Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2022; 10(6): 1937-1945
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1937
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1937
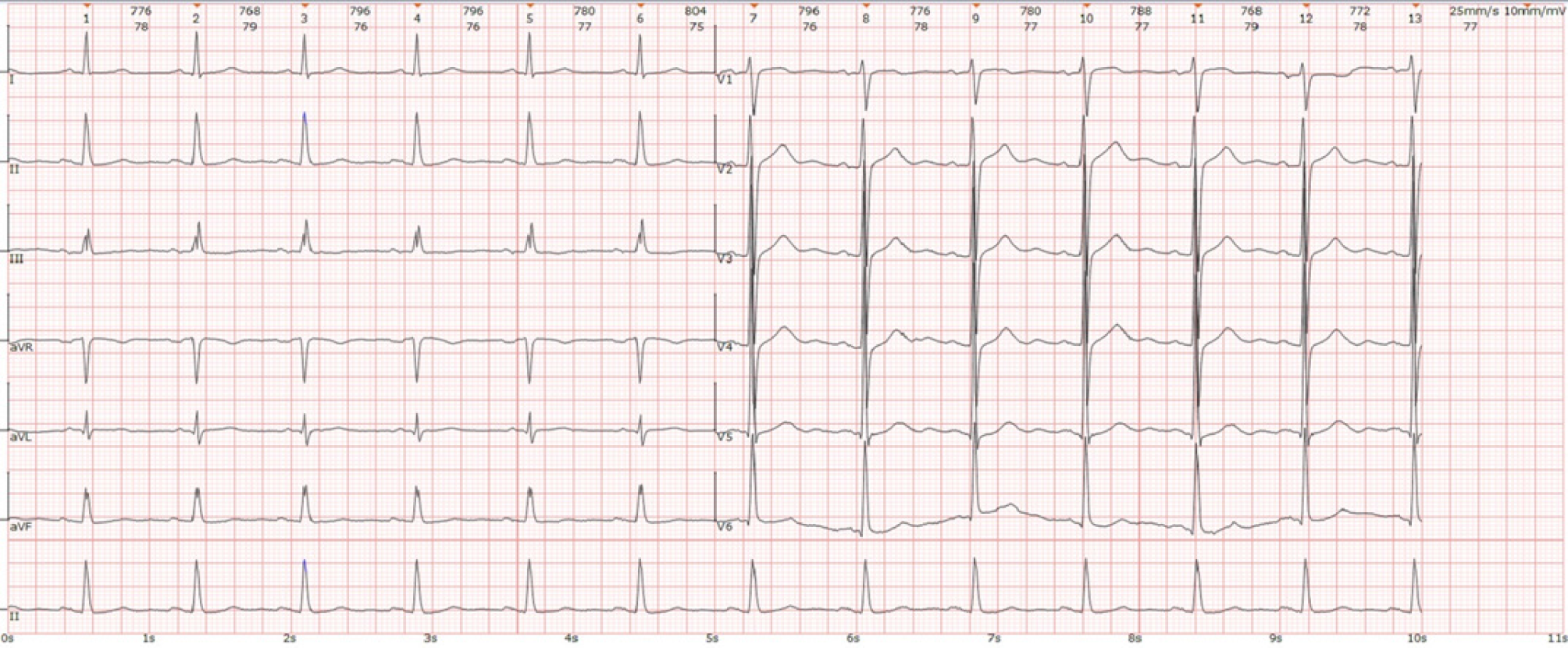
Figure 1
Electrocardiogram at hospital admission.
