Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 16, 2023; 11(2): 449-455
Published online Jan 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i2.449
Published online Jan 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i2.449
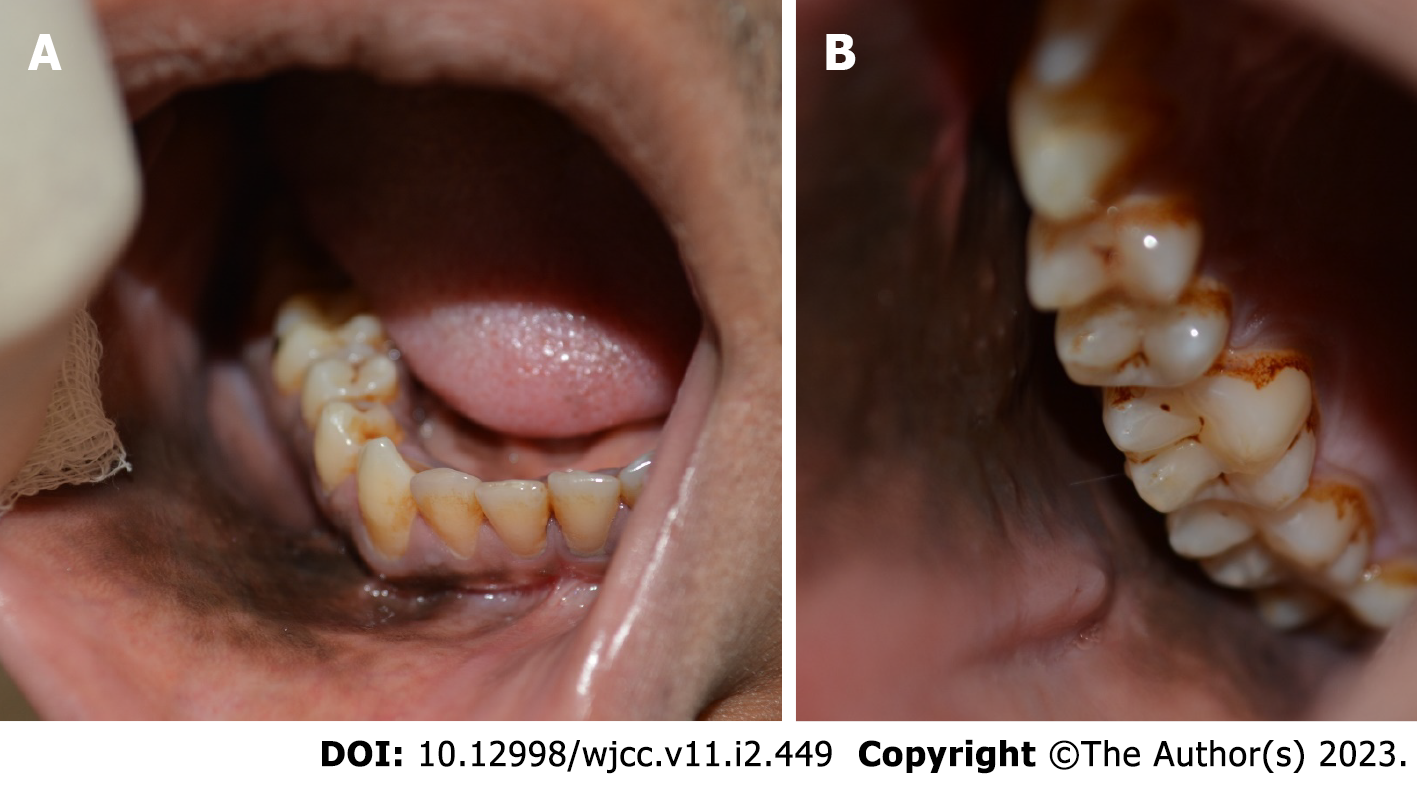
Figure 1 Intraoral examination.
A and B: Clinical photos of the oral cavity illustrate a diffuse dark brownish-black pigmented lesion with an ill-defined margin covering the right lower gingiva, right buccal and labial vestibules, and right buccal mucosa.
