Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2022; 10(7): 2127-2137
Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2127
Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2127
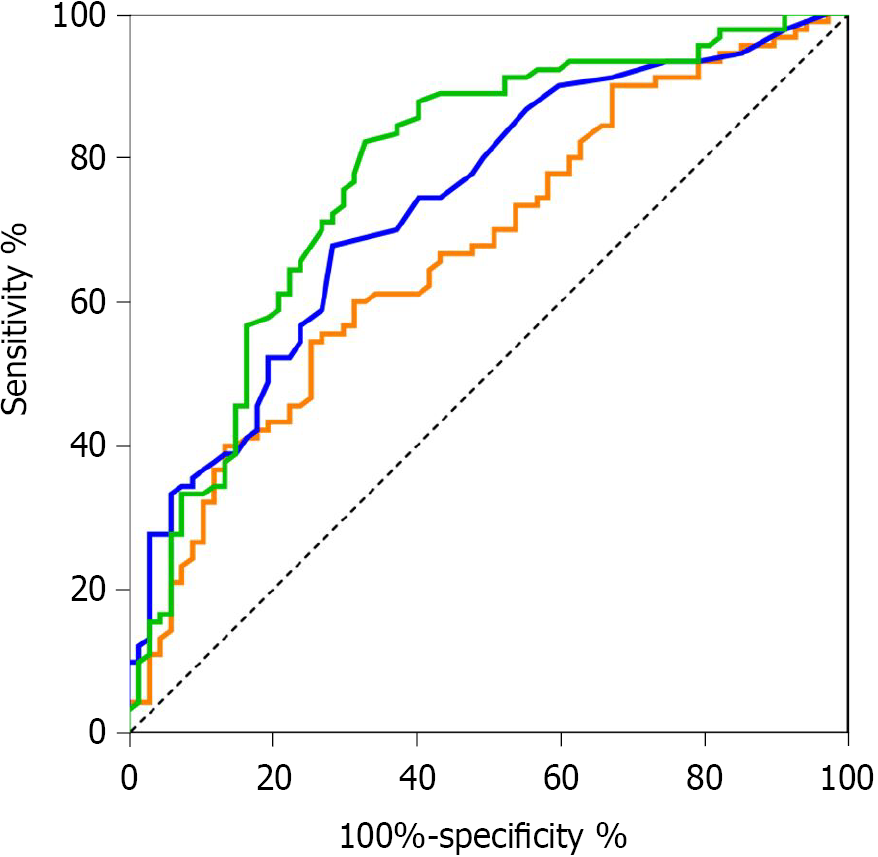
Figure 1 Receiver-operating characteristic curves comparing the neutrophil CD64 index, procalcitonin and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein to predict early sepsis in hematological patients.
