Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2023; 11(17): 4142-4151
Published online Jun 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4142
Published online Jun 16, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4142
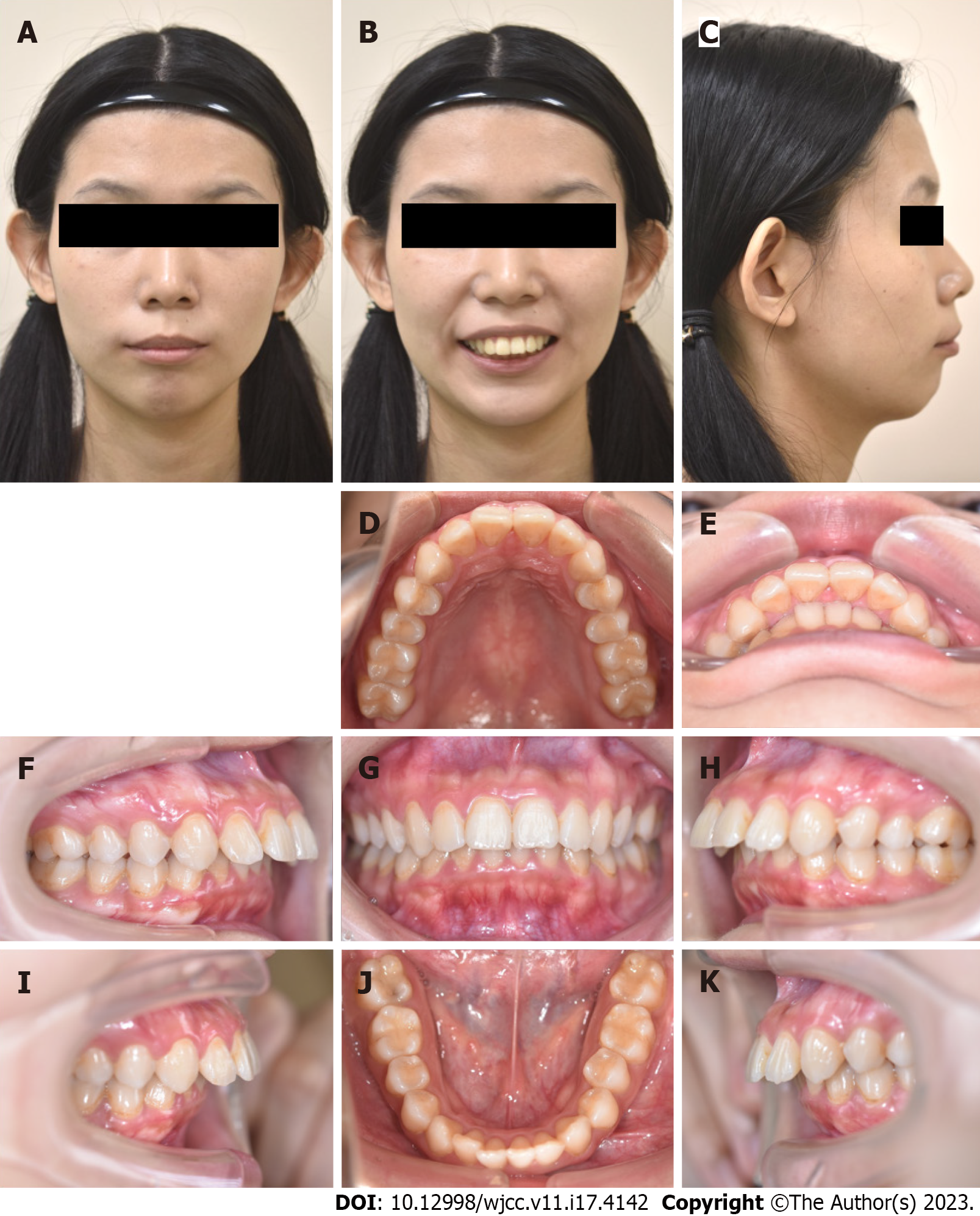
Figure 1 Pretreatment photographs (21 years 4 months old).
