Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. May 26, 2023; 11(15): 3612-3618
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i15.3612
Published online May 26, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i15.3612
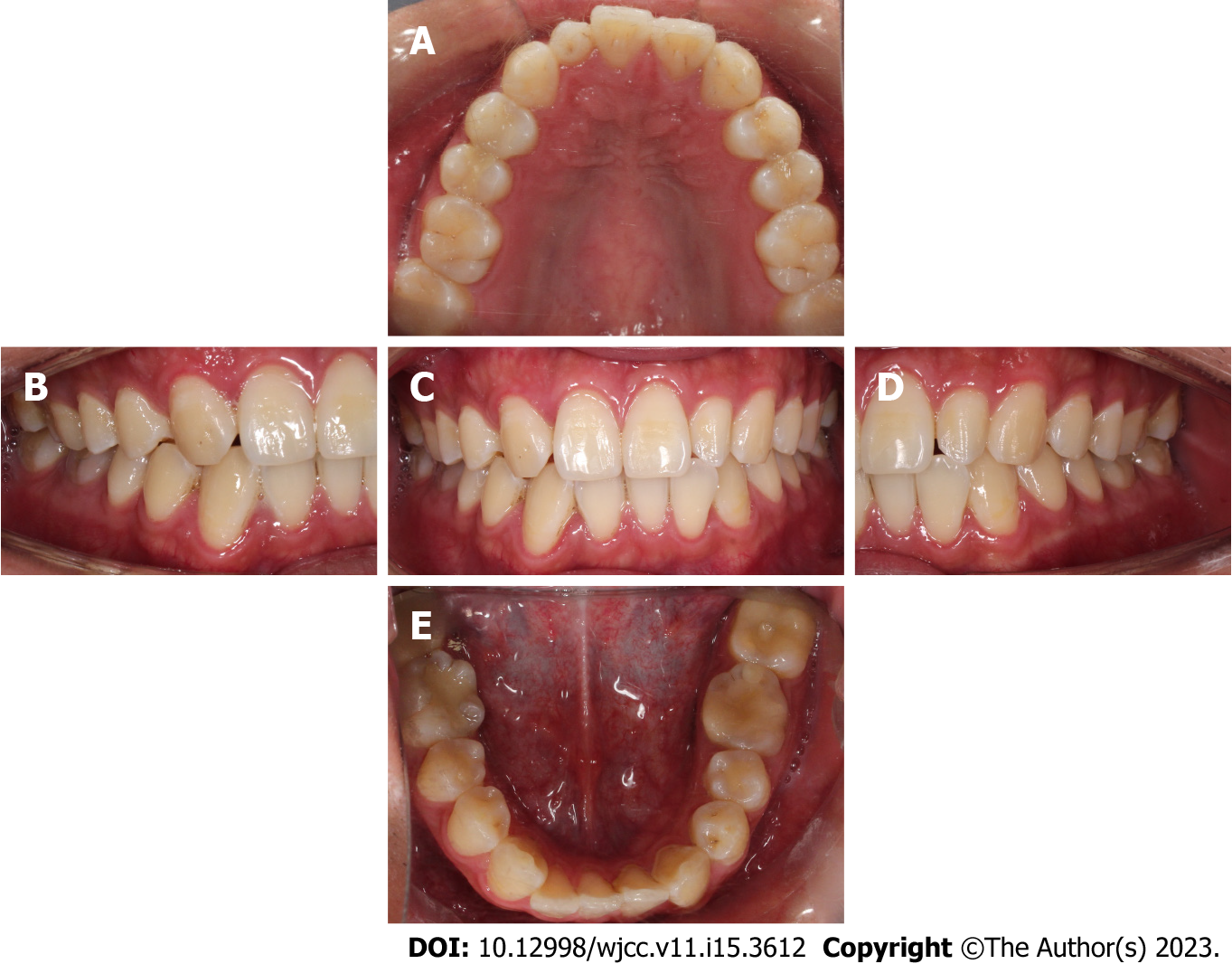
Figure 1 Intraoral photographs before treatment.
A: Maxillary occlusal view; B: Right buccal view; C: Frontal view; D: Left buccal view; E: Mandibular occlusal view.
