Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 6, 2023; 11(1): 177-186
Published online Jan 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.177
Published online Jan 6, 2023. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.177
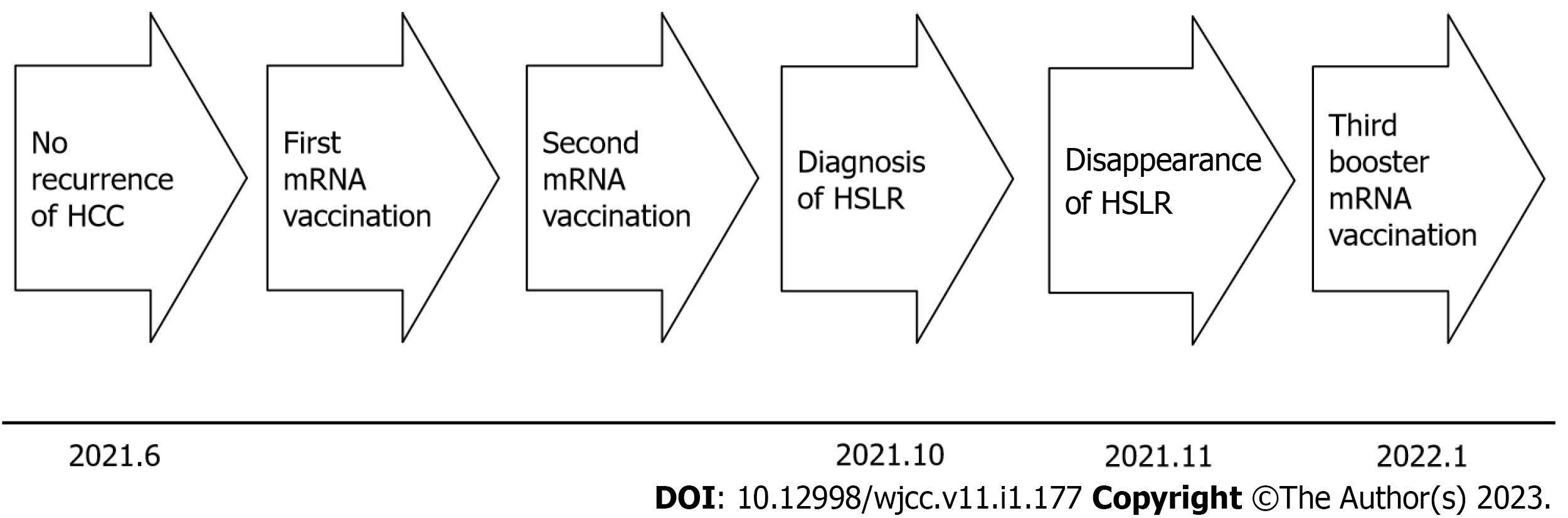
Figure 1 Clinical course of the patient.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HSLR: Hepatic sarcoidosis-like reaction.
