Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2023; 11(22): 5252-5272
Published online Aug 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5252
Published online Aug 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5252
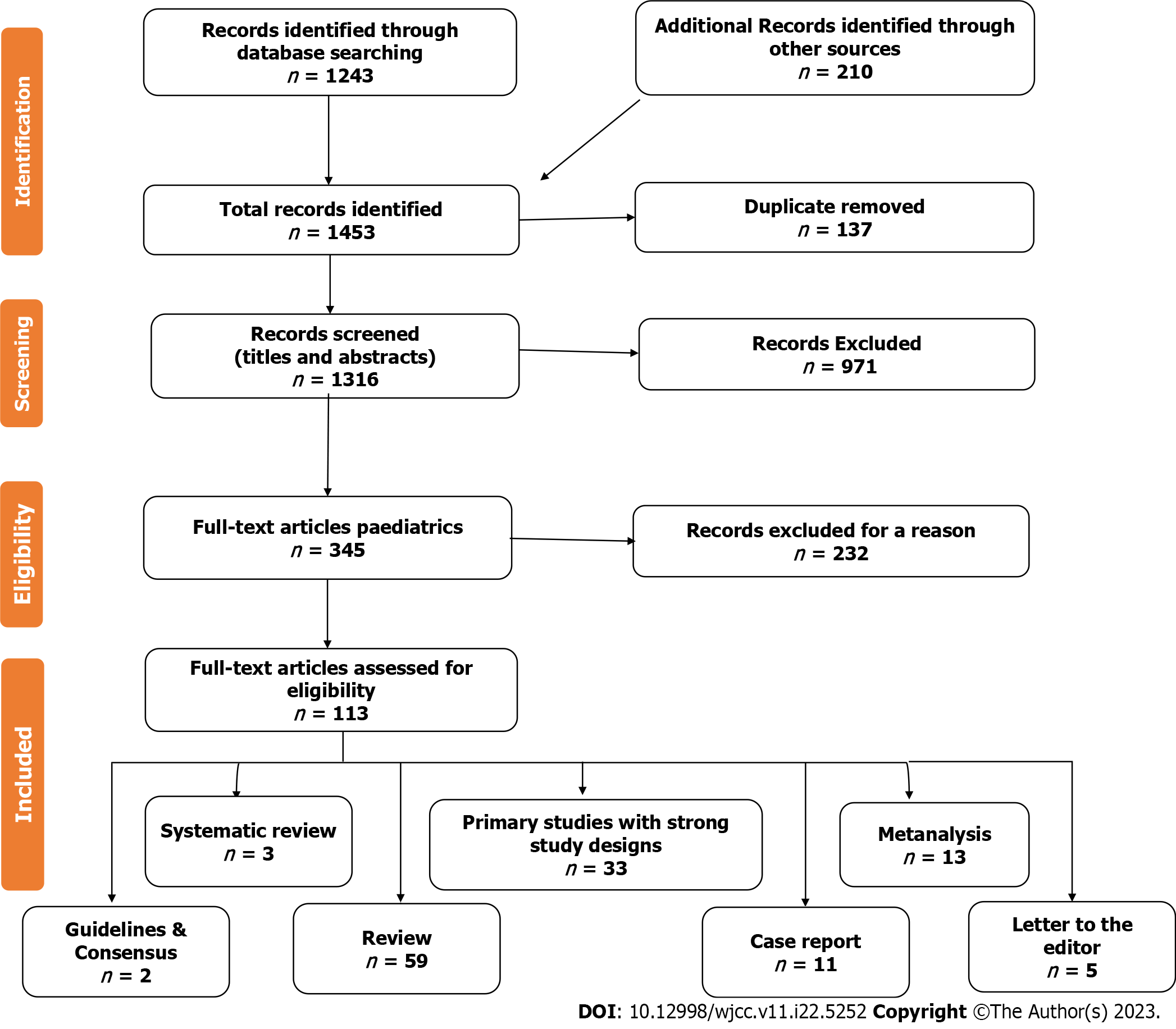
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study.