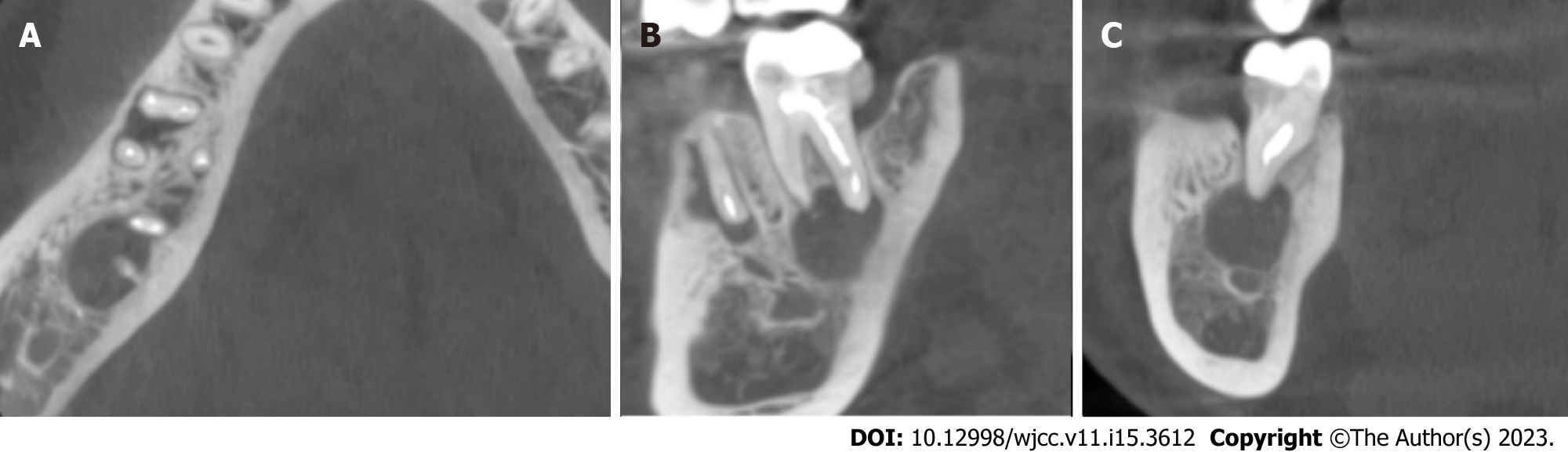
Figure 2 Cone-beam computed tomography of the mandibular second molar with a radicular cyst.
A: Axial sections of the mandibular second molar with a radicular cyst; B: Sagittal sections of the mandibular second molar with a radicular cyst; C: Coronal sections of the mandibular second molar with a radicular cyst.
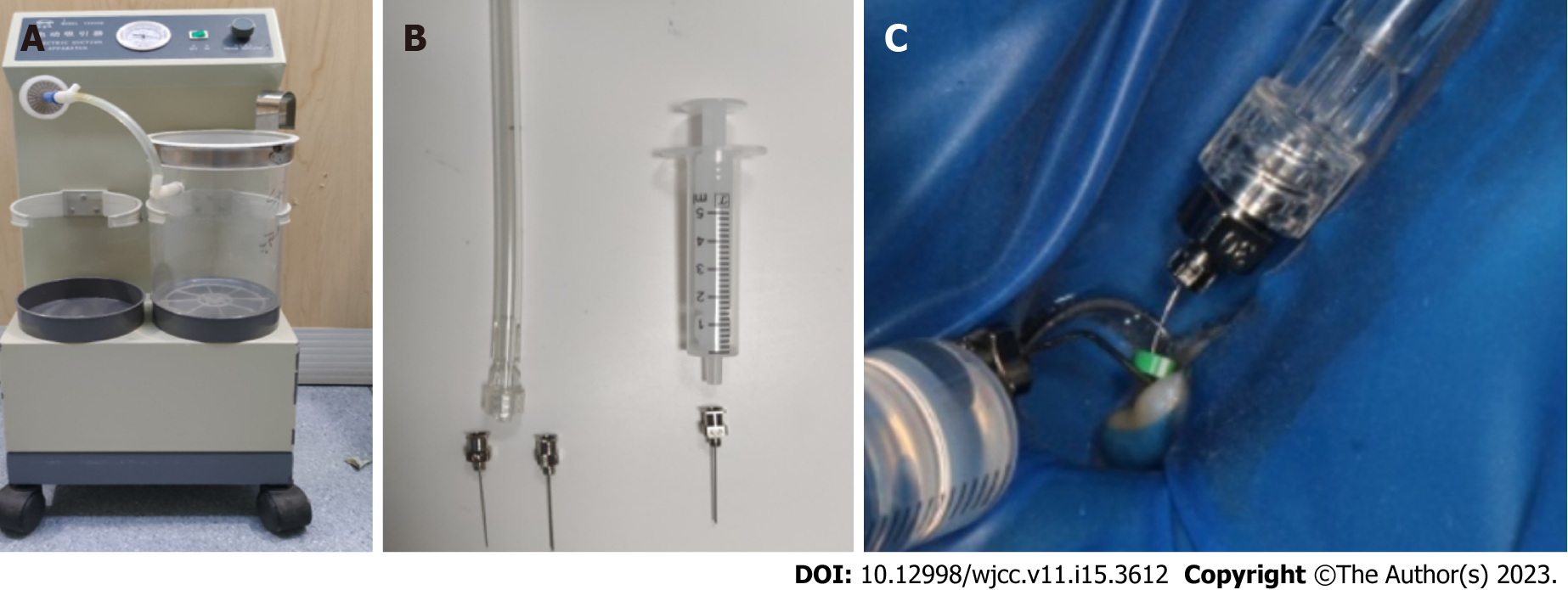
Figure 3 Construction of apical negative pressure irrigation system with commonly used clinical instruments.
A: Electric aspirator (Smanfeng, Shanghai); B: Flat bottom metal needle and 10 mL disposable