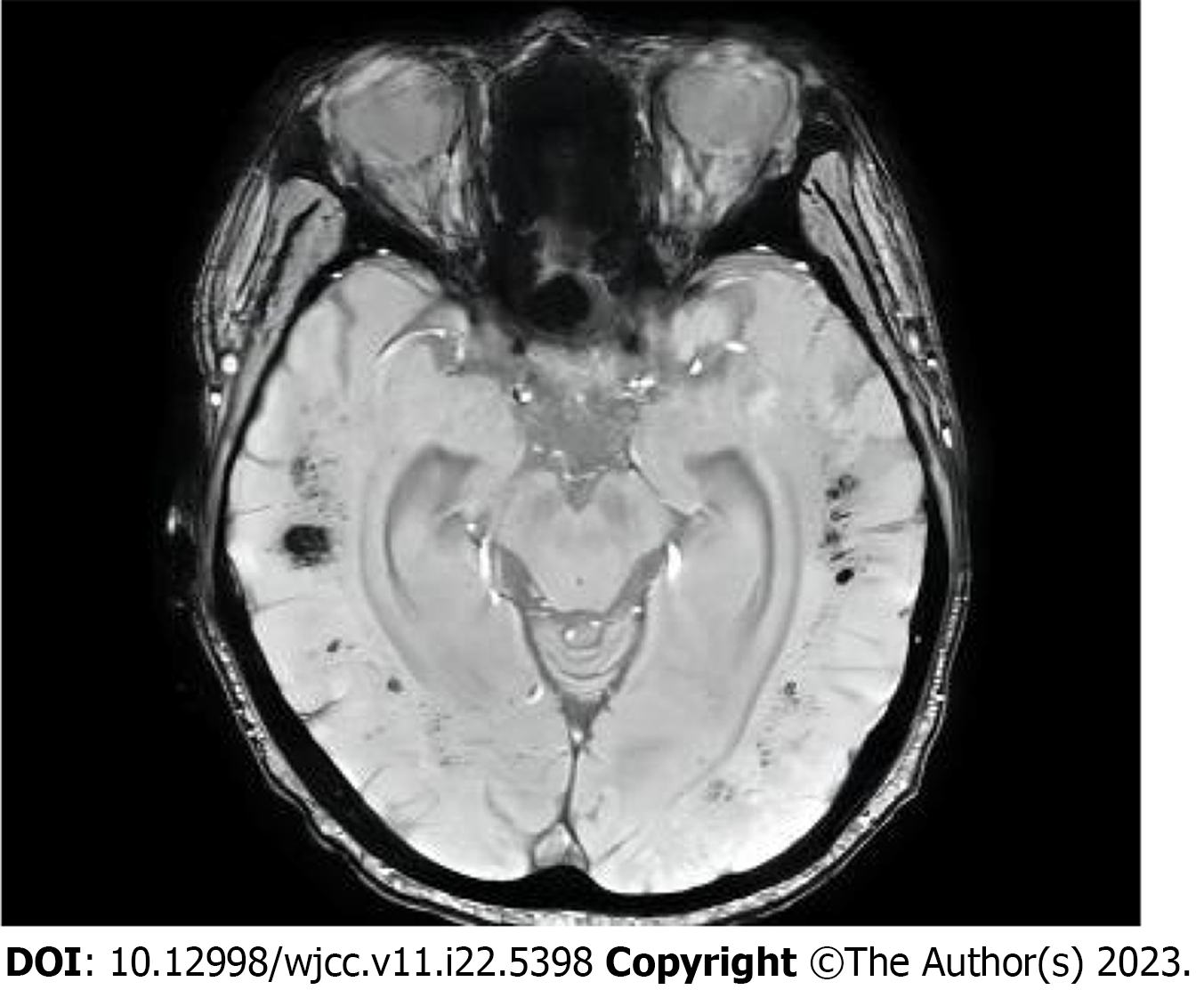
Figure 3 Cranial magnetic resonance imaging showed multifocal perivascular hemorrhage, but the patient had cerebral hemispherical white matter degeneration, cerebral atrophy, and ventricle enlargement on head magnetic resonance imaging.
