Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2022; 10(7): 2095-2105
Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2095
Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2095
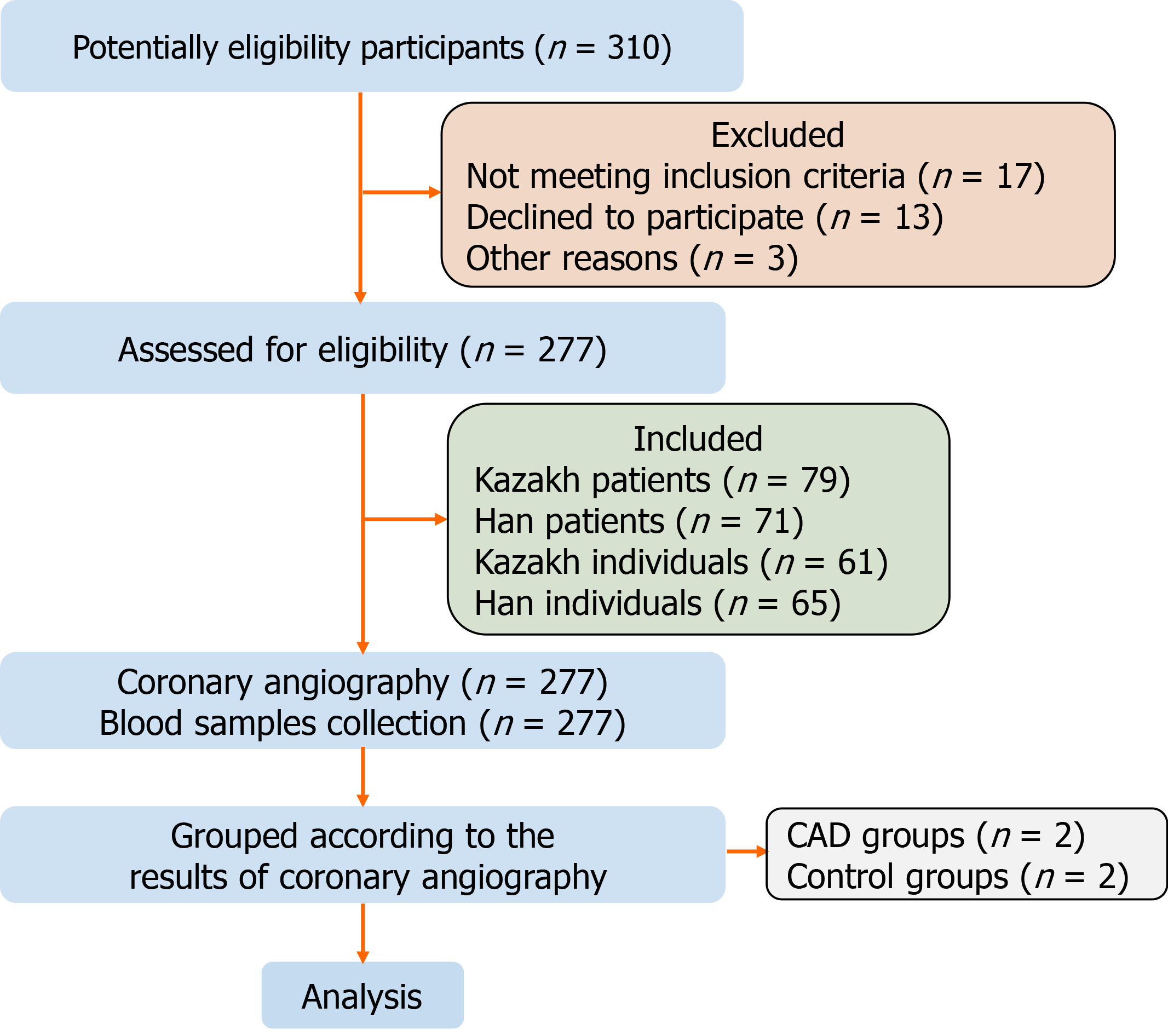
Figure 1 Flow diagram for research.
310 Potentially eligibility participants were included in the initial stage, after evaluation according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 277 patients completed coronary angiography and were eventually included in this study. The included cases were divided into groups according to the results of coronary angiography.