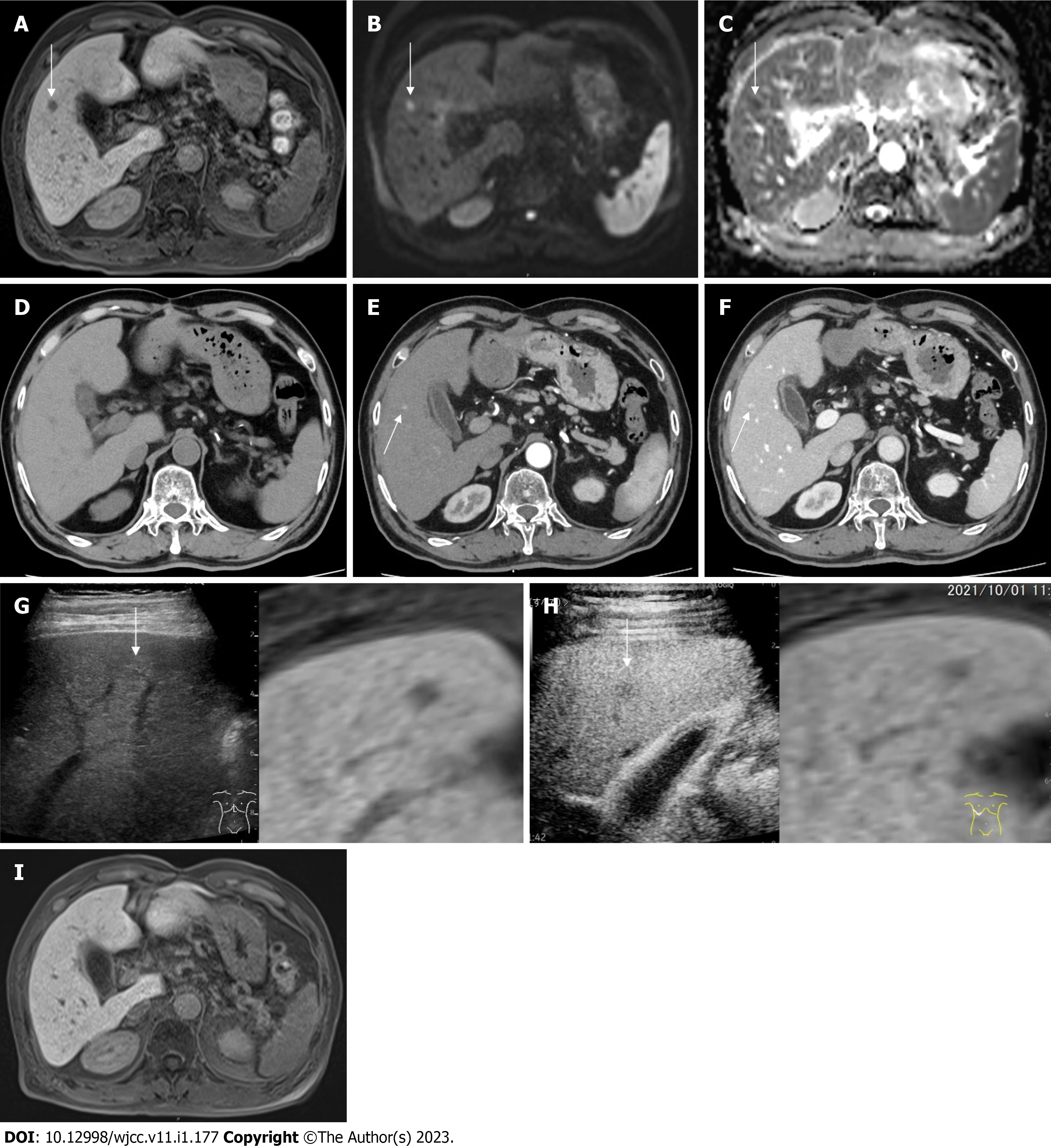
Figure 2 Image findings.
A: Gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (EOB-MRI) finding, 1 cm defect in S5 at the hepatobiliary phase (white arrow); B: EOB-MRI finding, 1 cm hyperintensity in S5 on diffusion weighted imaging (white arrow); C: EOB-MRI finding, 1 cm hypointensity in S5 on apparent diffusion coefficient map (white arrow); D: Computed tomography (CT) finding, no nodule in S5; E: Contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) finding, 1 cm hypervascular nodule in S5 at the early phase; F: CECT finding, 1 cm delayed contrast enhancement at the late phase; G: Plain ultrasound (US) finding, 1 cm iso-hyperechoic nodule in S5 (reference with EOB-MRI), hepatobiliary phase (white arrow); H: Contrast-enhanced US finding, Incomplete defect in S5 at the late vascular phase (reference with EOB-MRI), hepatobiliary phase (white arrow); I: MRI finding, disappearance of the defect in S5 at the hepatobiliary phase.