hs-CRP: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein; nCD64: Neutrophil CD64; PCT: Procalcitonin.
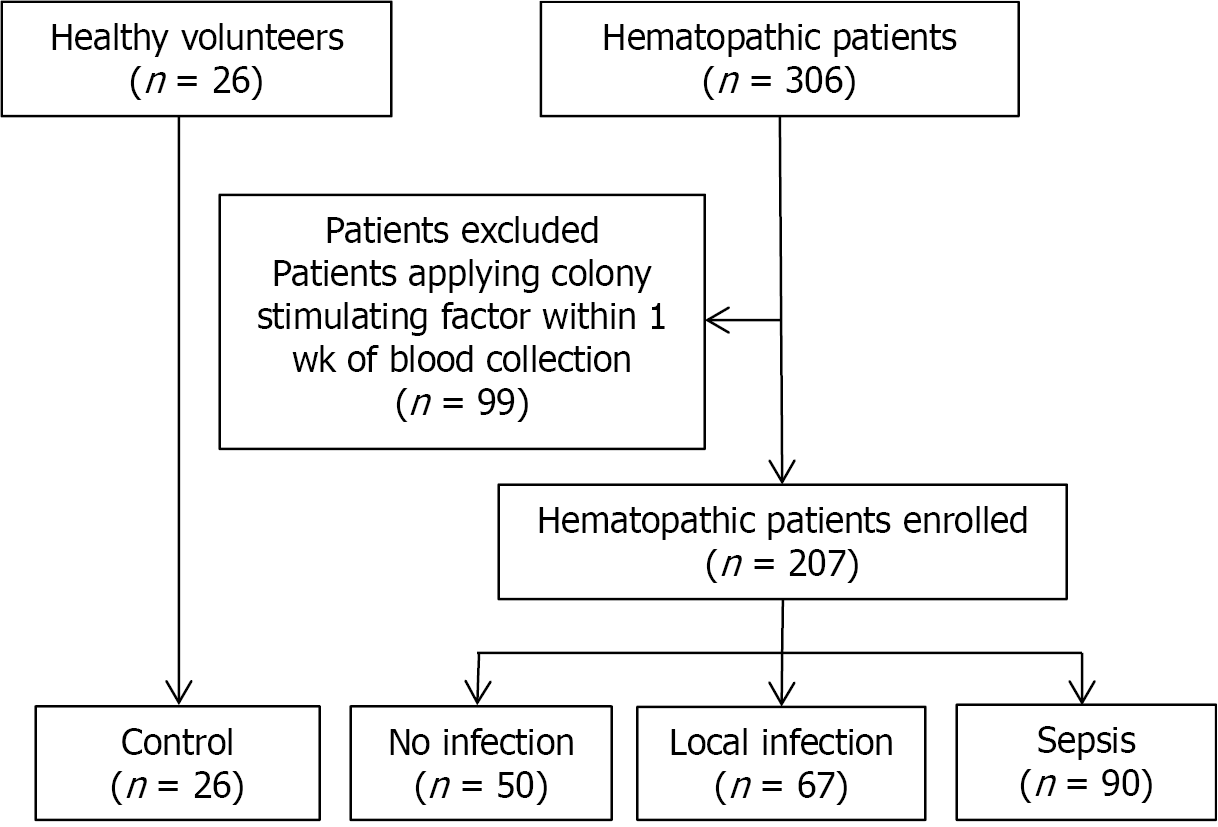
Figure 2 Consort diagram of the study.
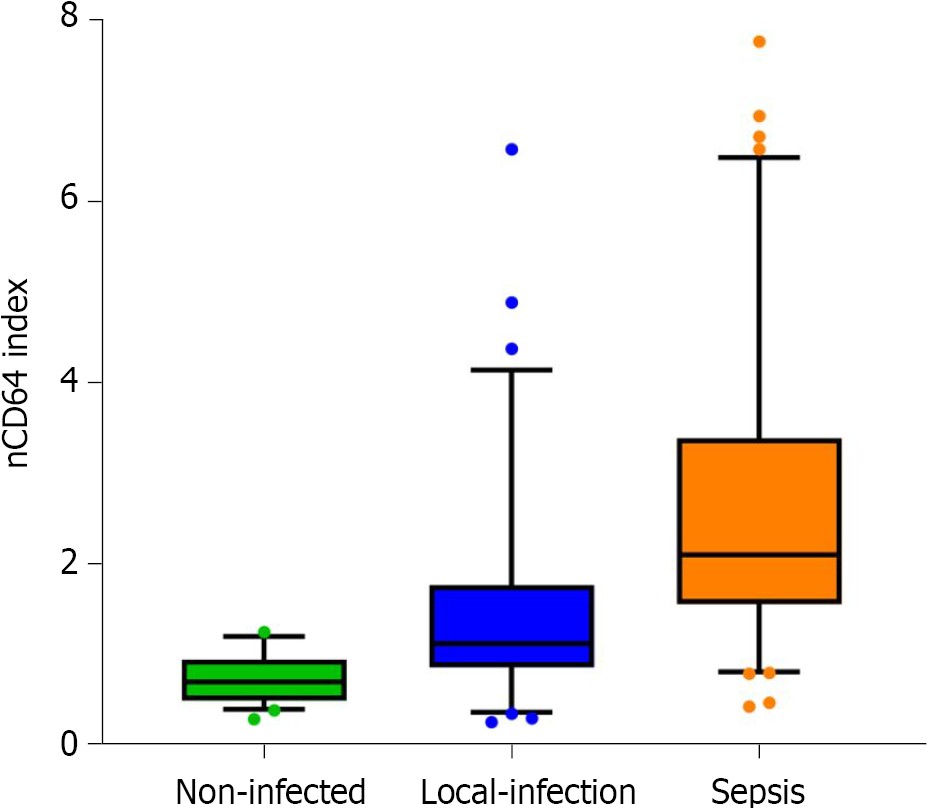
Figure 3 The level of neutrophil CD64 index in patients with hematological diseases as a function of infection status.
nCD64: Neutrophil CD64.