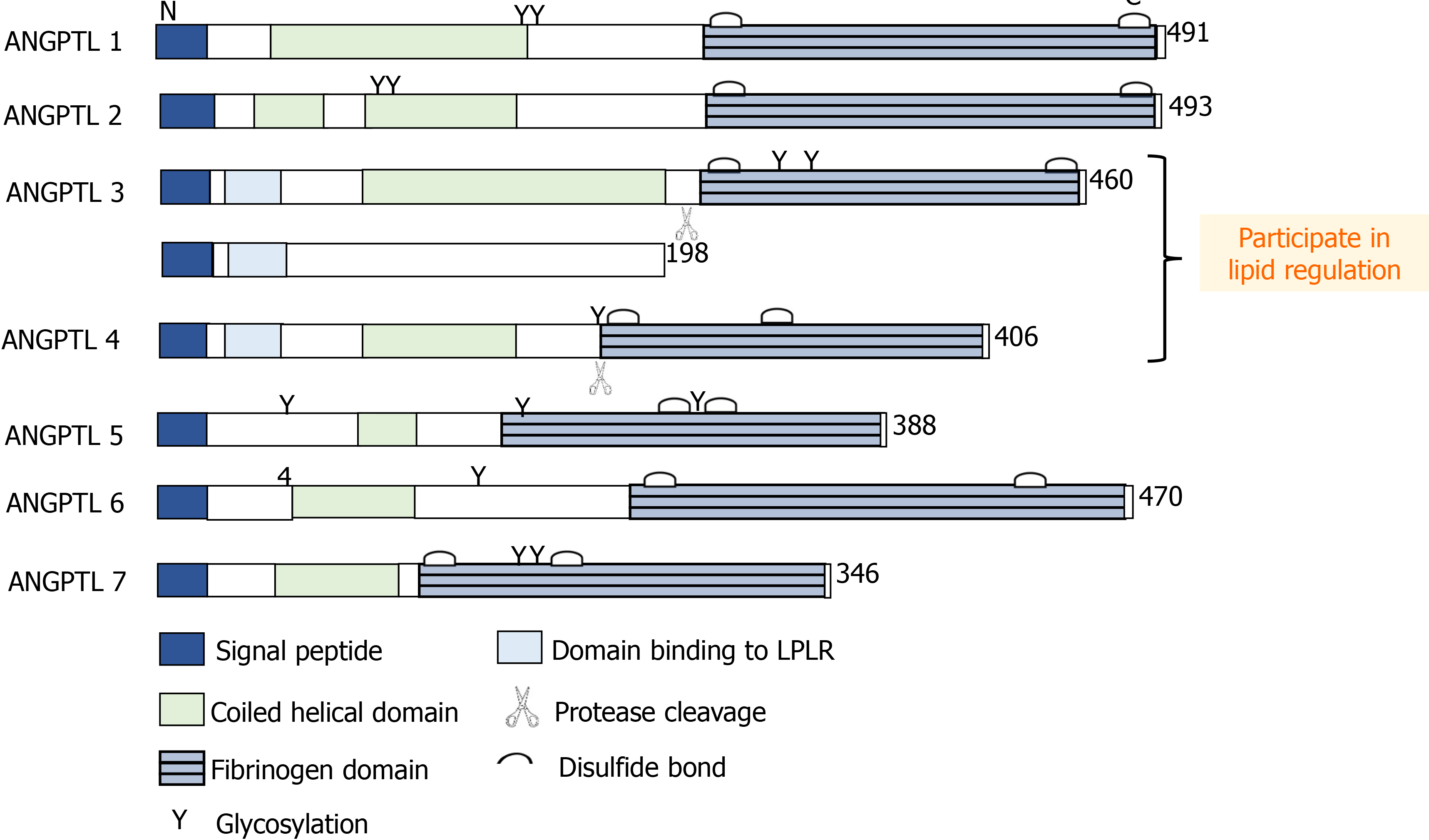
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of structural characteristics of angiopoietin-like proteins members.
The members of the angiopoietin-like proteins (ANGPTLs) have their own different structural characteristics, betatrophin is considered an atypical new member of the ANGPTLs because of the lack of the C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain. However, betatrophin, angiogenin-likeprotein3, and angiogenin-likeprotein4 all possess protein domains that bind to low density lipoprotein receptor. These characteristics provide evidence for their joint participation in lipid regulation.
