Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2022; 10(9): 2969-2975
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2969
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2969
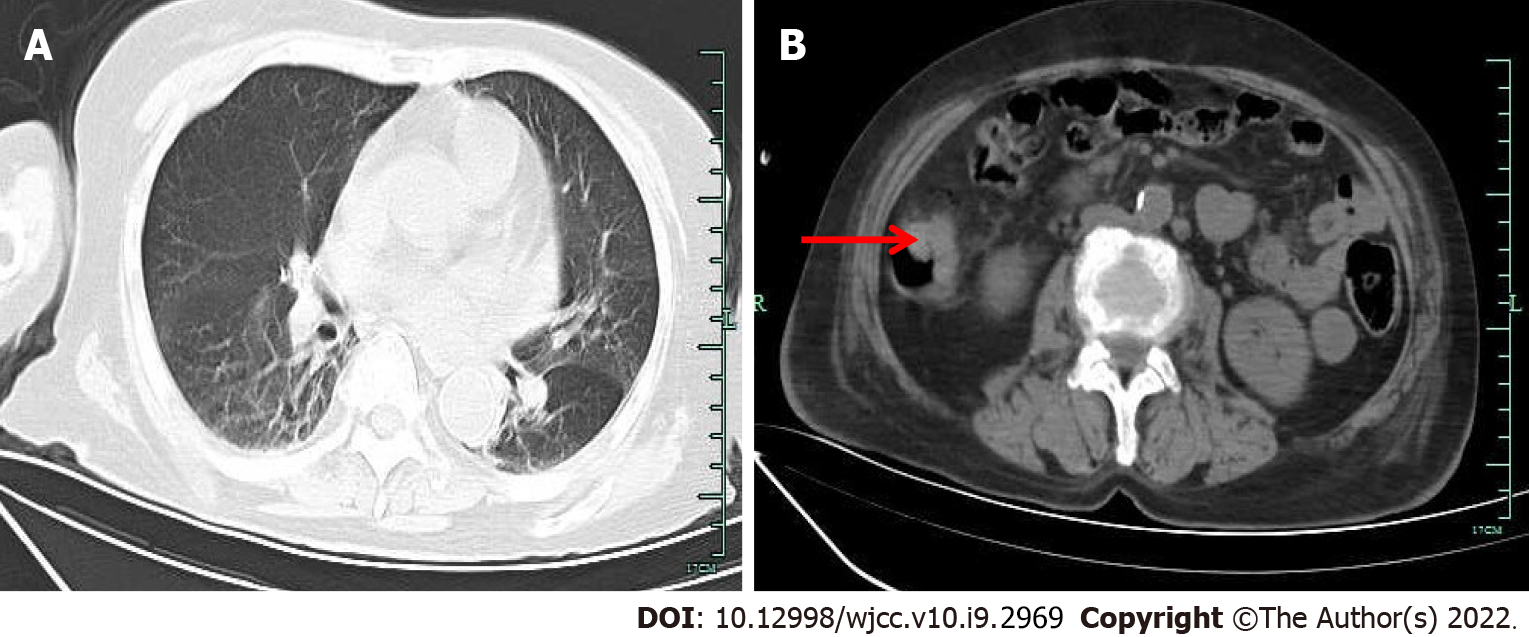
Figure 1 Computed tomography.
A: The chest computed tomography (CT) revealed mild inflammation in both lungs, obvious in the right lung; B: Abdominal CT examination revealed thickening of the local intestinal wall in the ascending colon (pointed by the arrow).
