Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2022; 10(7): 2087-2094
Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2087
Published online Mar 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2087
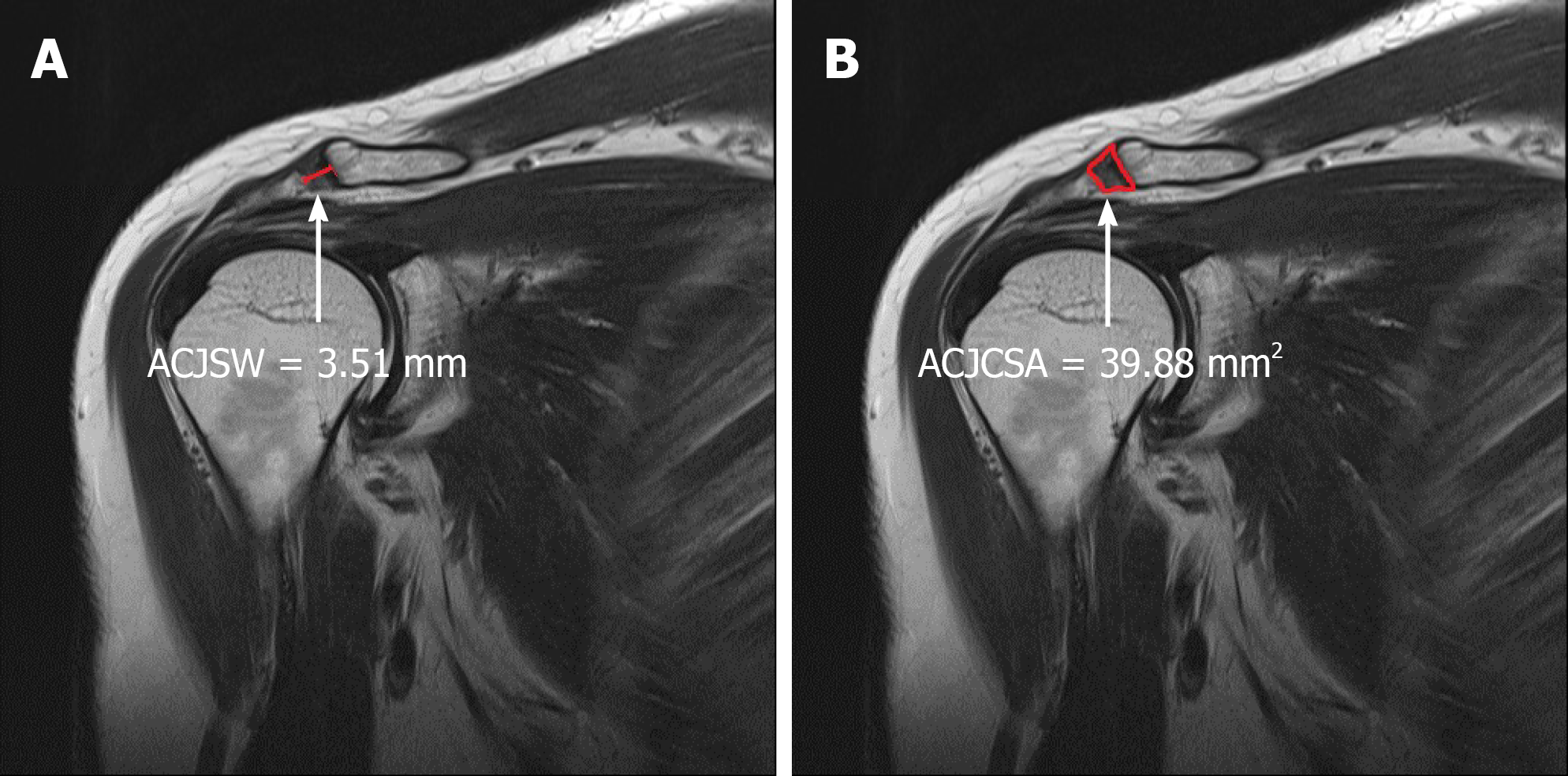
Figure 1 Measurement of both the acromioclavicular joint space width (A) and acromioclavicular joint cross-sectional area (B) in the normal control group was carried out on coronal T2-weighted shoulder-MR acromioclavicular joint images.
