Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2022; 10(9): 2783-2791
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2783
Published online Mar 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2783
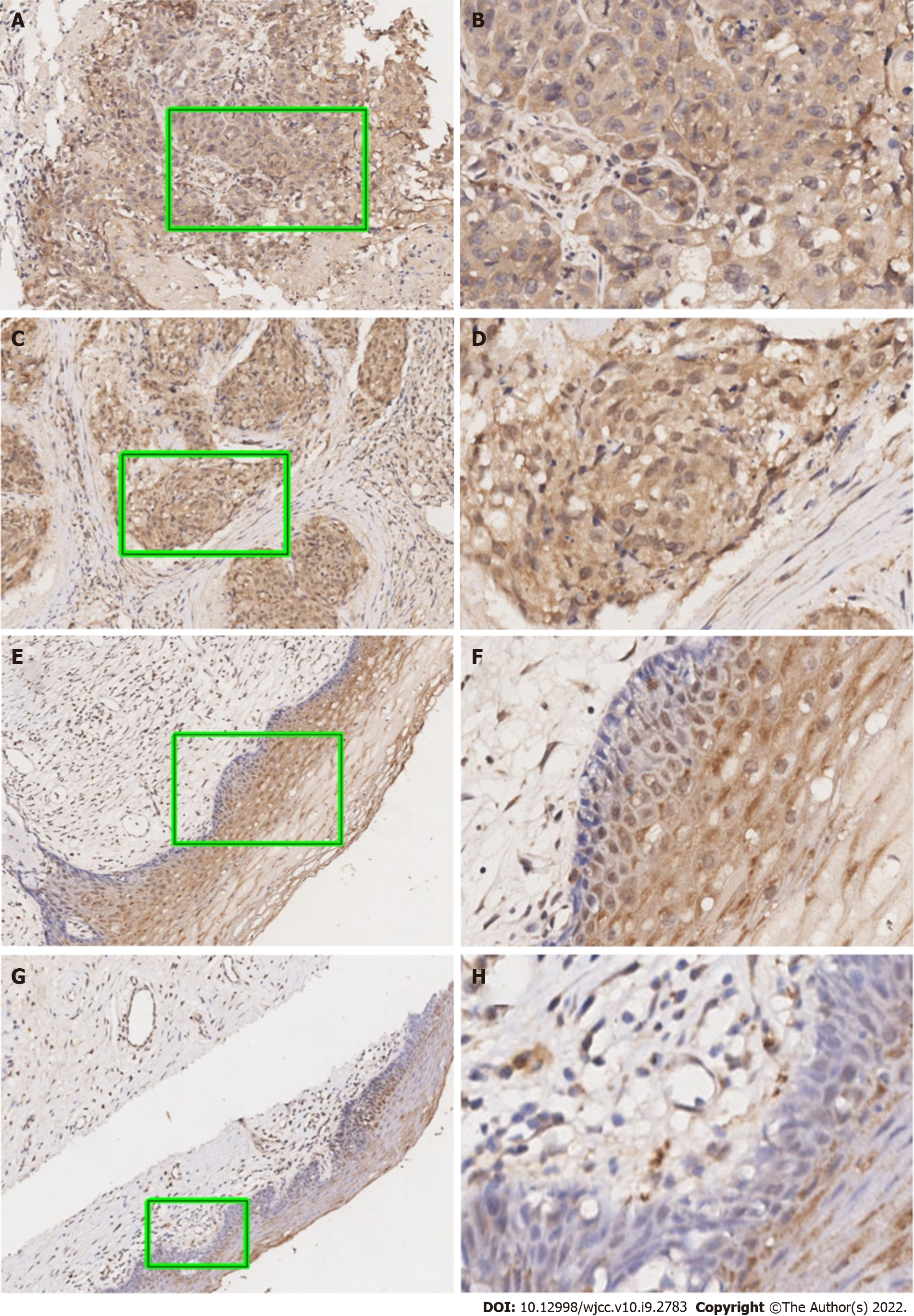
Figure 1 Representative immunohistochemical staining for Ubiquilin4 expression in cervical cancer specimens.
A and B: High expression of Ubiquilin4 (UBQLN4) in cervical cancer, score: 3; C and D: Low expression of UBQLN4 in cervical cancer, score: 2; E and F: Low expression of UBQLN4 in paracervical tissue, score: 1; G and H: Low expression of UBQLN4 in paracervical tissue, score: 0. (A, C, E, and G: Original magnification, 100 ×; B, D, F, and G: Original magnification, 200 ×).
