Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2023; 11(15): 3651-3657
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i15.3651
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i15.3651
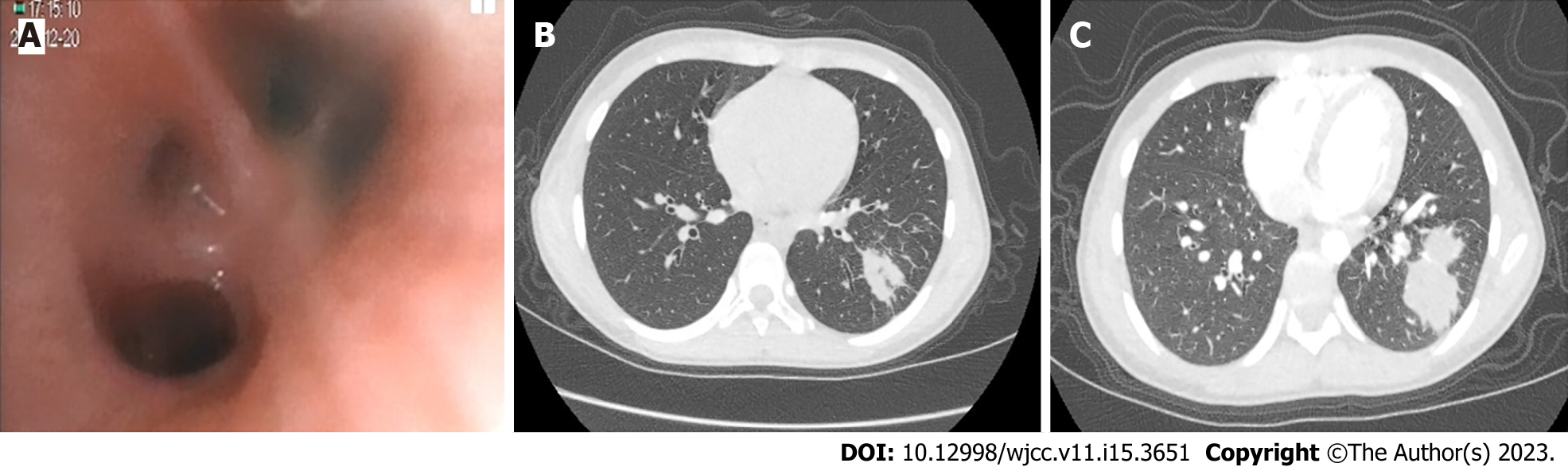
Figure 1 Bronchoscopy and computed tomography images at different stages of treatment.
A: Basal segment of the lower lobe of the left lung under conventional bronchoscopy during the first hospitalization; B: Computed tomography (CT) scan showed a lesion in the outer basal segment of the lower lobe of the left lung grew bigger during the first hospitalization; C: CT scan showed a lesion in the outer basal segment of the lower lobe of the left lung grew bigger after the first hospitalization.
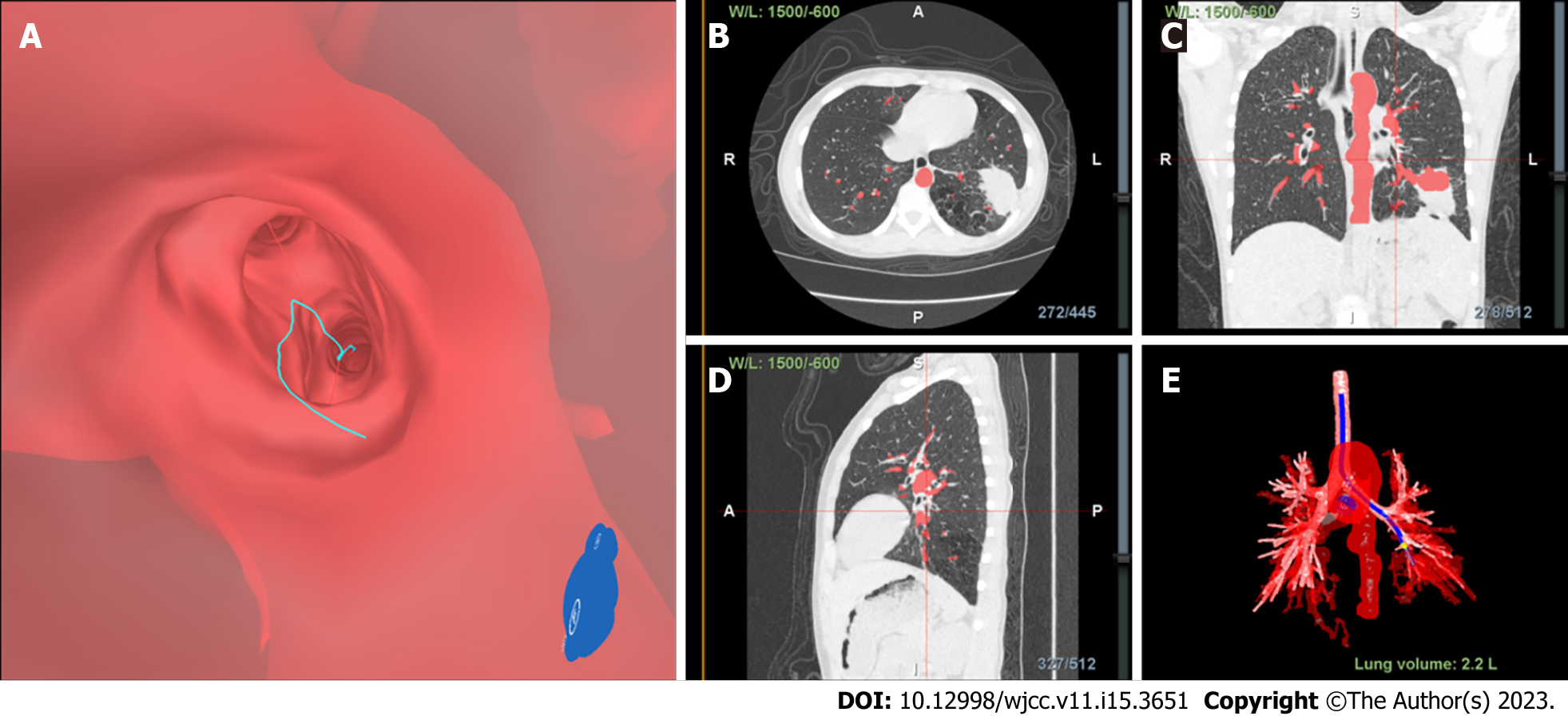
Figure 2 Three-dimensional reconstruction of thoracic computed tomography with the bronchial tree, tunnel path, and peripheral lung lesions location.
