Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2022; 10(7): 2357-2362
Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2357
Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2357
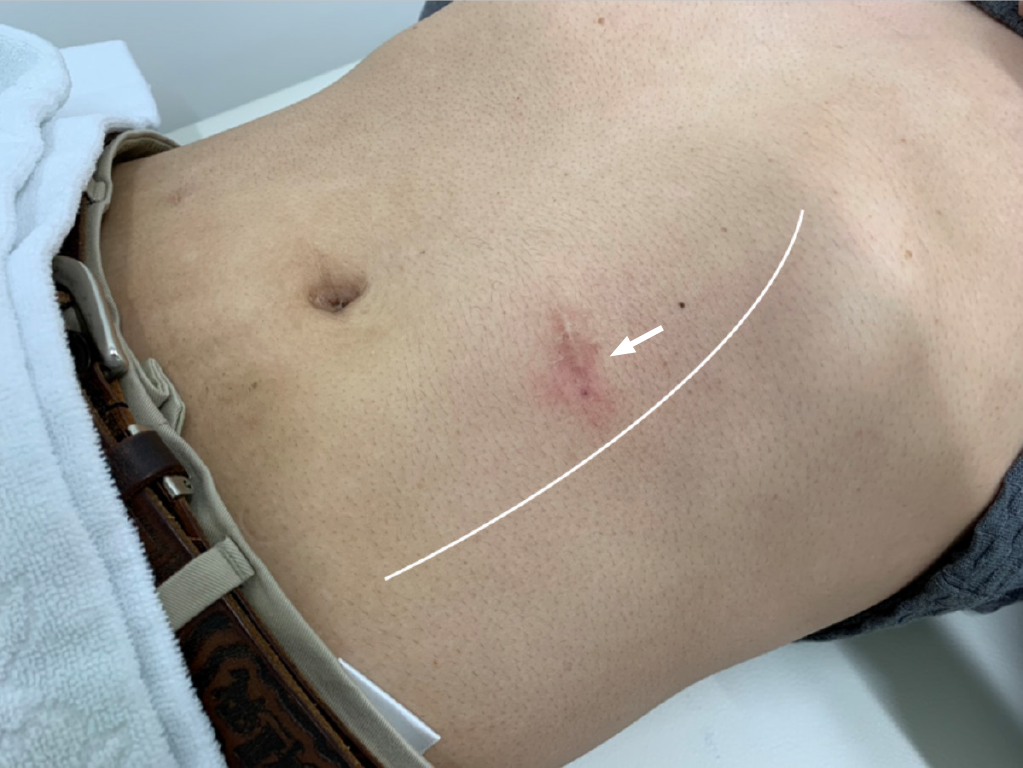
Figure 1 Postoperative scar in the anterior abdominal wall.
The white arrow indicates the position of the operative scar. The white line indicates the left lateral edge of the rectus abdominis muscle. The scar is located near the lateral edge of the rectus muscle.
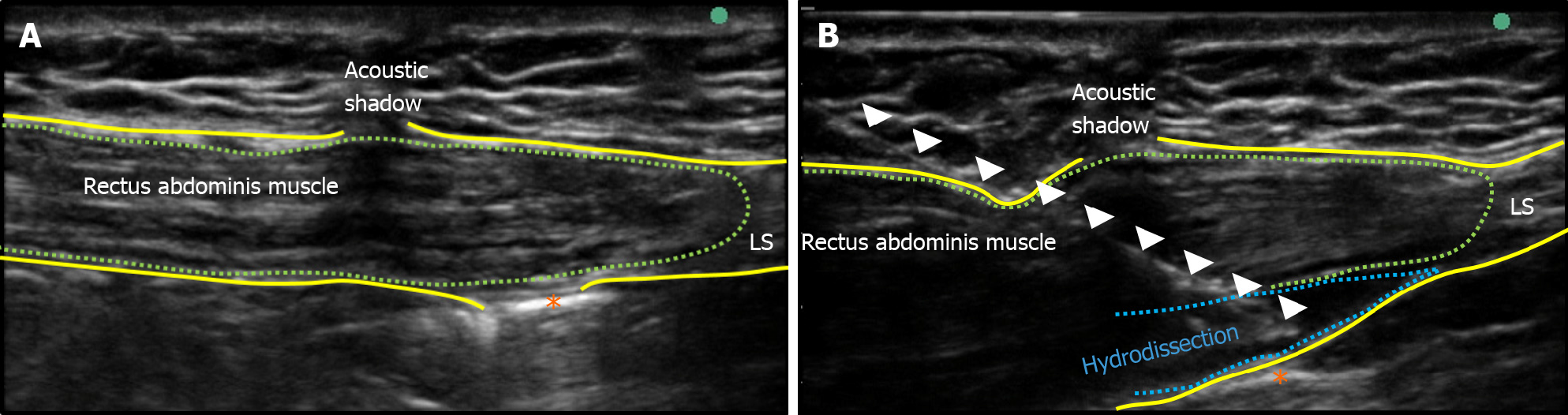
Figure 2 Ultrasound view at the site of the operative scar.
A: An acoustic shadow is present at the site of the scar. An adhesion-like object (orange asterisk) is observed behind the scar; B: White arrow heads indicate a needle. Through the needle, 0.1% lidocaine solution 20 mL is injected beneath the rectus abdominis muscle (green dashed line) above the posterior wall sheath. Hydrodissection proceeded between the rectus abdominis muscle and the posterior rectus sheath (rectus sheath block). Approach to the rectus sheath block is an in-plane approach from medial to lateral. LS: Linea semilunaris.
- Citation: Sawada R, Watanabe K, Tokumine J, Lefor AK, Ando T, Yorozu T. Ultrasound-guided rectus sheath block for anterior cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome after laparoscopic surgery: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(7): 2357-2362
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i7/2357.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2357