A-C: Facial profiles; D-K: Intraoral photographs.
Figure 2 Radiograph.
A: Pretreatment panoramic radiograph; B: Lateral cephalometric radiograph; C: Anteroposterior cephalometric radiograph (21 years 4 mo old).
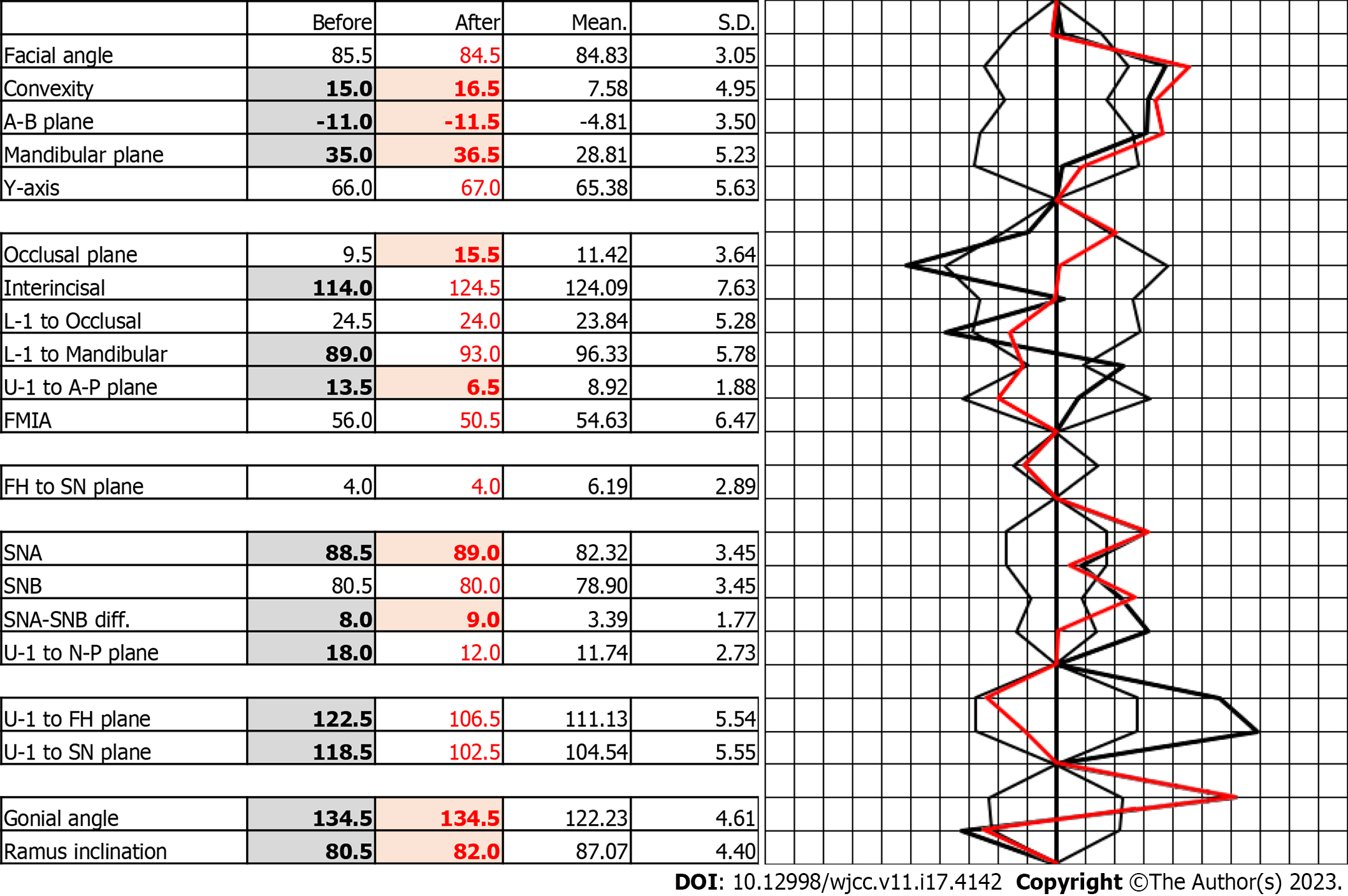
Figure 3 Polygon: Before active treatment.