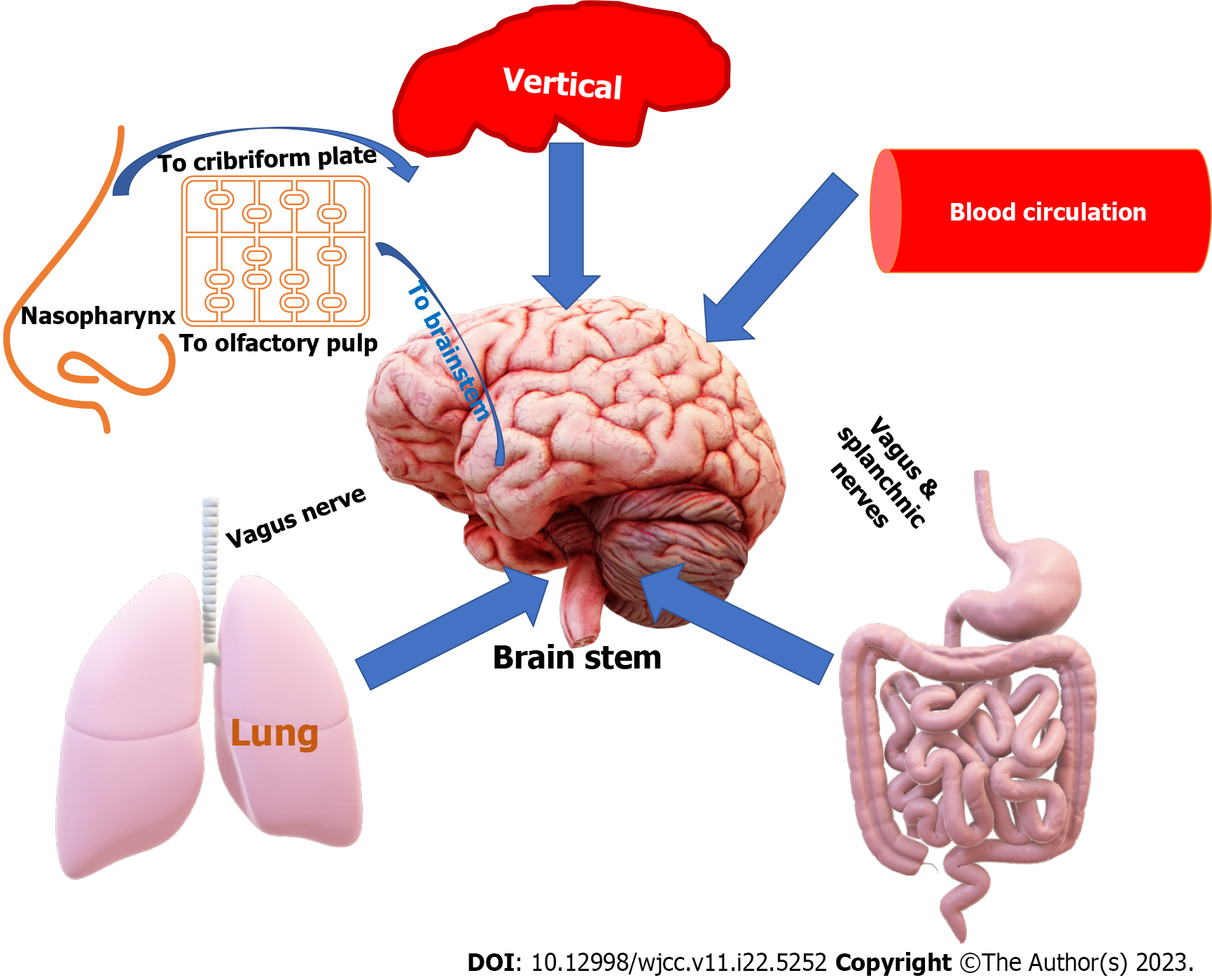
Figure 2 Potential entry pathways of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 into the brainstem.
This diagram illustrates the potential pathways for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 to enter the brainstem, including through the nasal passage and olfactory system, via the bloodstream, through the vagus nerve connecting the lungs and intestines, and through the placenta due to the virus' neurotropic properties.