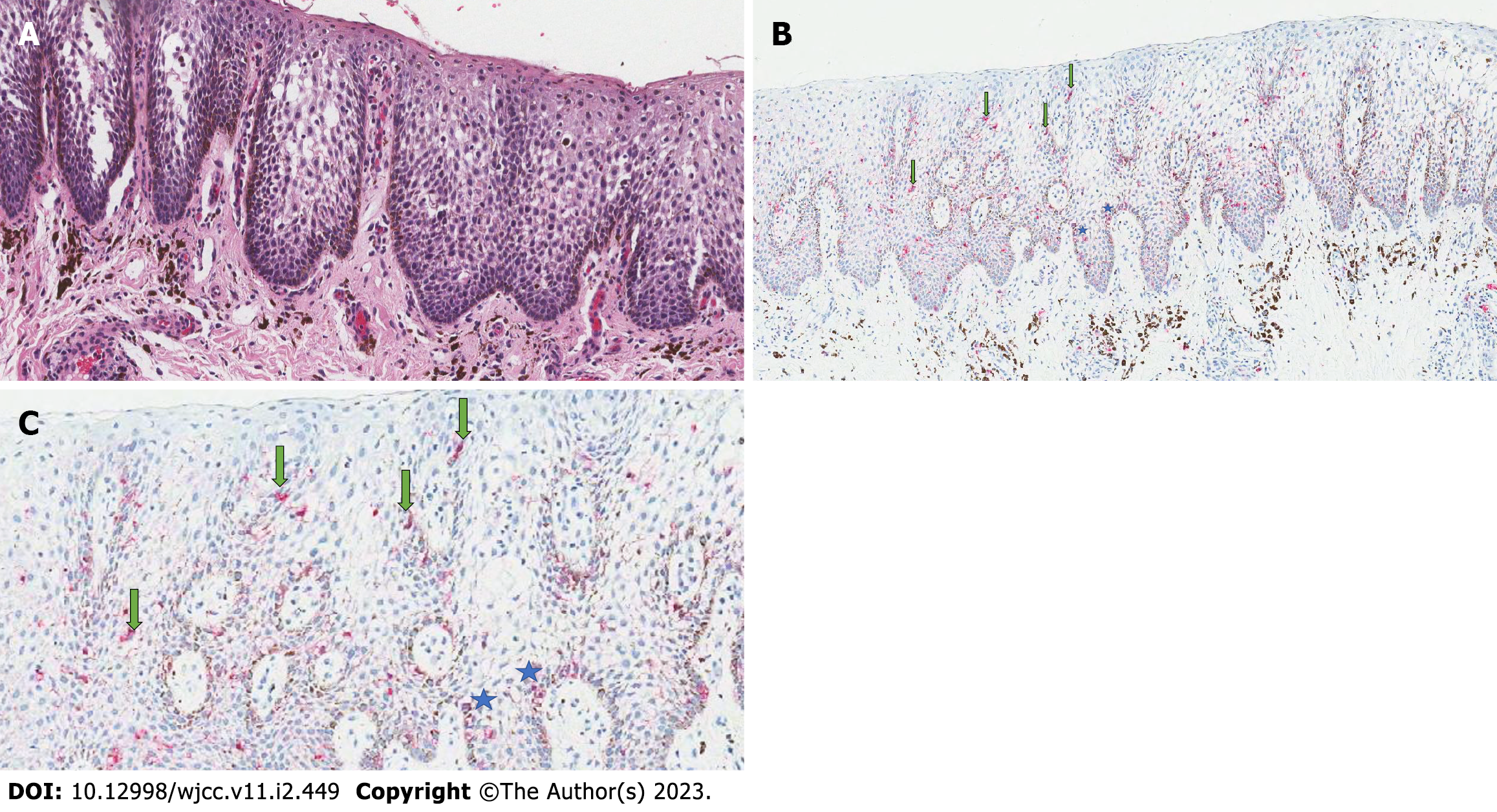
Figure 2 Histopathological photomicrographs.