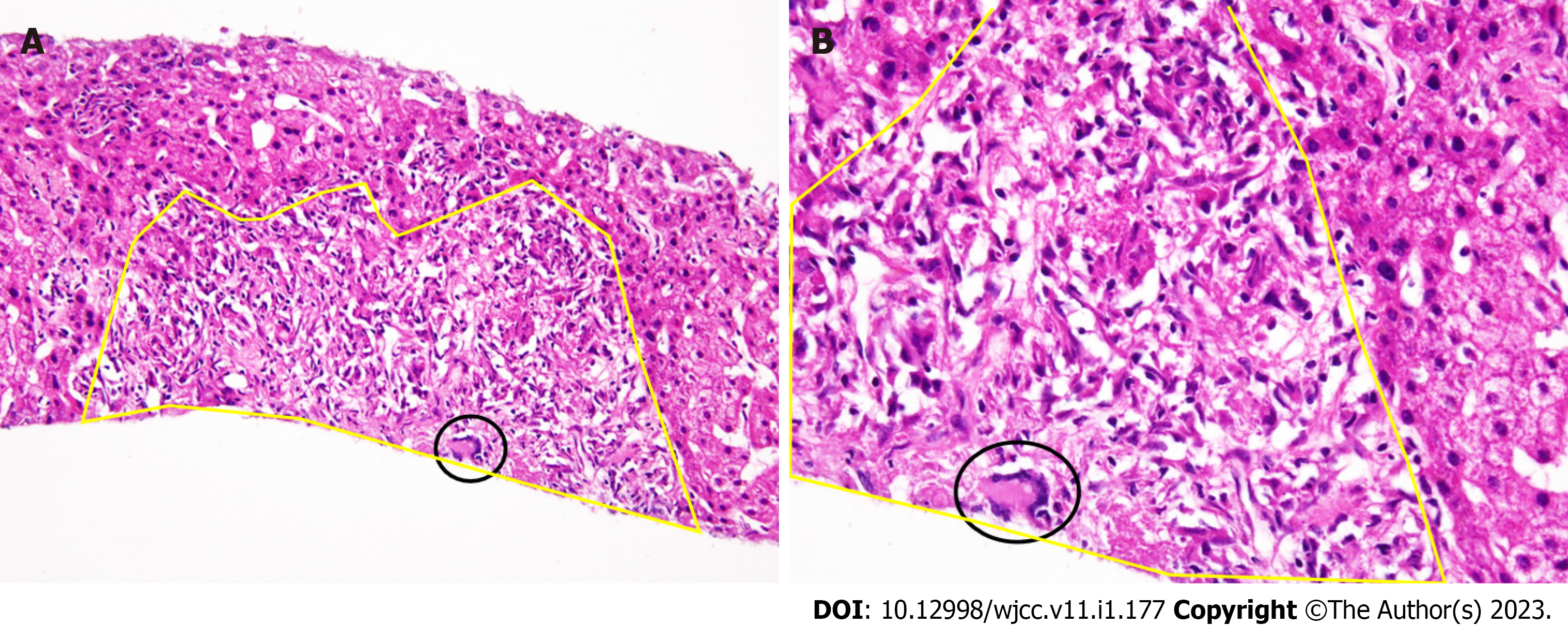
Figure 3 Histopathological findings.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, low magnification Noncaseating hepatic sarcoid-like epithelioid granuloma with spindle shaped epithelioid cells (encompassed by yellow line) harboring Langhans-type multinucleated giant cells (circled black) (HE × 40); B: HE staining, high magnification of A (HE × 100).
- Citation: Kim SR, Kim SK, Fujii T, Kobayashi H, Okuda T, Hayakumo T, Nakai A, Fujii Y, Suzuki R, Sasase N, Otani A, Koma YI, Sasaki M, Kumabe T, Nakashima O. Drug-induced sarcoidosis-like reaction three months after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccination: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2023; 11(1): 177-186
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v11/i1/177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v11.i1.177