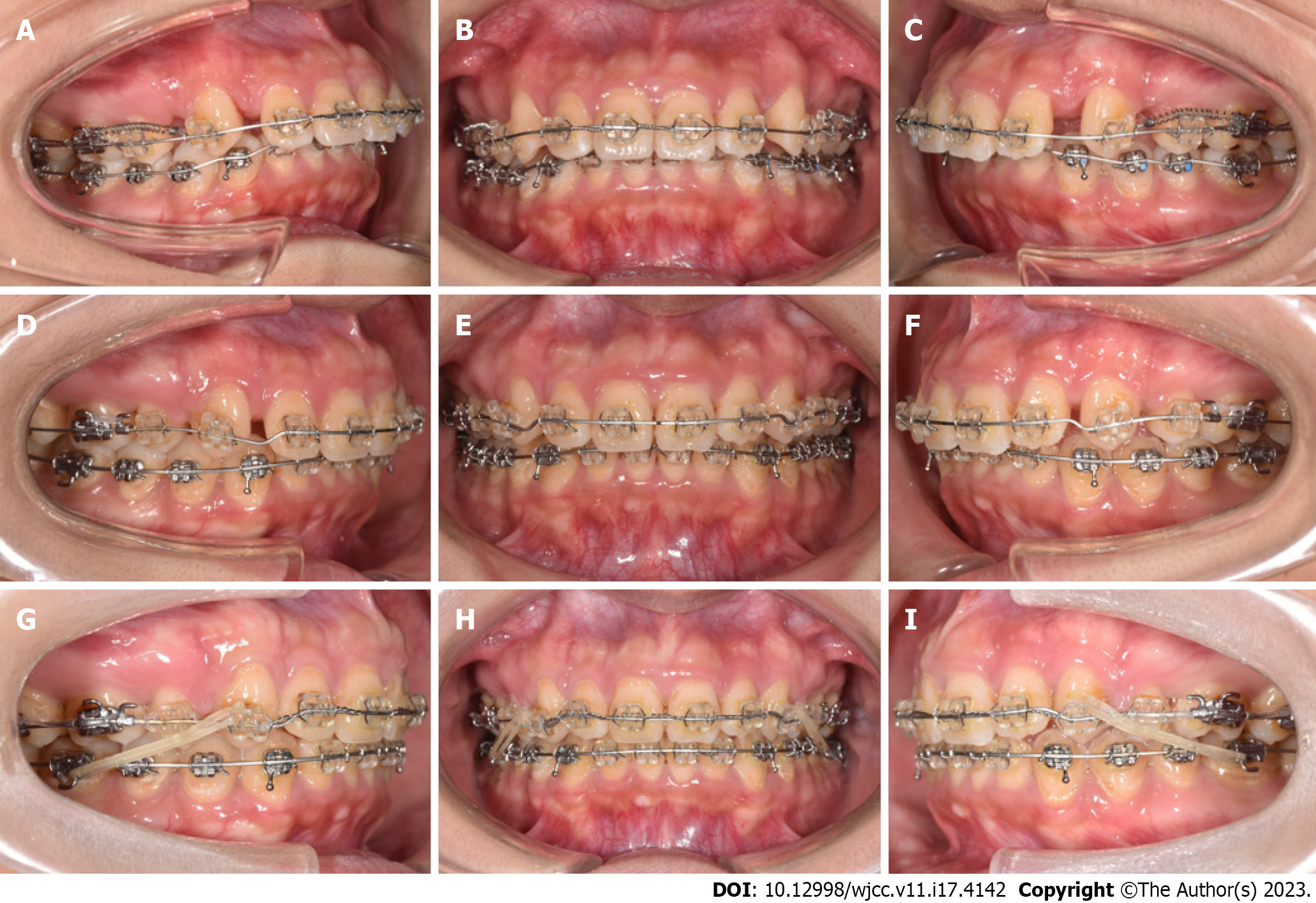
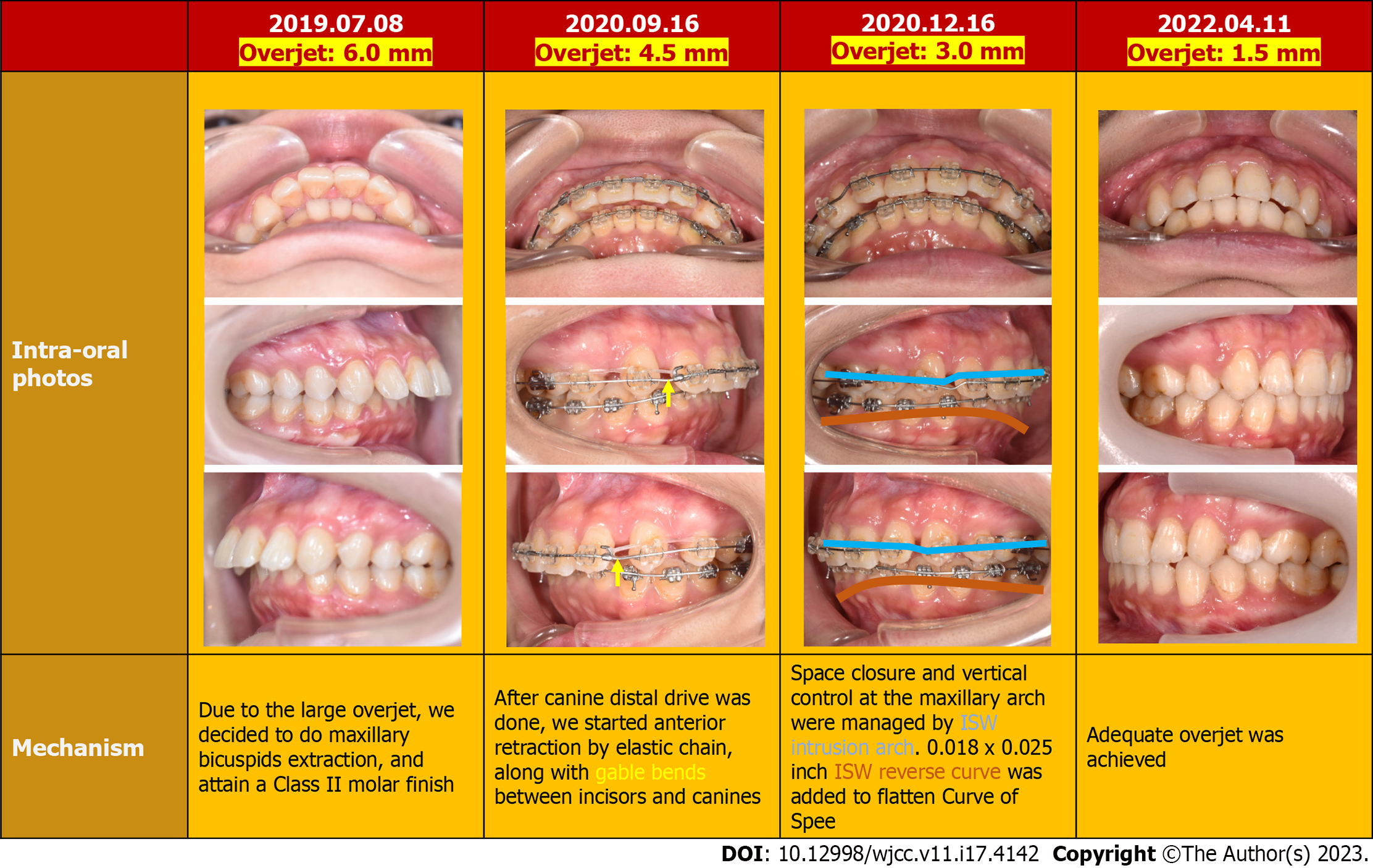
Figure 4 Progressive intraoral photographs.