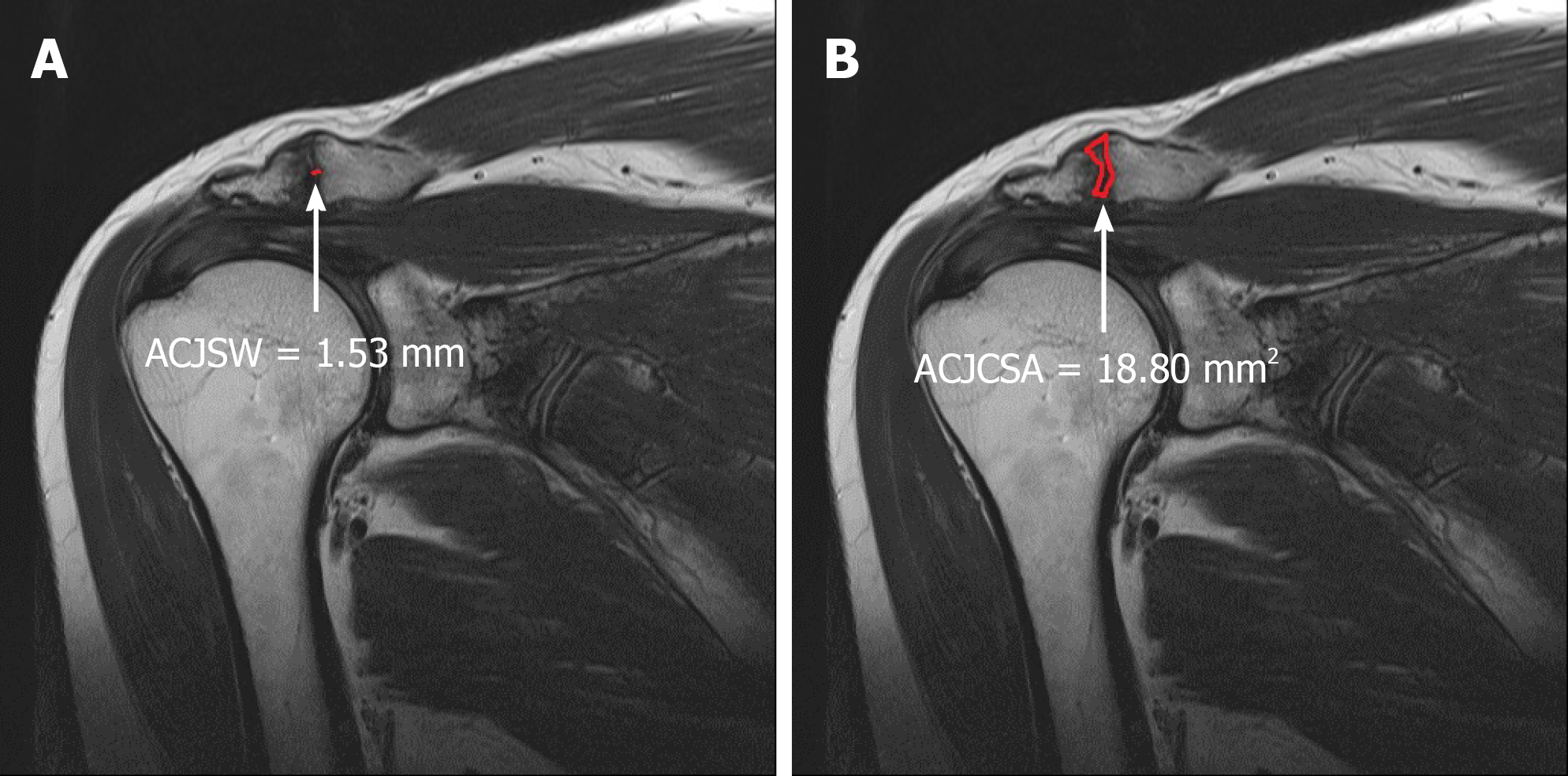
Figure 2 In the acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis group, both the acromioclavicular joint space width (A) and acromioclavicular joint cross-sectional area (B) were measured on coronal T2-weighted shoulder-MR images.