syringe; C: The negative pressure irrigation system is used clinically with a 30 G metal needle as a microtube for aspirating the irrigation fluid in the apical segment and a 27 G metal needle as a large cannula for aspirating the irrigation fluid in the middle and upper segments of the root canal. 25 G needle is used as a delivery needle for delivering a constant flow rate of irrigation fluid to the root canal orifice.
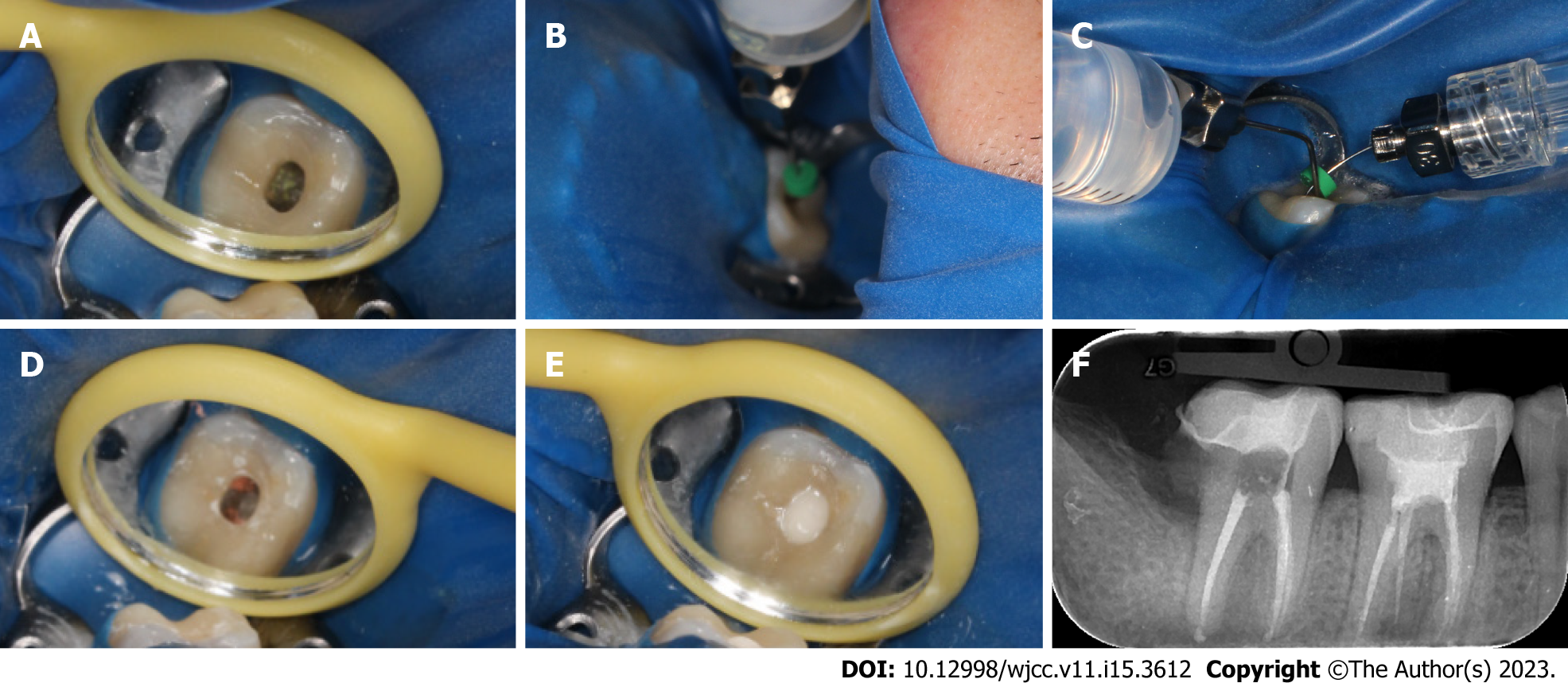
Figure 4 Root canal retreatment of tooth 47.