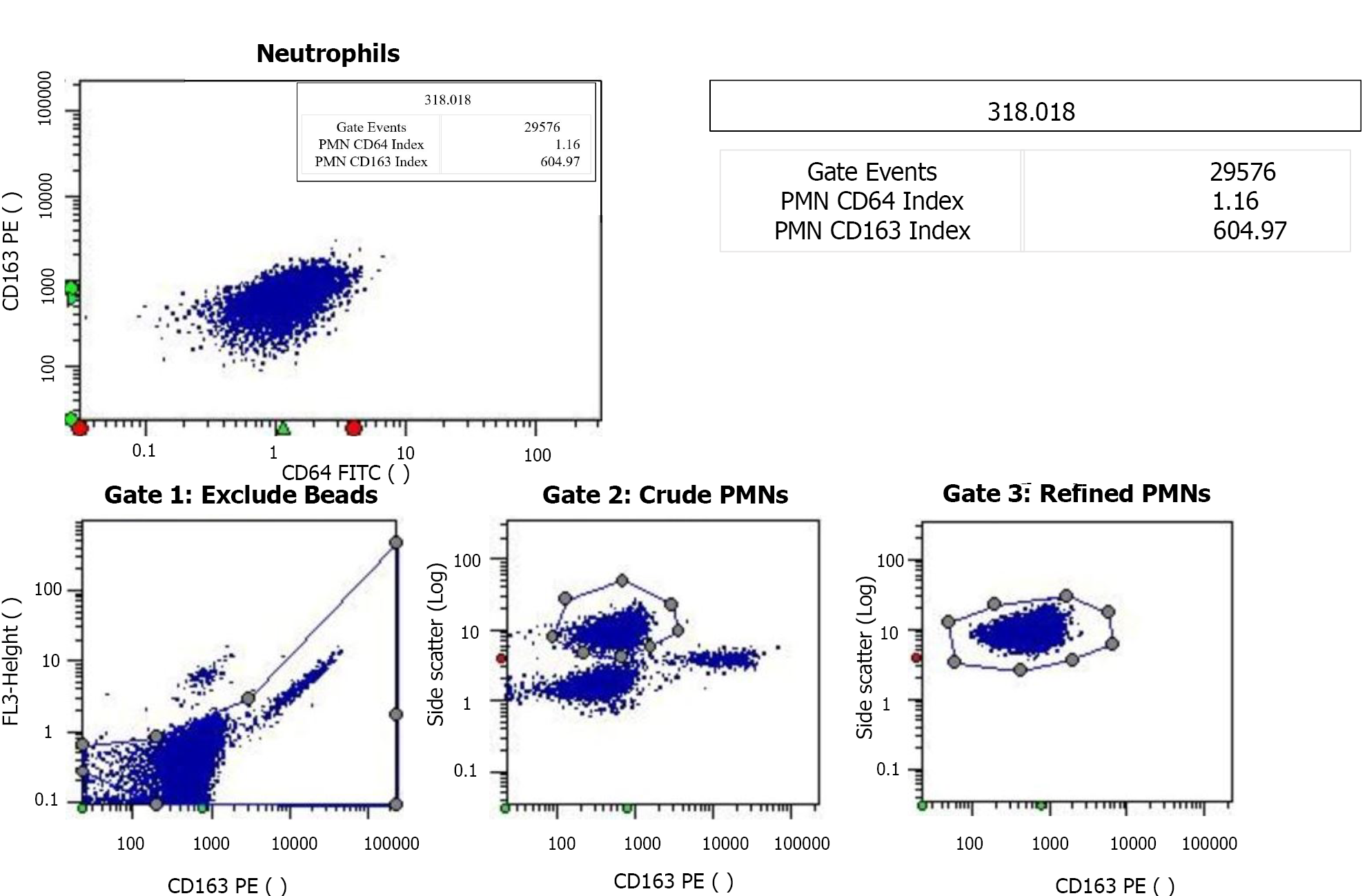
Figure 4 Test report for the neutrophil CD64 index.
The neutrophil CD64 (nCD64) index is typically < 1.20 in healthy individuals. The majority of hospitalized patients without infection or sepsis have a nCD64 index value of 1.00-2.00. Every laboratory should establish their own (no infection) reference range. Clinical decisions based on the nCD64 index may vary by age and disease type. PMN: Neutrophil count; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; PE: Phycoerythrin.
- Citation: Shang YX, Zheng Z, Wang M, Guo HX, Chen YJ, Wu Y, Li X, Li Q, Cui JY, Ren XX, Wang LR. Diagnostic performance of Neutrophil CD64 index, procalcitonin, and C-reactive protein for early sepsis in hematological patients. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(7): 2127-2137
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i7/2127.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2127