Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2022; 10(9): 2878-2882
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2878
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2878
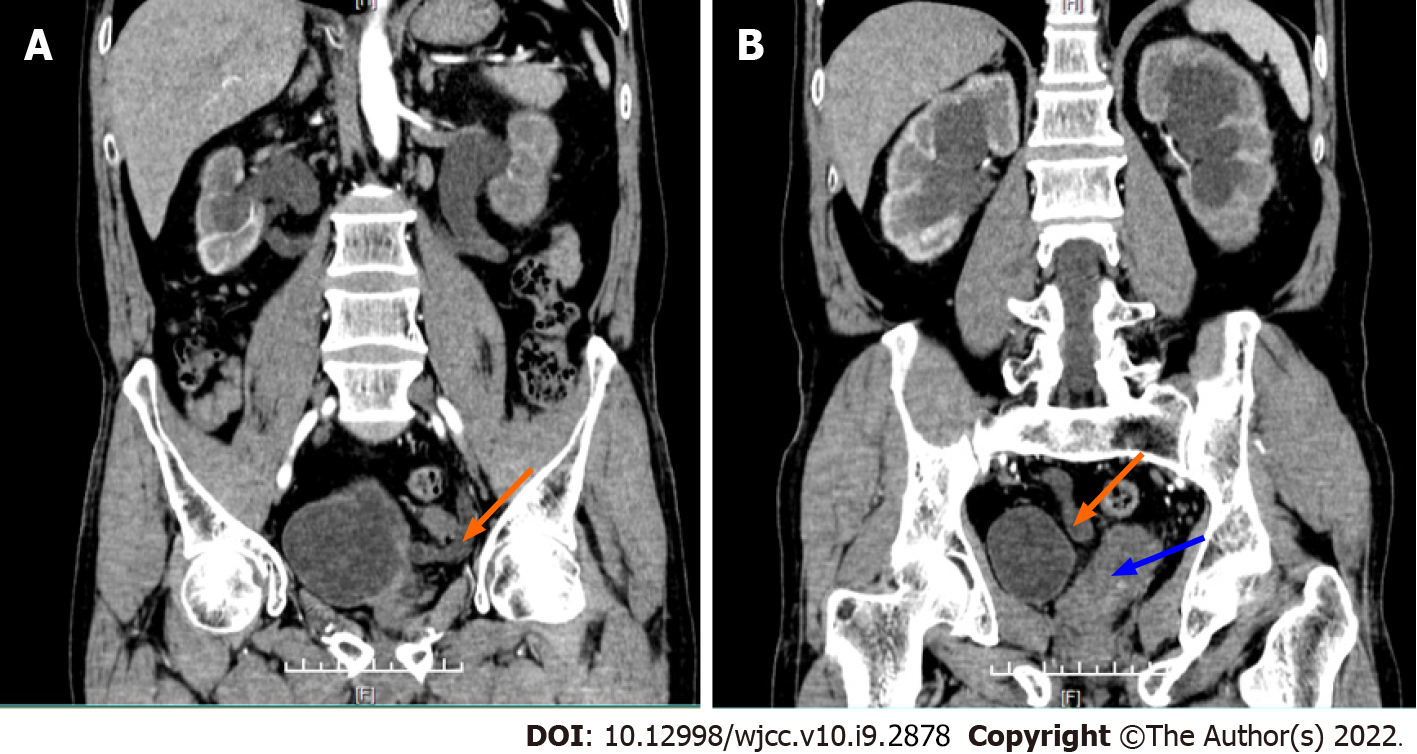
Figure 1 Urological plain and enhanced computed tomography coronal images.
A: A columnar soft tissue-like density shadow of around 8.0 cm × 2.0 cm in length on the left side of the pelvis during urological computed tomography (CT) (orange arrow); B: Enhanced CT showing mild homogeneous enhancement of the mass (orange arrow).