A: The access cavity was opened directly on the inlay and the original filling were removed under a microscope; B: A self-made apical negative pressure irrigation system was used to drain the cystic fluid; C: During the preparation, 1% sodium hypochlorite and 0.9% normal saline were used together with the self-made apical negative pressure irrigation system for irrigation; D: Complete canal obturation was achieved via single cone technique; E: Image of the access cavity sealed glass ionomer; F: A final digital PAX revealed that the canals were well-obturated.
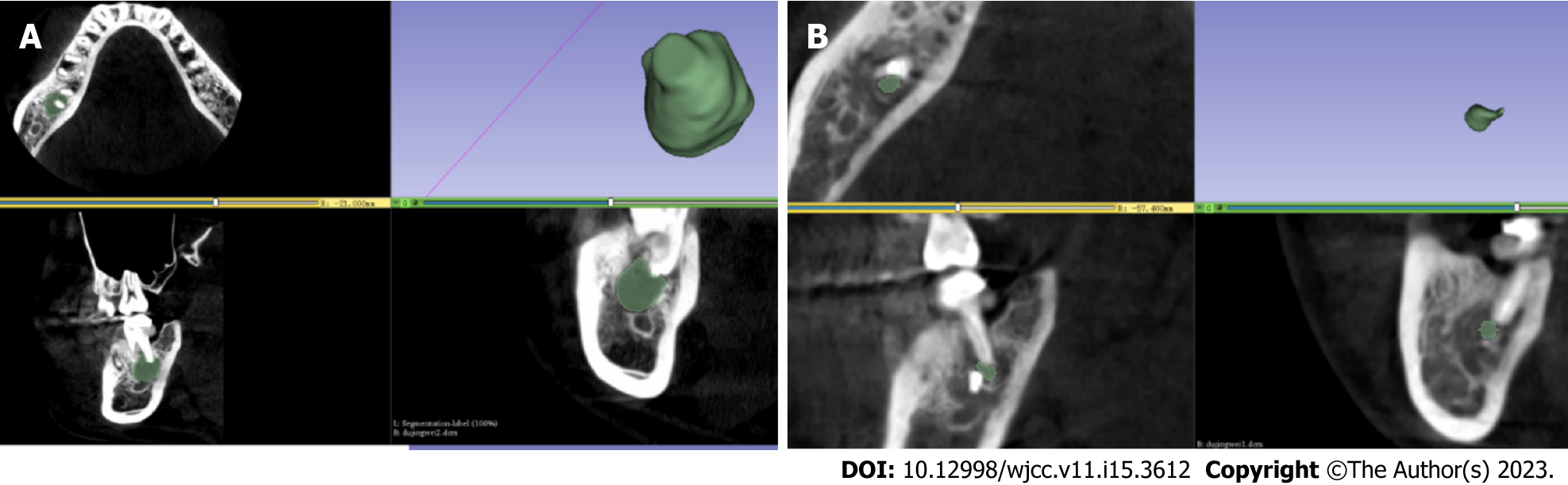
Figure 5 3D model of the radicular cyst reconstructed by 3Dslicer 5.
