Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2023; 11(1): 65-72
Published online Jan 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.65
Published online Jan 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.65
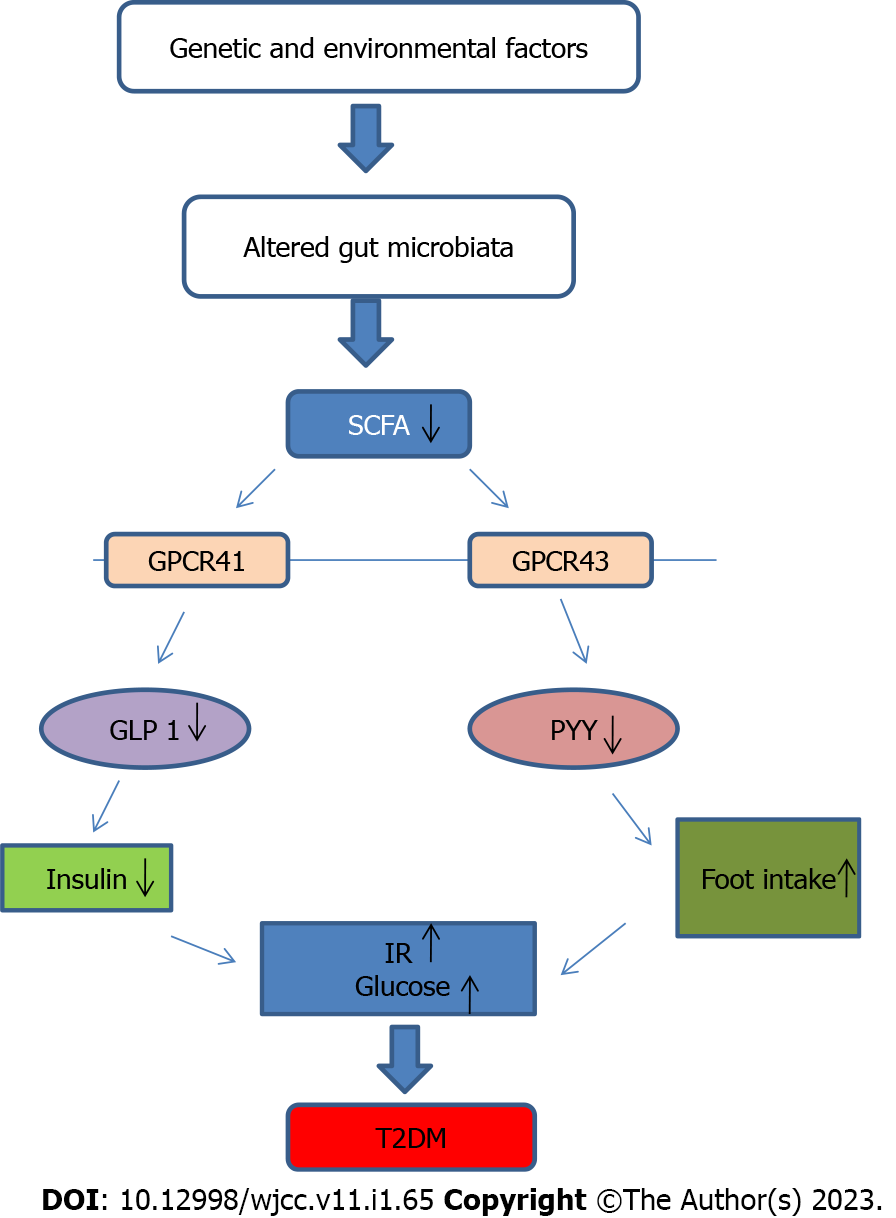
Figure 1 Schematic view of gut microbiota, short chain fatty acids and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
GLP 1: Glucagon like peptide 1; GPCR41: G-protein-coupled receptor 41; GPCR43: G-protein-coupled receptor 43; IR: Insulin