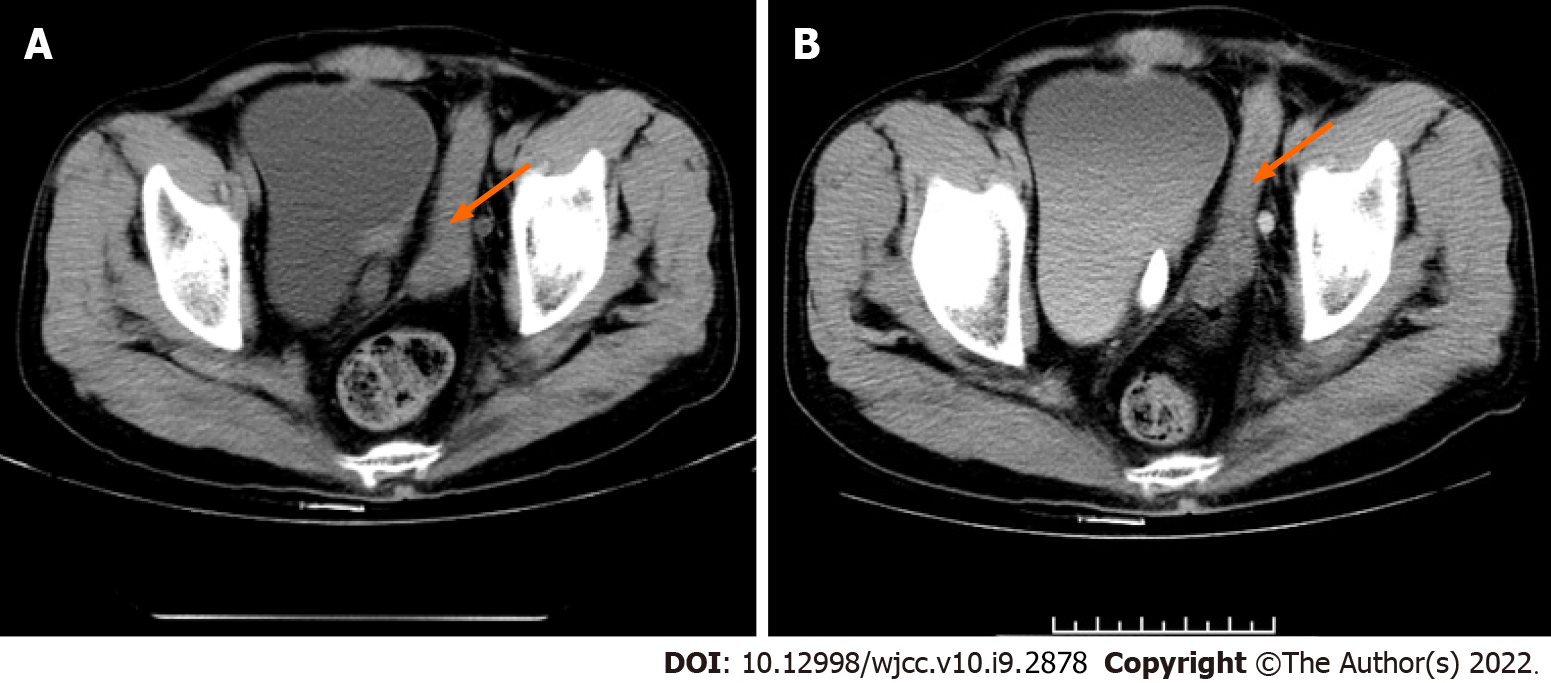
Figure 2 Urological scan and enhanced computed tomography sagittal images.
A: Left ureteral orifice (orange arrow); B: Ectopic opening of the right ureter opens on the left side of the bladder wall (orange arrow); soft tissue shadow on the left side of the bladder is identified as intra-abdominal ectopic penis (blue arrow).
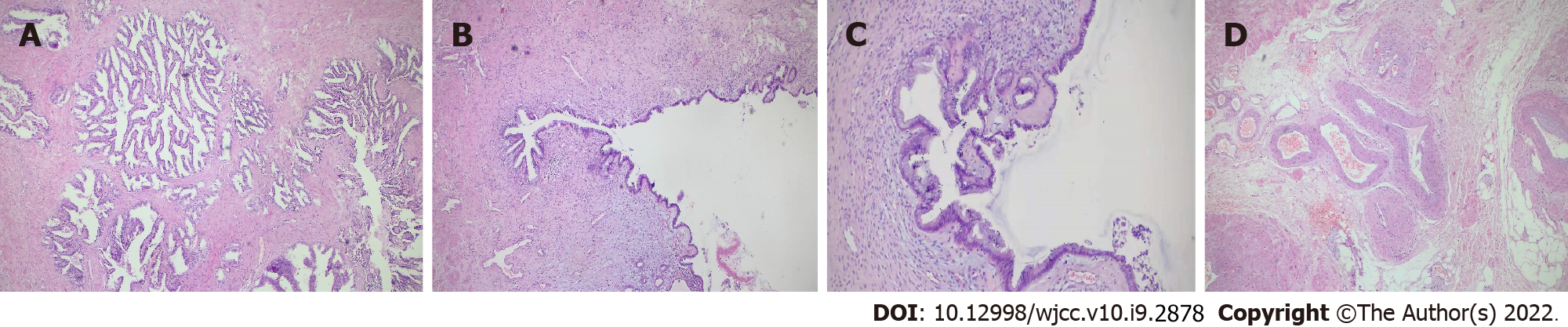
Figure 3 Postoperative pathological findings.
A: Adenoid tissue of seminal vesicle, × 50; B: Central catheter of the swelling, × 50; C: The central duct of the swelling is covered with ciliated columnar epithelium, × 100; D: More thick-walled vessels were seen around the smooth muscle bundle, and sinusoidal dilated vessels were seen within the muscle bundle, which was considered penile cavernous-like tissue, × 50.
- Citation: Jia YT, Shi BL, Zhang J, Li YY, Zhu J. Bilateral ureteral reimplantation in a patient with an intraperitoneal ectopic bipenis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(9): 2878-2882
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i9/2878.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2878