0.3 software. A: 3D model of the radicular cyst reconstructed by 3Dslicer 5.0.3 software before treatment; B: 3D model of the radicular cyst reconstructed by 3Dslicer 5.0.3 software after 6 mo.
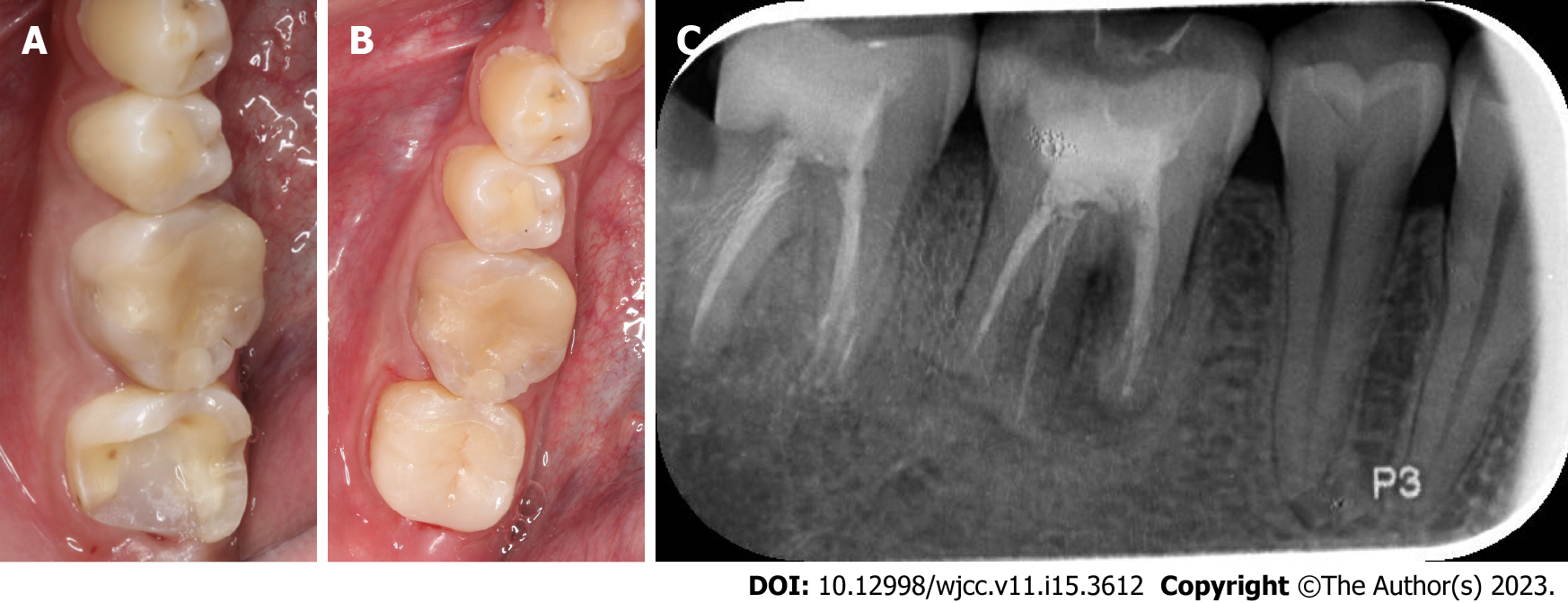
Figure 6 Deep margin elevation and lava ultimate high toughness porcelain inlay.
A: Image of the tooth after deep margin elevation; B: Intraoral photographs of lava ultimate high toughness porcelain inlay; C: A digital PAX at 1-year recall.
- Citation: Chen GP, Zhang YZ, Ling DH. Application of apical negative pressure irrigation in the nonsurgical treatment of radicular cysts: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(15): 3612-3618
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i15/3612.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i15.3612