resistance; PYY: Peptide tyrosine-tyrosine; SCFA: Short chain fatty acid; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
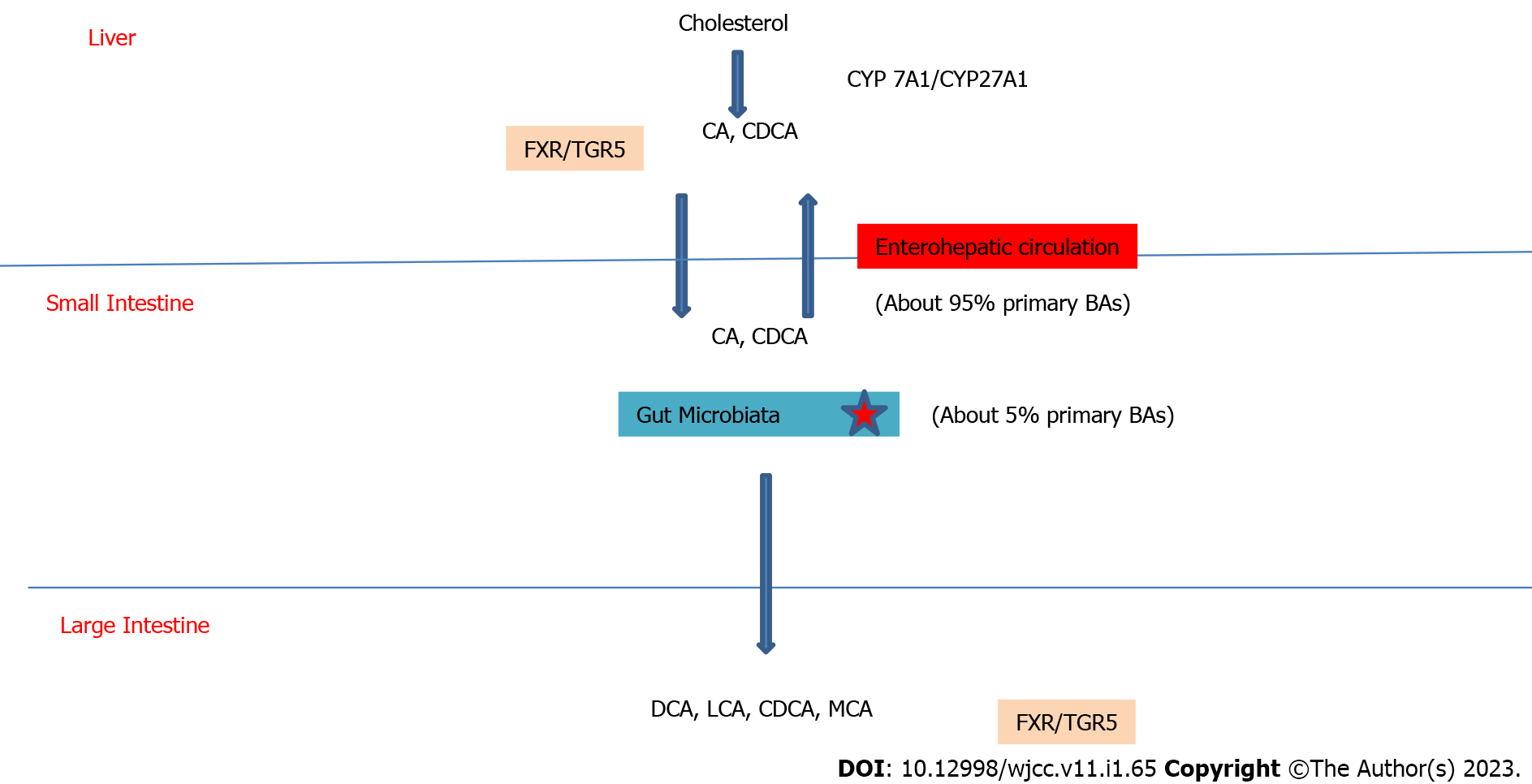
Figure 2 Schematic view of bile acids and the role of gut microbiota.
BA: Bile acid; CA: Cholic acid; CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid; DCA: Deoxycholic acid; CYP: Cytochrome P450; FXR: Farnesoid X Receptor; LCA: Lithocholic acid; MCA: Muricholic acid; TGR5: G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 5.