A-C: 4 mo; D-F: 15 mo; G-I: 24 mo.
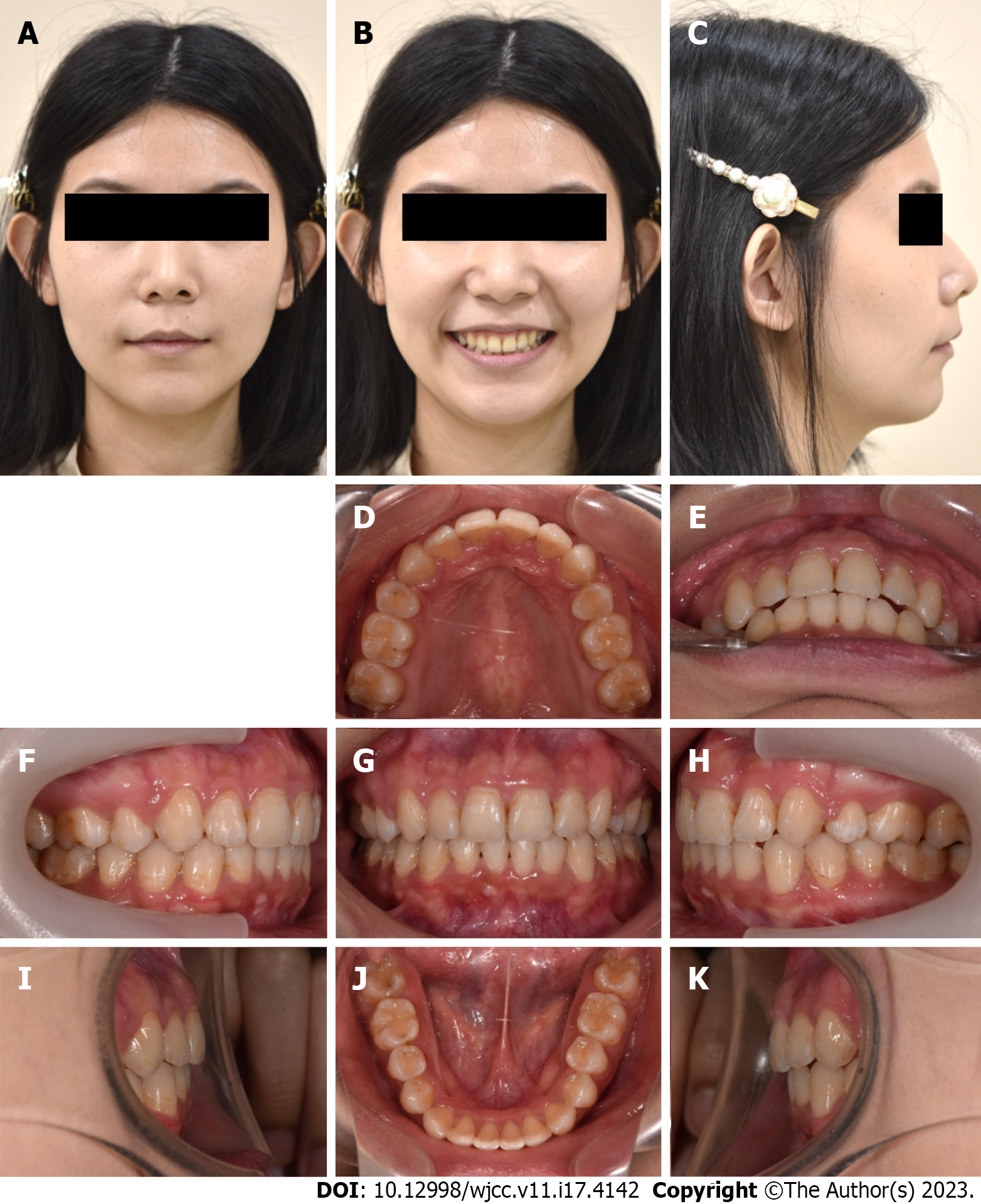
Figure 5 Posttreatment photographs (24 years 2 mo old).
A-C: Facial profiles; D-K: Intraoral photographs.