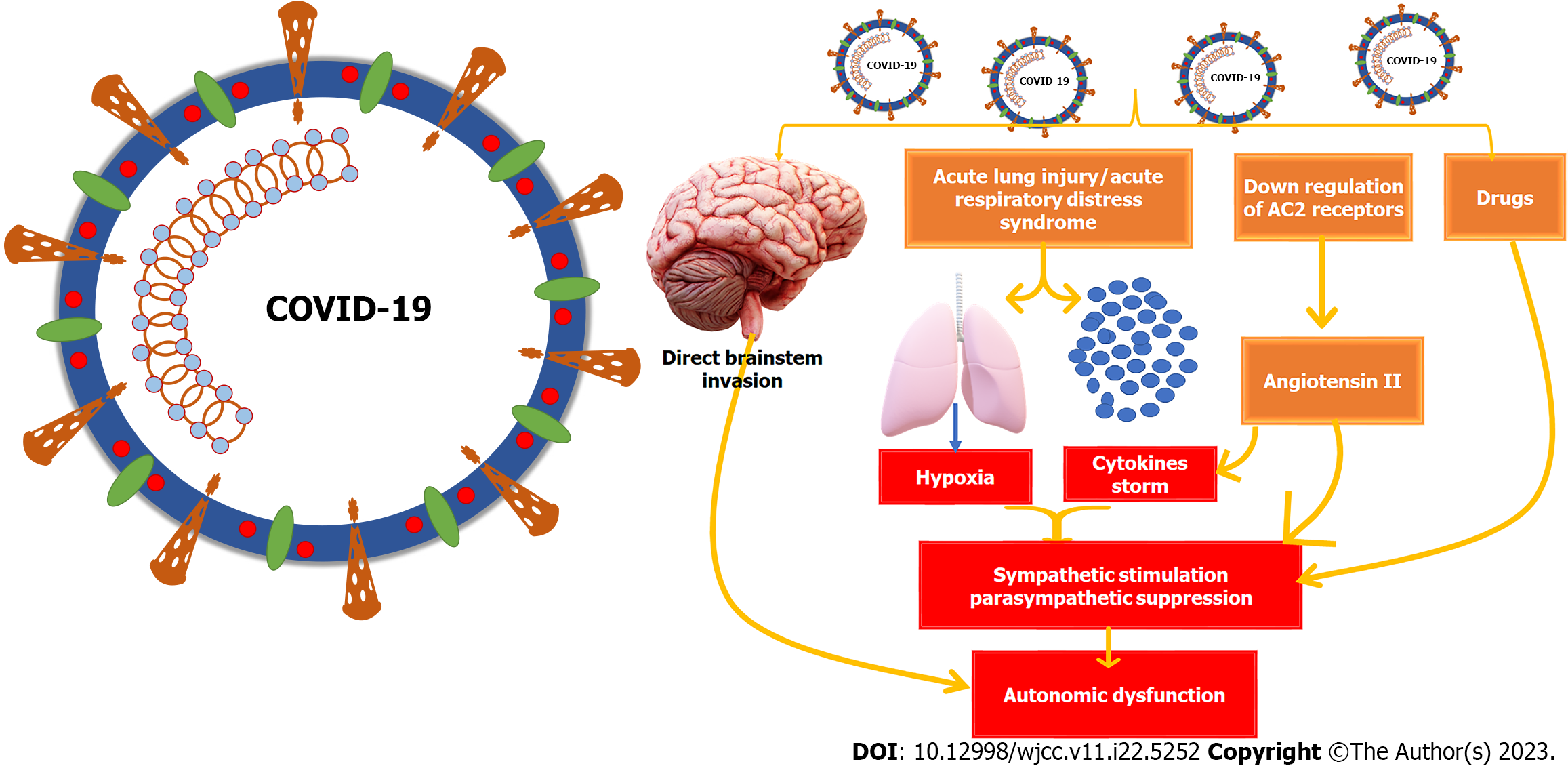
Figure 3 Mechanism of autonomic dysfunction induced by coronavirus disease 2019.
The exact mechanism is not clear but could be due to the direct viral invasion of the brainstem affecting the dorsal vagal complex located in the medulla oblongata, due to the resultant cytokine storm-induced sympathetic stimulation, due to the hypoxia resulting from the lung injury causing sympathetic stimulation and parasympathetic depression, due to the down-regulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors causing excess angiotensin II, or as a complication of various medications used to treat coronavirus disease 2019 patients, particularly those requiring intensive care.
- Citation: Elbeltagi R, Al-Beltagi M, Saeed NK, Bediwy AS. COVID-19-induced gastrointestinal autonomic dysfunction: A systematic review. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(22): 5252-5272
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i22/5252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i22.5252