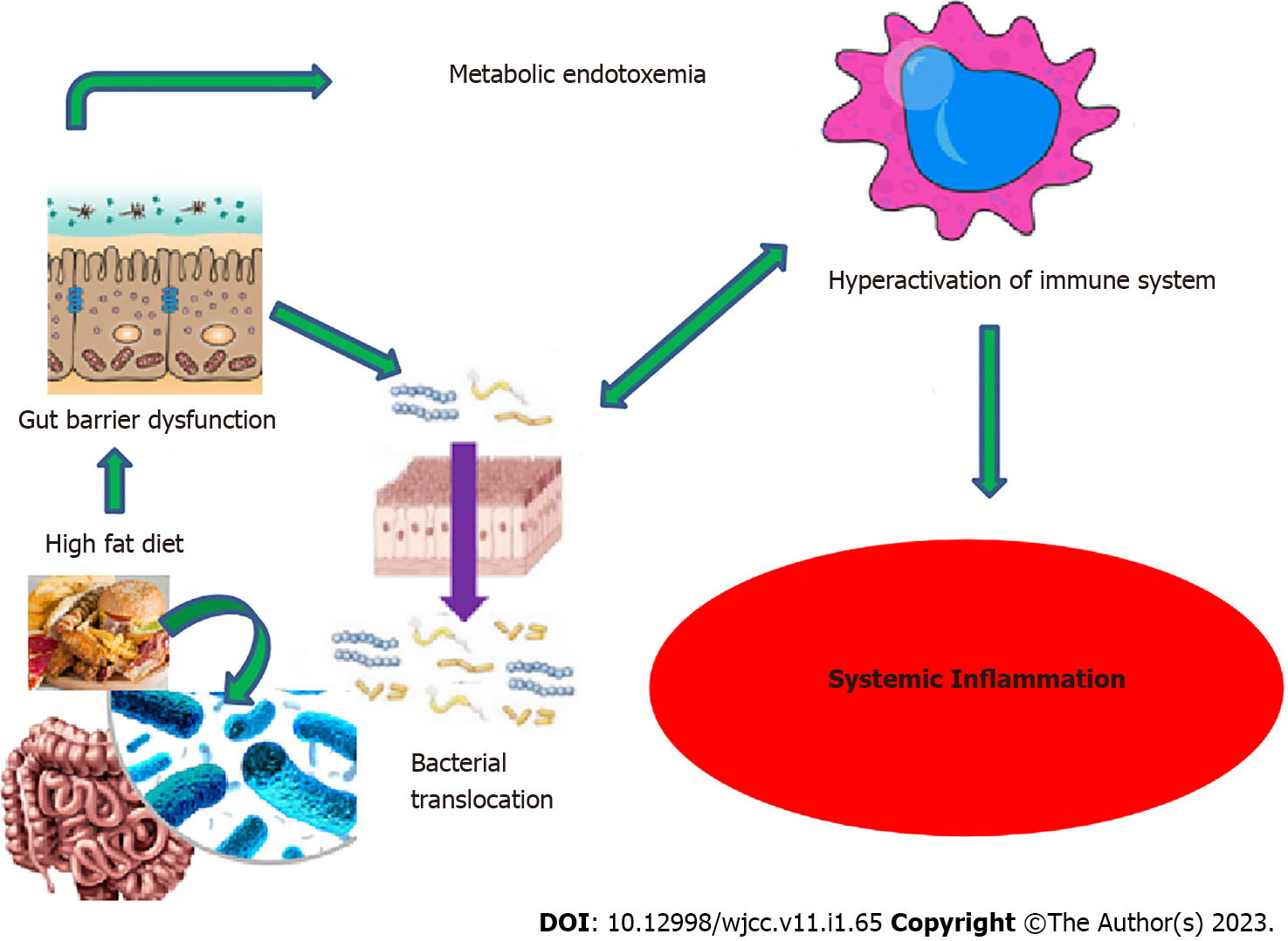
Figure 3 Schematic view of diet, gut microbiota and systemic inflammation.
- Citation: Aydin OC, Aydın S, Barun S. Role of natural products and intestinal flora on type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(1): 65-72
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i1/65.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.65