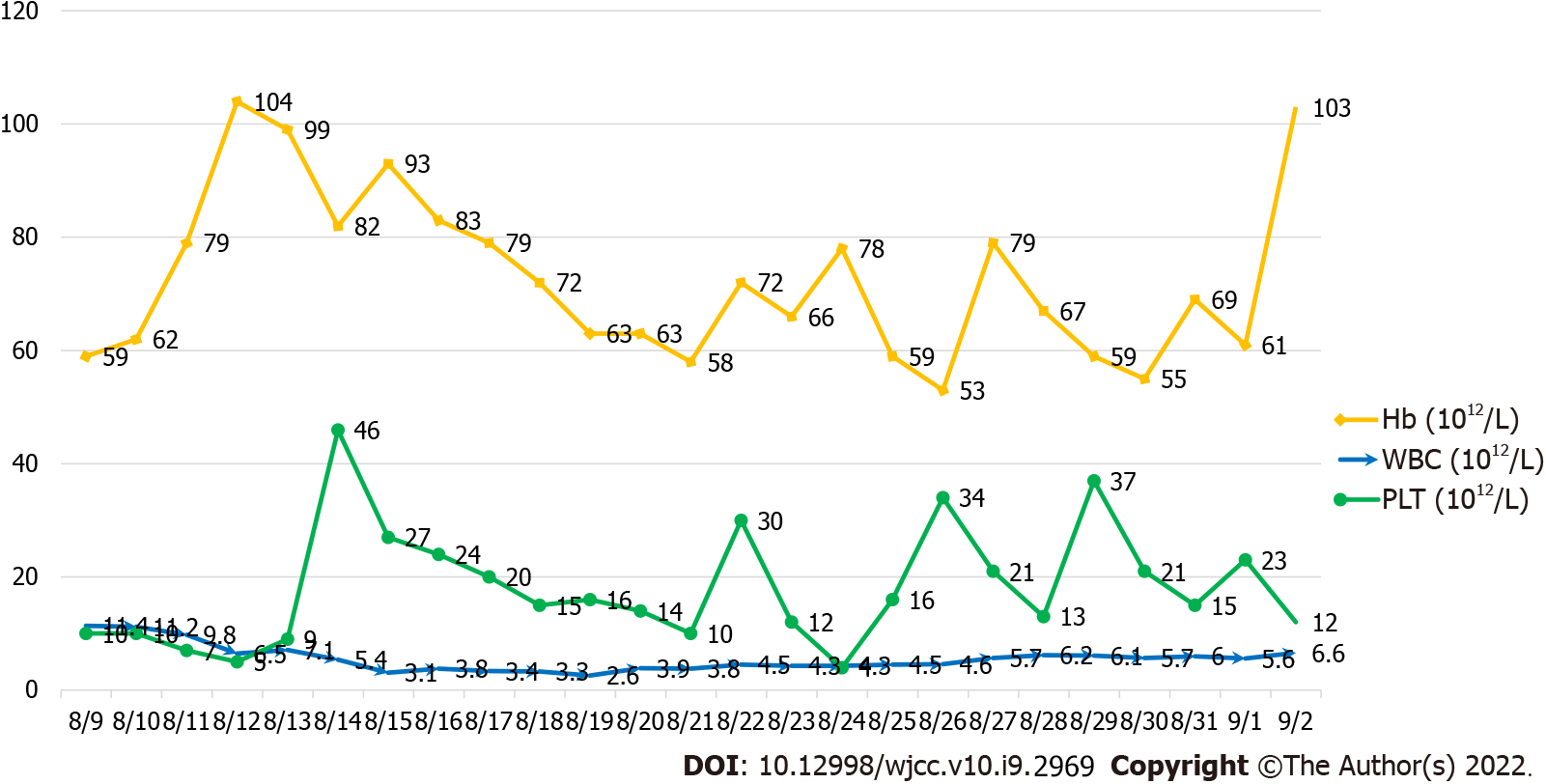
Figure 2 The platelet count is severely depressed, while the white blood cell count and hemoglobin levels improve after treatment.
Hb: Hemoglobin; WBC: White blood cell; PLT: Platelet.
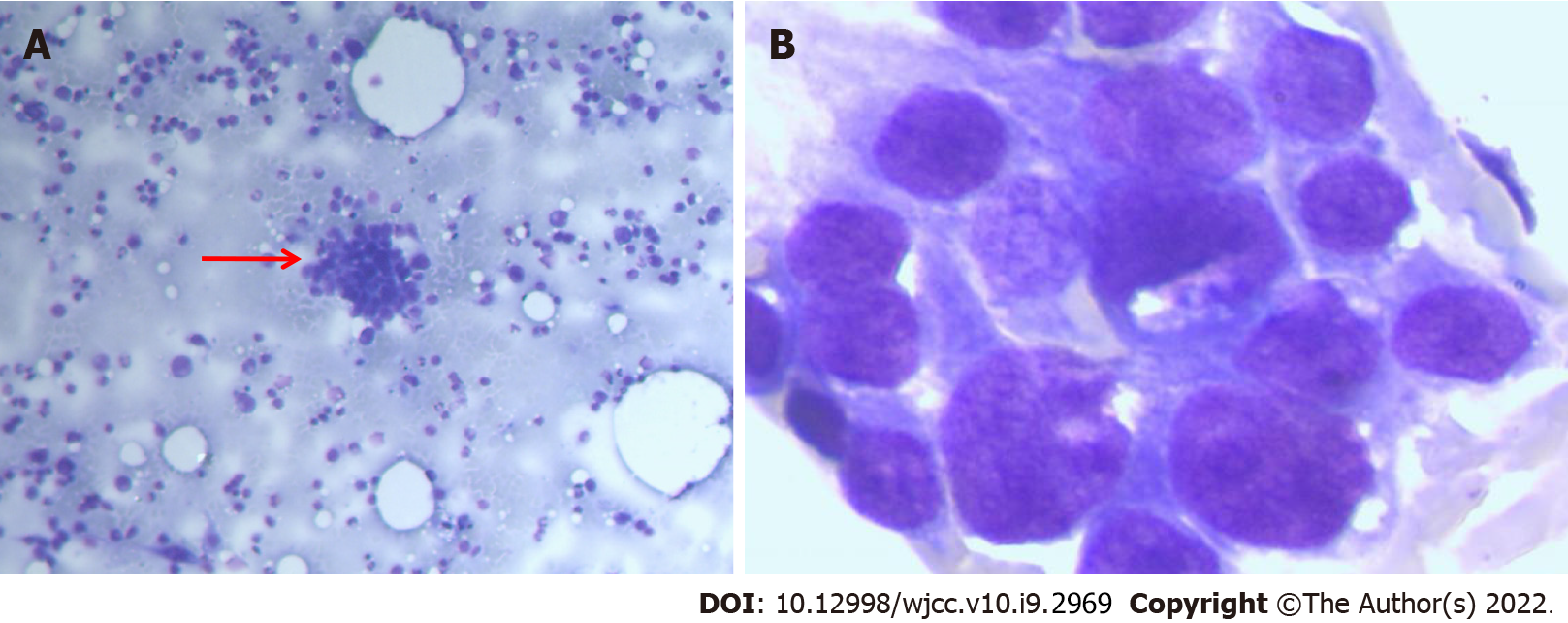
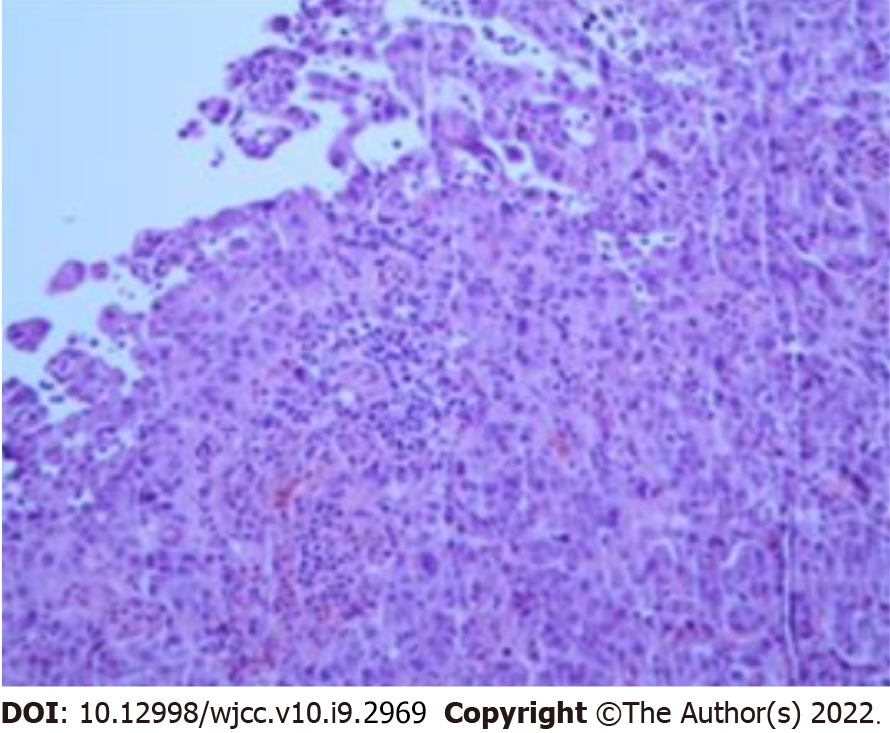
Figure 3 Bone marrow biopsy.
A: The bone marrow smear stained with Wright’s stain showed a class of abnormal cells (arrow points × 10); B: Clumps of cohesive cells, uneven size, abundant cytoplasm, irregular margins, rough chromatin, visible with 1-3 faint nucleoli (× 100).