A: Virtual bronchoscopic navigation images on LungPro indicate a bronchial route; B: Cross-sectional view; C: Coronal reconstruction view; D: Sagittal view; E: Three-dimensional view.
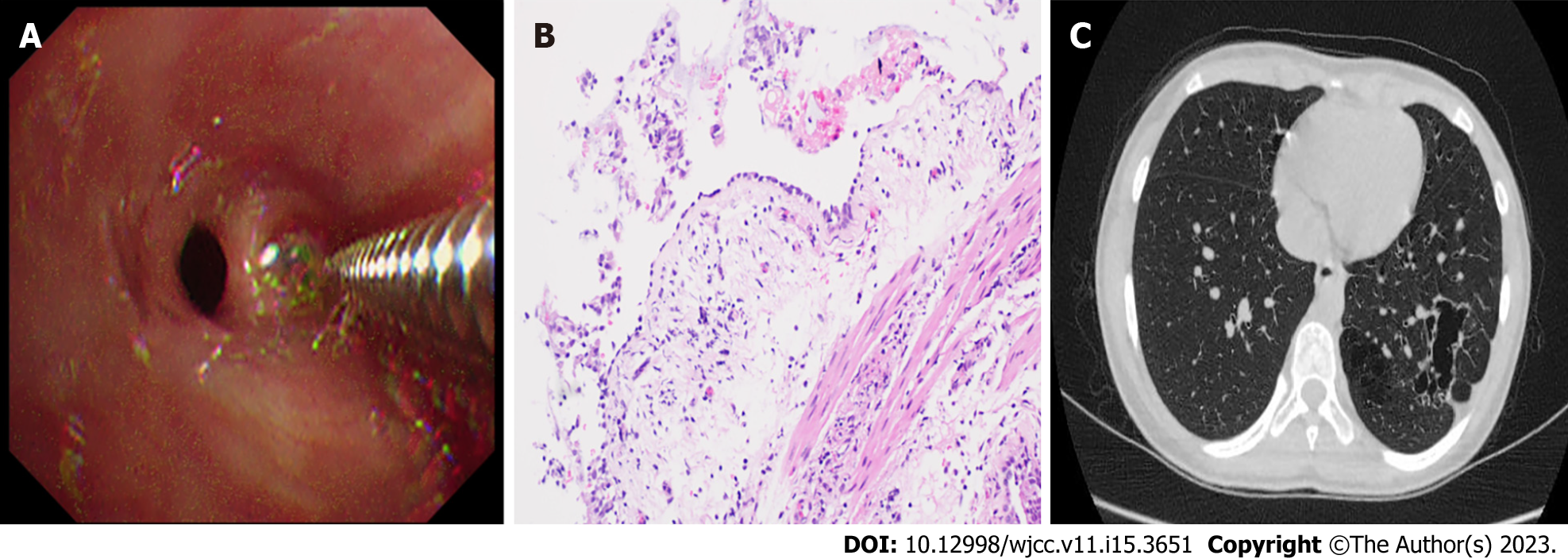
Figure 3 Transbronchial lung biopsy, postoperative pathological examination and computed tomography image results after treatment.
A: Transbronchial lung biopsy under bronchoscopy; B: Endotracheal biopsy showing bacterial colonization, 200× magnification; C: High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) obtained after treatment. Chest HRCT scans show the transparency of the basal segment of the left lower lobe increased, multiple lesions of unequal size, multilocular thin-walled air bag cavity can be seen. Compared with the former chest CT, some lesions are absorbed.
- Citation: Meng FZ, Chen QH, Gao M, Zeng L, Lin JR, Zheng JY. Diagnosis based on electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy-guided biopsied peripheral lung lesions in a 10-year-old girl: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(15): 3651-3657
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i15/3651.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i15.3651