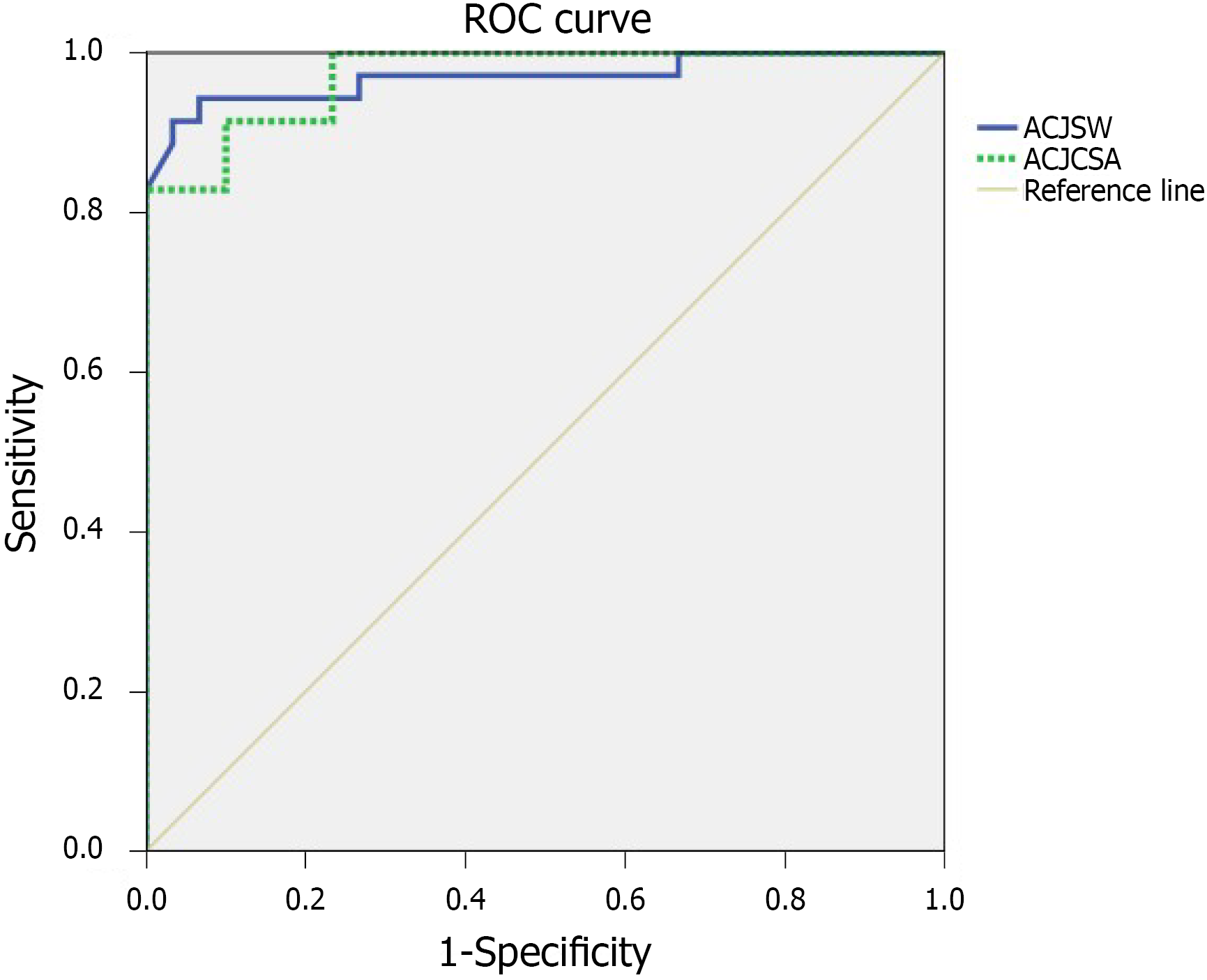
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve of both the acromioclavicular joint cross-sectional area and the acromioclavicular joint space width to detect acromioclavicular joint osteoarthritis.
The most suitable acromioclavicular joint cross-sectional area cutoff point was 26.14 mm2 vs 2.37 mm for the acromioclavicular joint space width, with 91.4% sensitivity vs 88.6%, and 90.0% specificity vs 96.7%, respectively.
- Citation: Joo Y, Moon JY, Han JY, Bang YS, Kang KN, Lim YS, Choi YS, Kim YU. Usefulness of the acromioclavicular joint cross-sectional area as a diagnostic image parameter of acromioclavicular osteoarthritis. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(7): 2087-2094
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i7/2087.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i7.2087