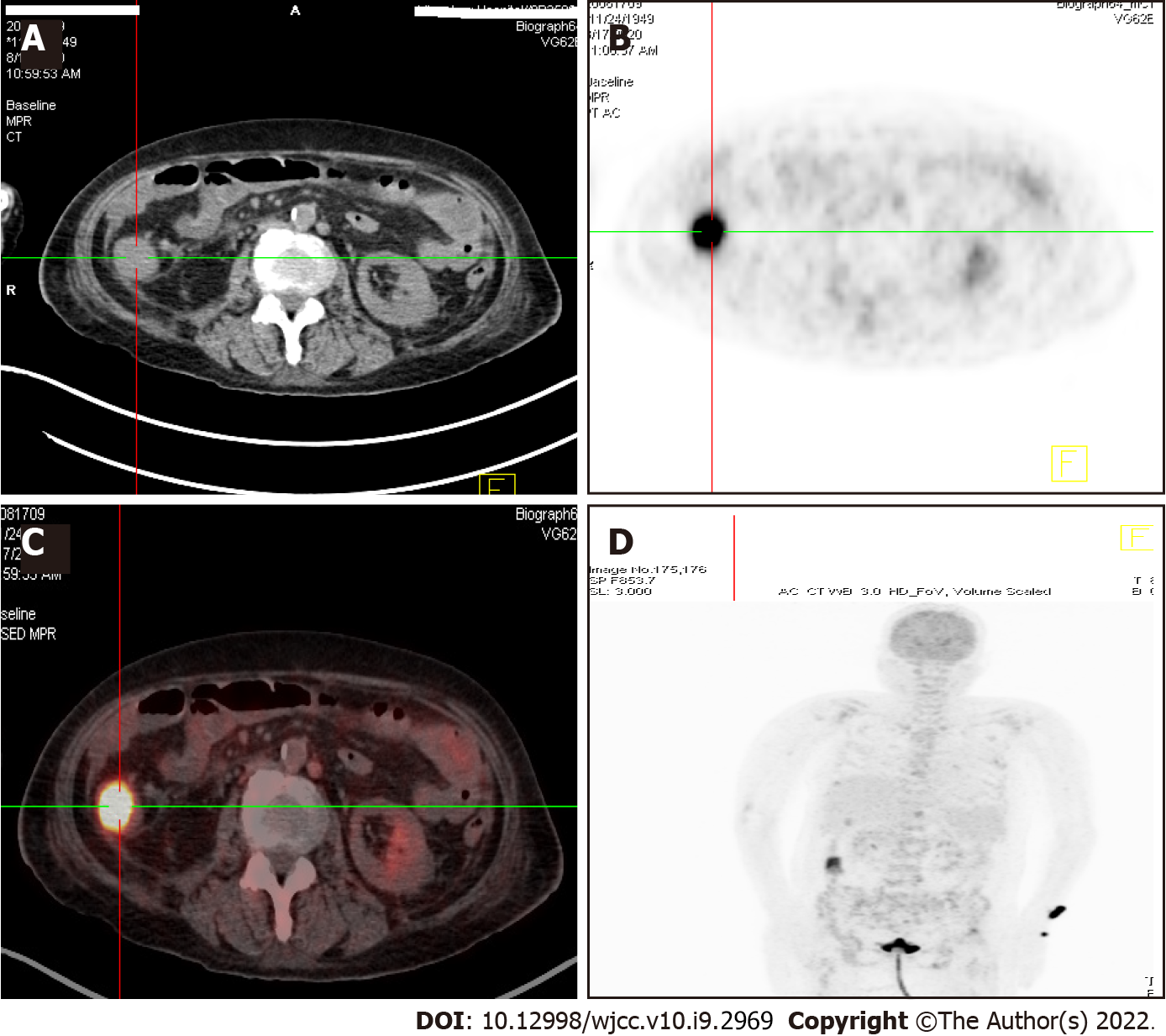
Figure 4 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography showed abnormally high signals in the ascending colon and left radius.
A: Abdomen computed tomography (CT) showed a soft tissue mass in the right ascending colon, about 3 × 4 cm; B: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (PET) showed that the mass of the right ascending colon showed significantly high uptake of 18F-FDG, with SUVMax = 8; C: PET/CT examination showed a mass in the right ascending colon with significantly high uptake of 18F-FDG; D: 18F- fluorodeoxyglucose PET showed high signals in the ascending colon and left radius.
Figure 5 Autopsy and pathological results of the patient showed colon adenocarcinoma.
- Citation: Wang HJ, Zhou CJ. Occult colon cancer with sepsis as the primary manifestation identified by bone marrow puncture: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(9): 2969-2975
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i9/2969.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2969