Figure 6 Radiograph.
A: Posttreatment panoramic radiograph; B: Lateral cephalometric radiograph; C: Anteroposterior cephalometric radiograph (24 years 2 mo old).
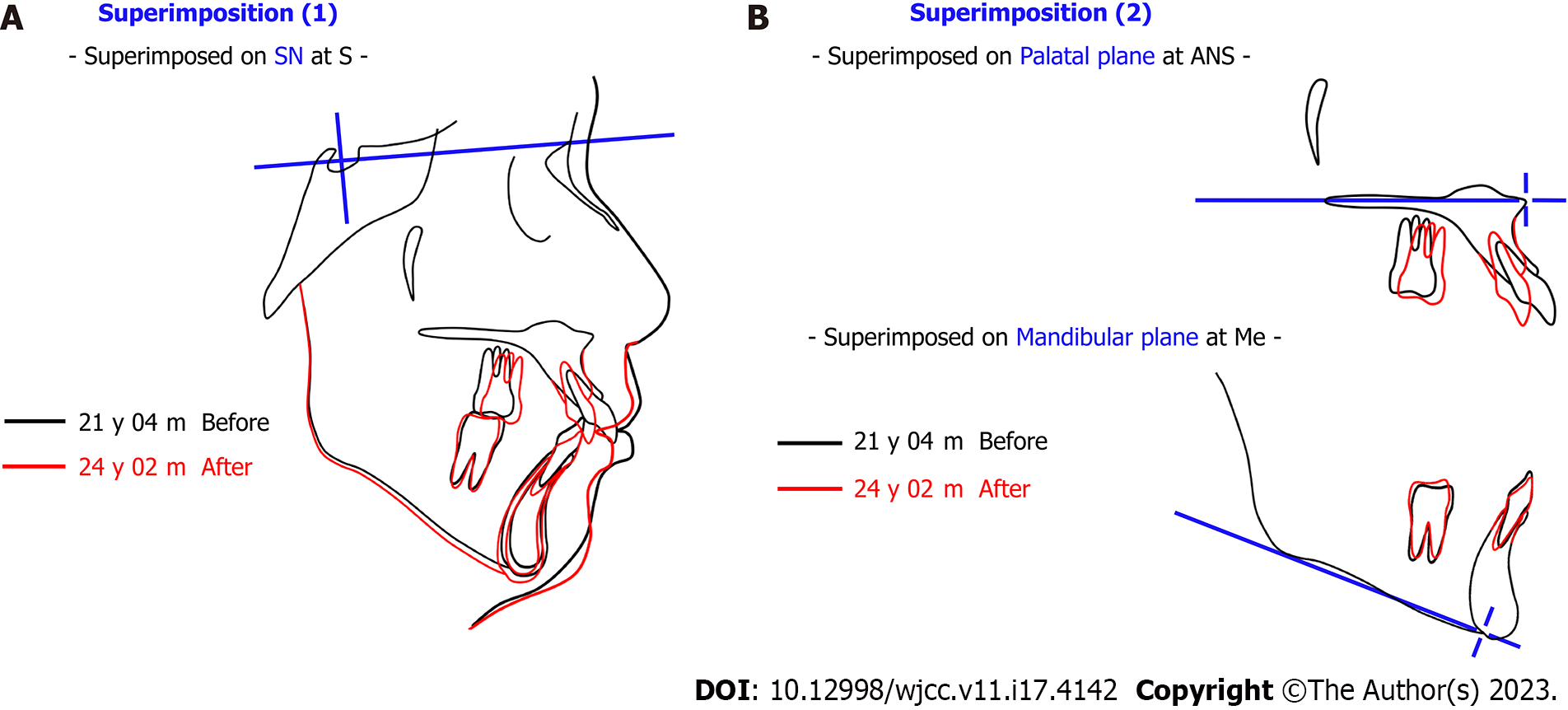
Figure 7 Superimposition of pretreatment and posttreatment.