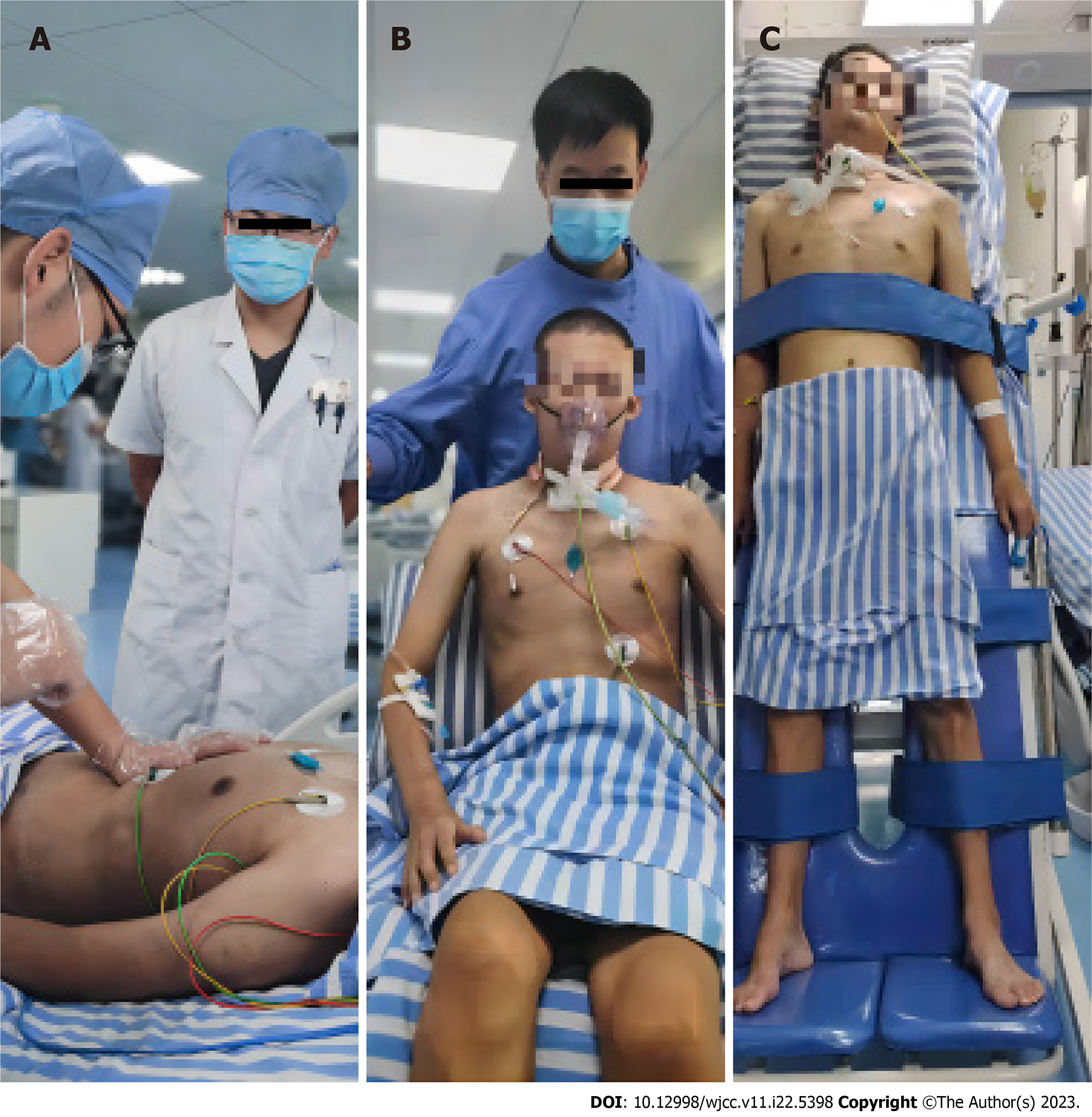
Figure 4 Respiratory therapy, physiotherapy, and rehabilitation.
A: The patient was undergoing respiratory function training; B: The patient was sitting in a chair and doing active muscle training (e.g. shrugging the shoulders); C: The patient was doing standing training with standing bed.
- Citation: Chen L, Shuai TK, Gao YW, Li M, Fang PZ, Christian W, Liu LP. Treatment of a patient with severe lactic acidosis and multiple organ failure due to mitochondrial myopathy: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(22): 5398-5406
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i22/5398.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5398