A: Histopathological photomicrograph of Hematoxylin and Eosin stained section shows spongiosis, acanthosis, and dendritic melanocytes in the parakeratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Also, show the lamina propria with melanin deposit; B: Histopathological photomicrograph of Melan-A-stained section shows dendritic melanocytes (green arrows) and melanocytic hyperplasia (blue stars) throughout the epithelium; C: Histopathological photomicrograph (higher magnitude) of Melan-A-stained section shows dendritic melanocytes (green arrows) and melanocytic hyperplasia (blue stars) throughout the epithelium.
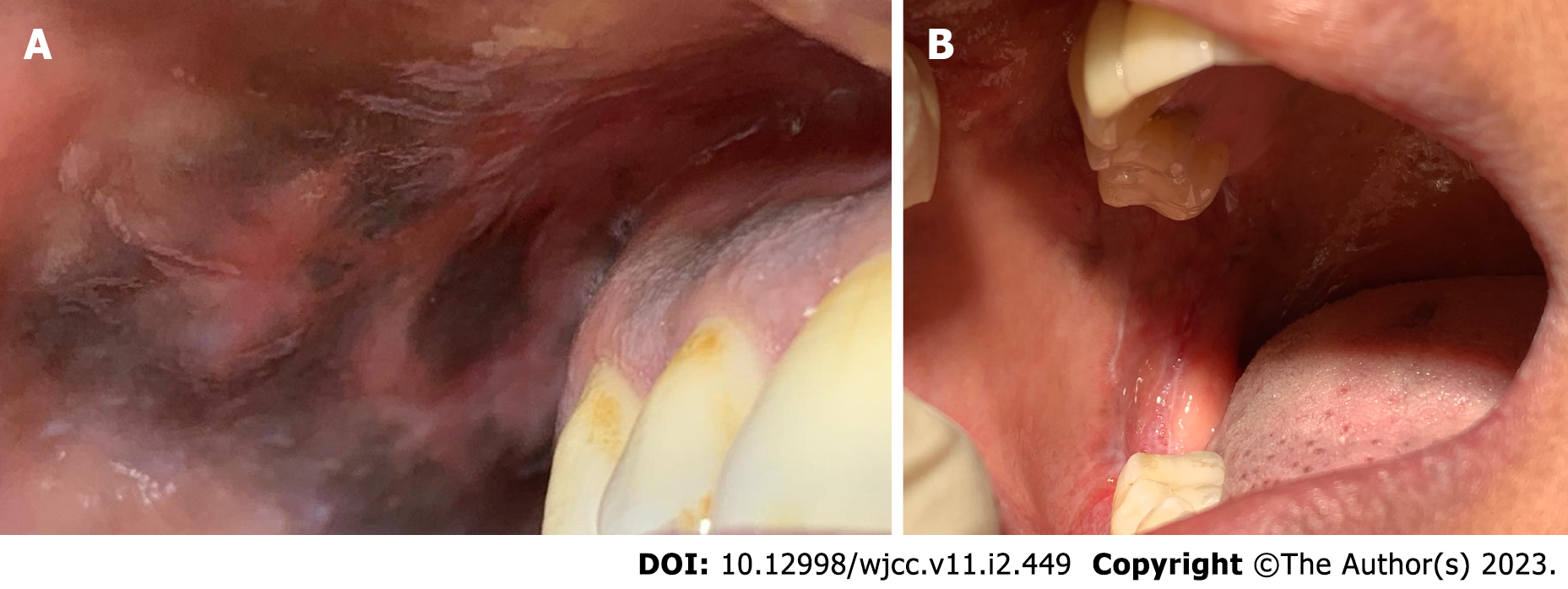
Figure 3 Follow-up clinical photos.
A: Two-month follow-up clinical photos of the right buccal mucosa showing partial resolution of the oral lesion; B: A 4-mo follow-up clinical photo of the oral cavity illustrates the complete resolution of the oral melanoacanthoma.
- Citation: Albagieh H, Aloyouny A, Alshagroud R, Alwakeel A, Alkait S, Almufarji F, Almutairi G, Alkhalaf R. Habitual khat chewing and oral melanoacanthoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(2): 449-455
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i2/449.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i2.449