A: Superimposed on sella-nasion plane at S; B: Superimposed on palatal plane at anterior nasal spine and Mandibular plane at Me. SN: Sella-Nasion plane; S: Sella; ANS: Anterior Nasal Spine; Me: Menton.
Figure 8 Polygon: Before and after active treatment.
SN: Sella-Nasion plane; FMIA: The Frankfort-Mandibular Incisor Angle; FH: Frankfort horizontal plane; SNA: Sella-nasion-A point; SNB: Sella-nasion-B point.
Figure 9 Overjet reduction methods.
ISW: Improved super-elastic Ti–Ni alloy wire.
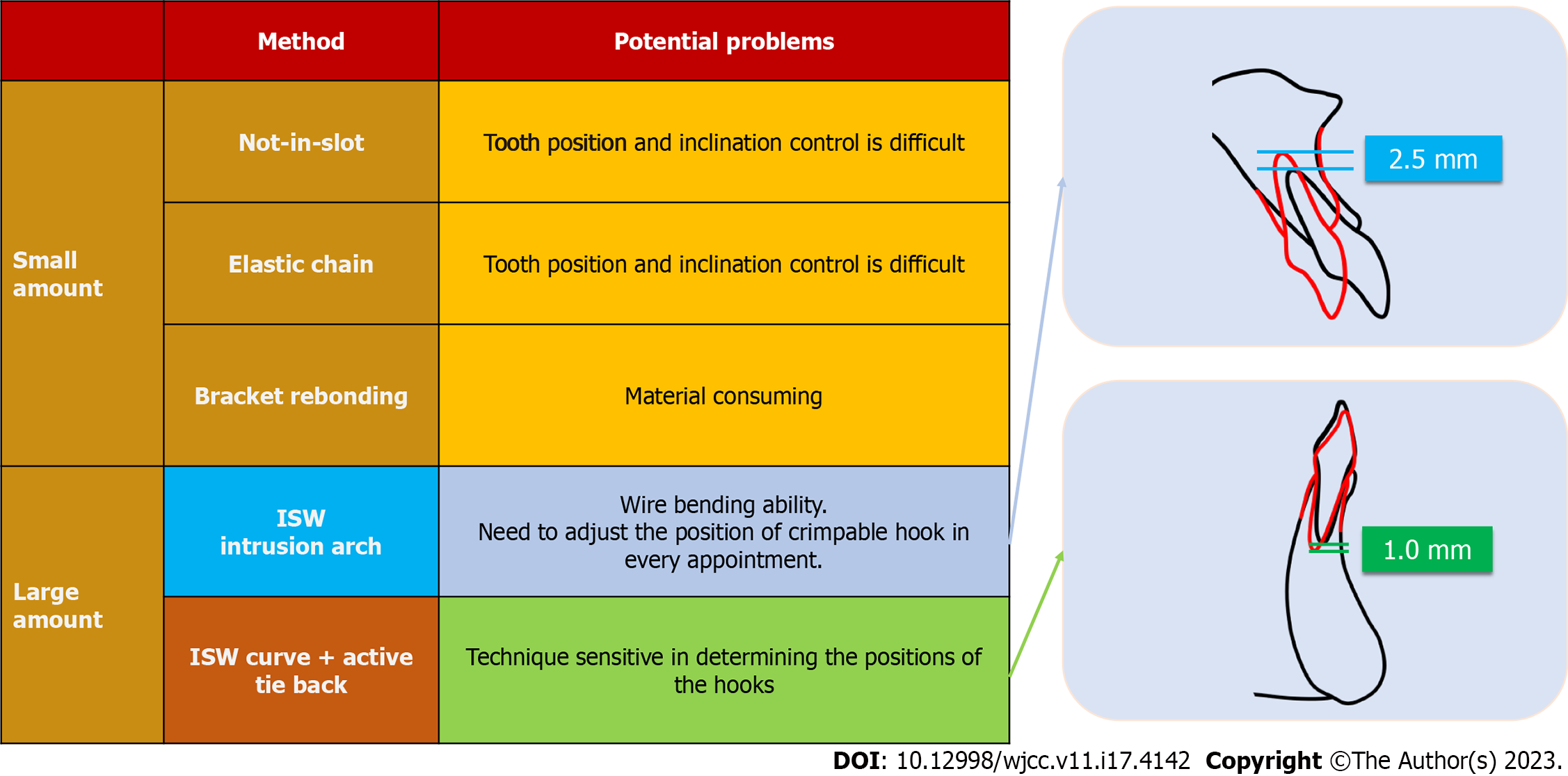
Figure 10 Strategy of intrusion.