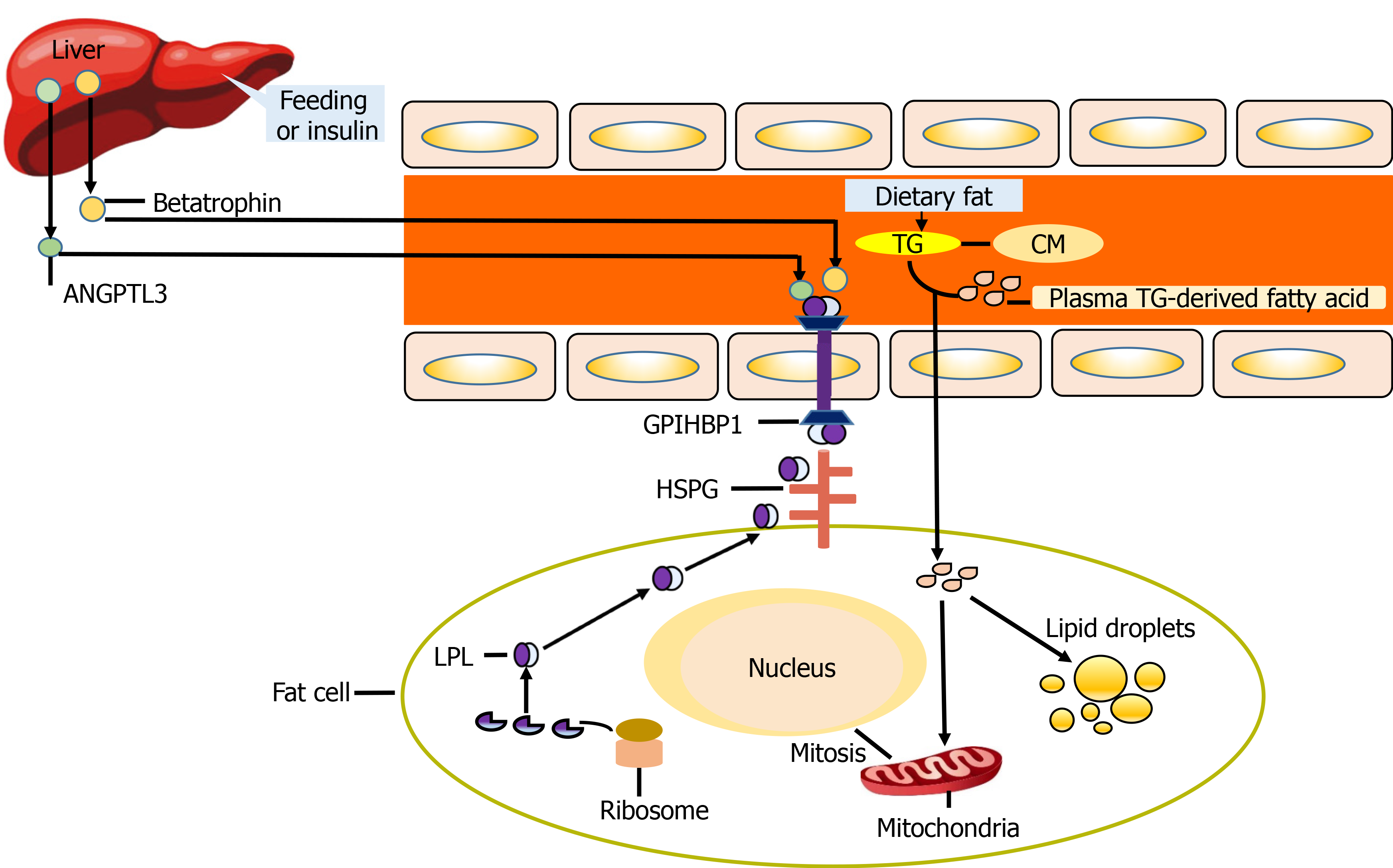
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of betatrophin and angiogenin-likeprotein3 participating in lipid regulation.
Betatrophin synthesized by the liver under the stimulation of feeding or insulin can promote the cleavage of angiogenin-likeprotein3 (ANGPTL3) to release the active N-terminal catalytic core domain (CCD) domain, which leads to a decrease in the inhibitory effect of ANGPTL3 on Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity and indirectly promotes LPL to participate in lipid metabolism. When triglyceride- derived fatty acids enter the adipocytes, some of them form lipid droplets, while the other part induces the increase of LPL synthesis in adipocytes, and enters the blood circulation to participate in lipid metabolism mediated by glycosylphosphatidylinositol high density lipoprotein binding protein 1. GPIHBP1: Glycosylphosphatidylinositol high density lipoprotein binding protein 1; HSPG: Heparan sulfate proteoglycan; CM: Chylomicrons; TG: Triglycerides.
- Citation: Qin L, Rehemuding R, Ainiwaer A, Ma X. Correlation between betatrophin/angiogenin-likeprotein3/lipoprotein lipase pathway and severity of coronary artery disease in Kazakh patients with coronary heart disease. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(7): 2095-2105
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i7/2095.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2095