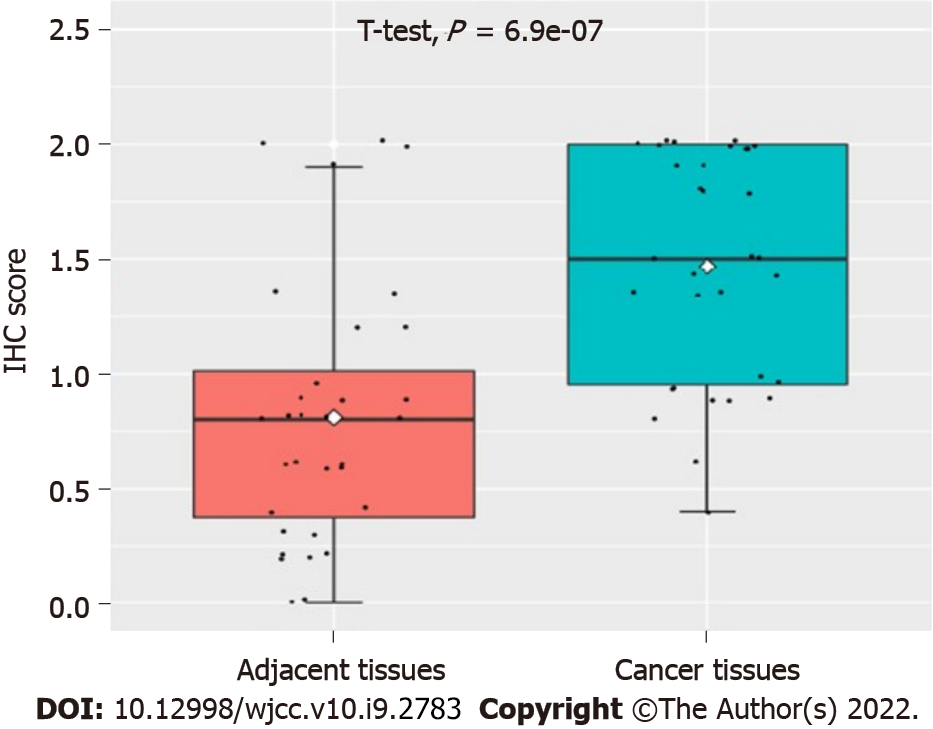
Figure 2 Expression of the Ubiquilin4 protein in cervical cancer tissue and pericervical tissue cells.
The UBQLN4 protein was overexpressed in cervical cancer tissues. IHC: Immunohistochemistry.
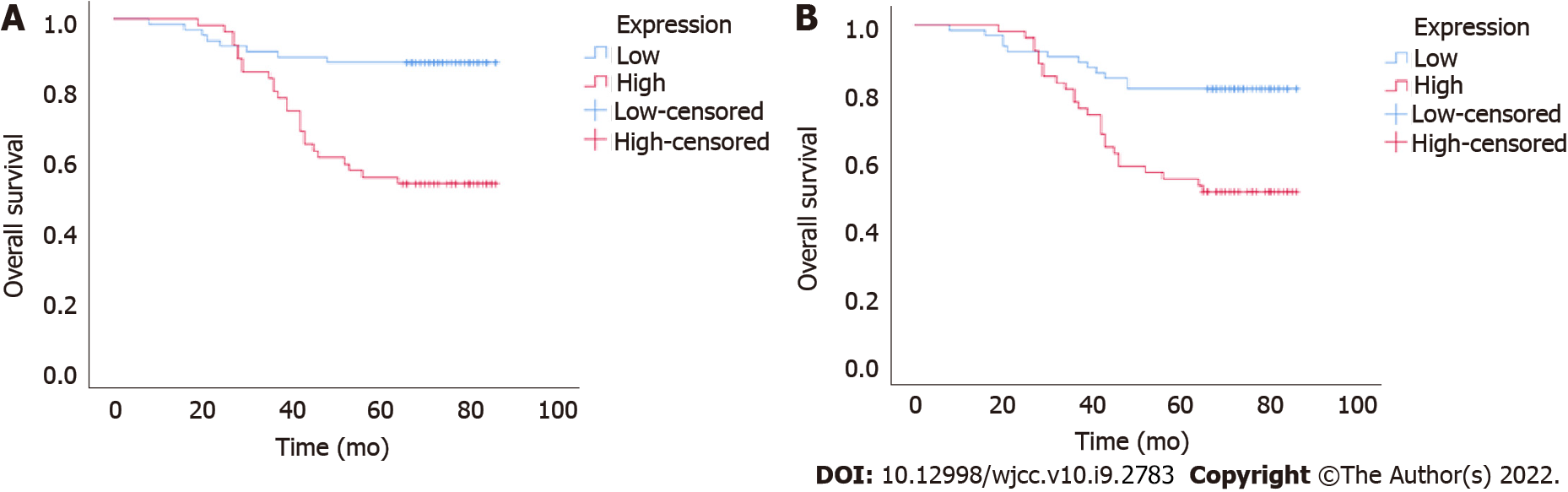
Figure 3 Results of the Kaplan–Meier analysis of the association between Ubiquilin4 expression and survival.
The overall and the progression-free survival of cervical cancer patients with high and low expression. Log-rank test results showed that the patients with low UBQLN4 staining had a significantly better overall and progression-free survival than the patients with high expression. A: Overall survival; B: Progression-free survival.
- Citation: Wang LN, Huang KJ, Wang L, Cheng HY. Overexpression of Ubiquilin4 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with cervical cancer. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(9): 2783-2791
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i9/2783.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i9.2783