ISW: Improved super-elastic Ti–Ni alloy wire.
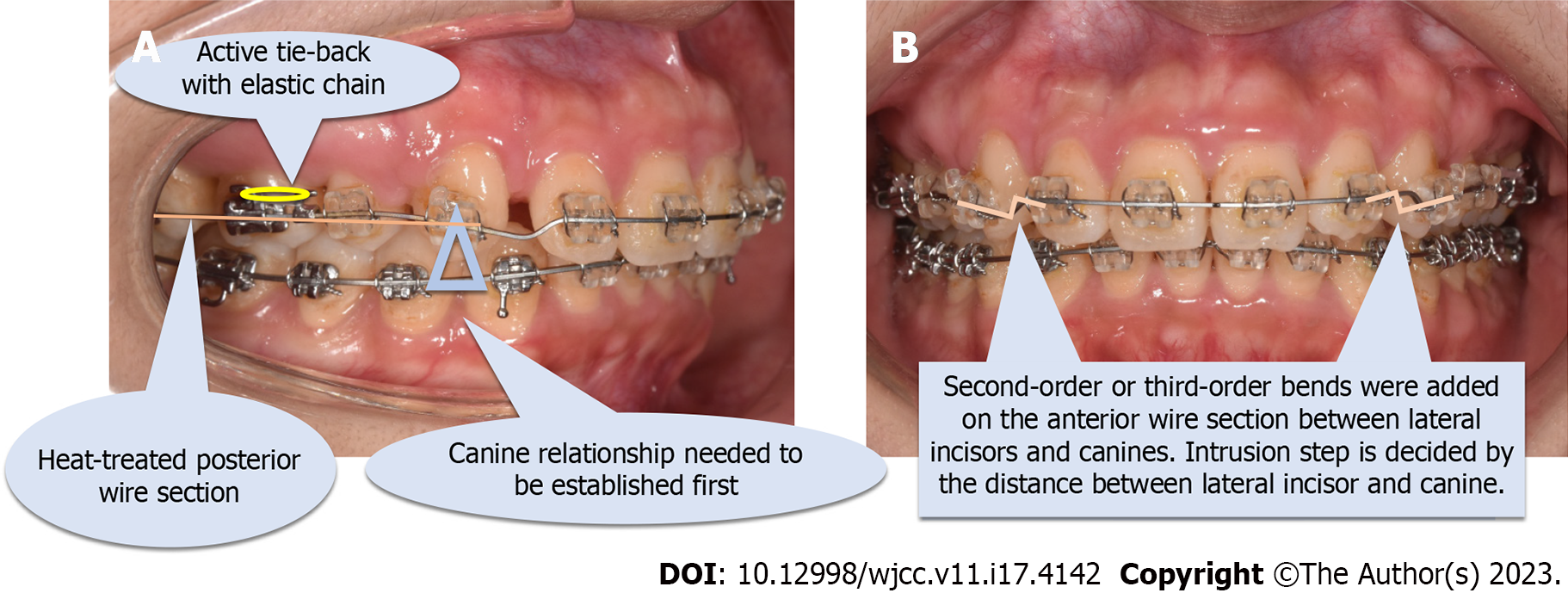
Figure 11 Introduction of an improved super-elastic Ti–Ni alloy wire intrusion arch.
A: Lateral view; B: Frontal view.
- Citation: Yang CY, Lin CC, Wang IJ, Chen YH, Yu JH. Improved super-elastic Ti–Ni alloy wire intrusion arch for skeletal class II malocclusion combined with deep overbite: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(17): 4142-4151
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i17/4142.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i17.4142