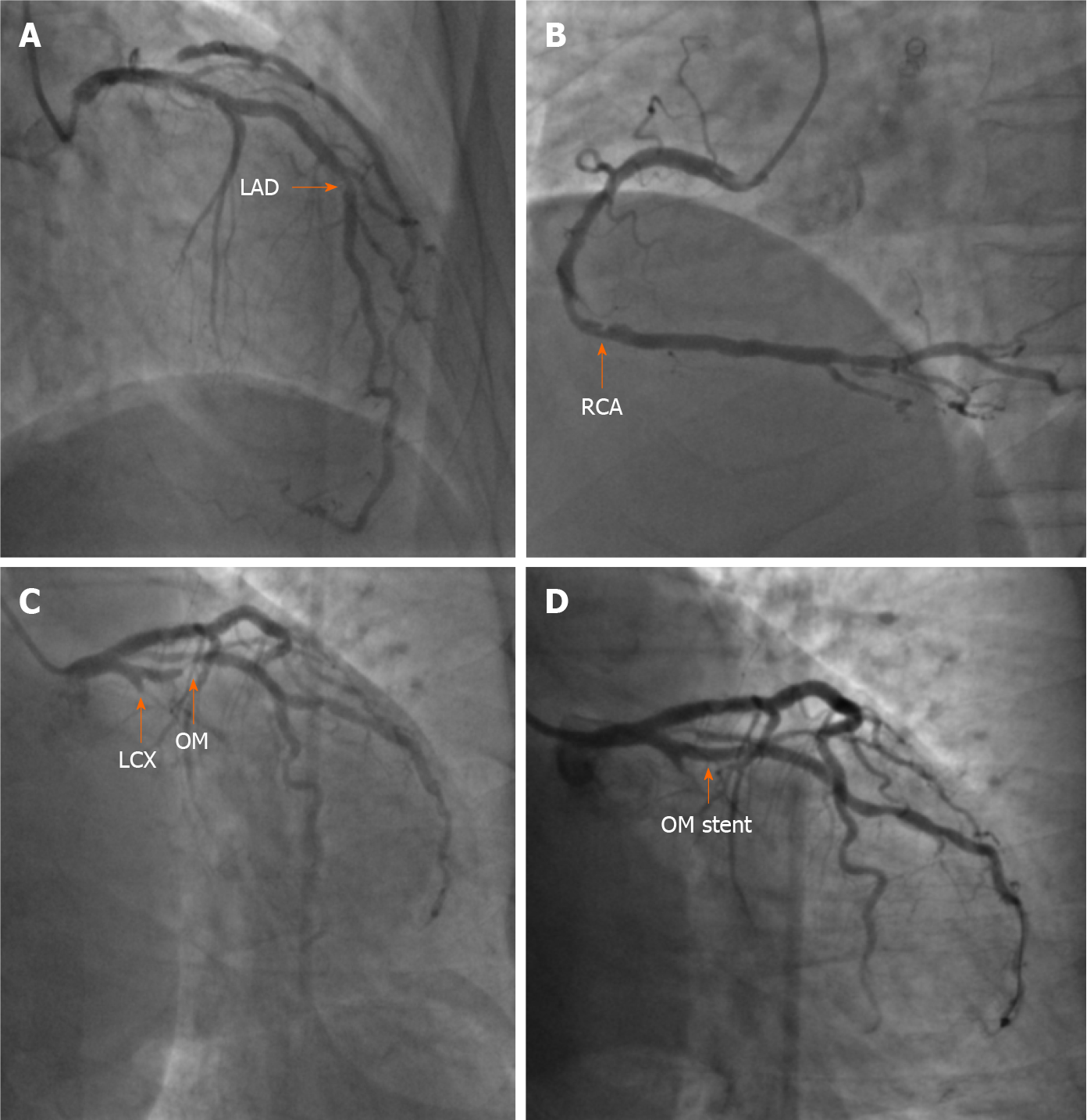
Figure 2 Coronary angiogram and stent implantation.
A: Coronary angiogram showing 60%-70% in-stent restenosis at the middle left anterior descending artery (orange arrow); B: Coronary angiogram showing 60%-70% stenosis of the distal right coronary artery (orange arrow); C: Coronary angiogram showing total occlusion of the proximal left circumflex artery and subtotal occlusion at the opening of the first obtuse marginal branch (OM) (orange arrow); D: After deployment of a stent in the OM, stenosis was eliminated (orange arrow). LAD: Left anterior descending artery; LCX: Left circumflex artery; OM: Obtuse marginal branch; RCA: Right coronary artery.
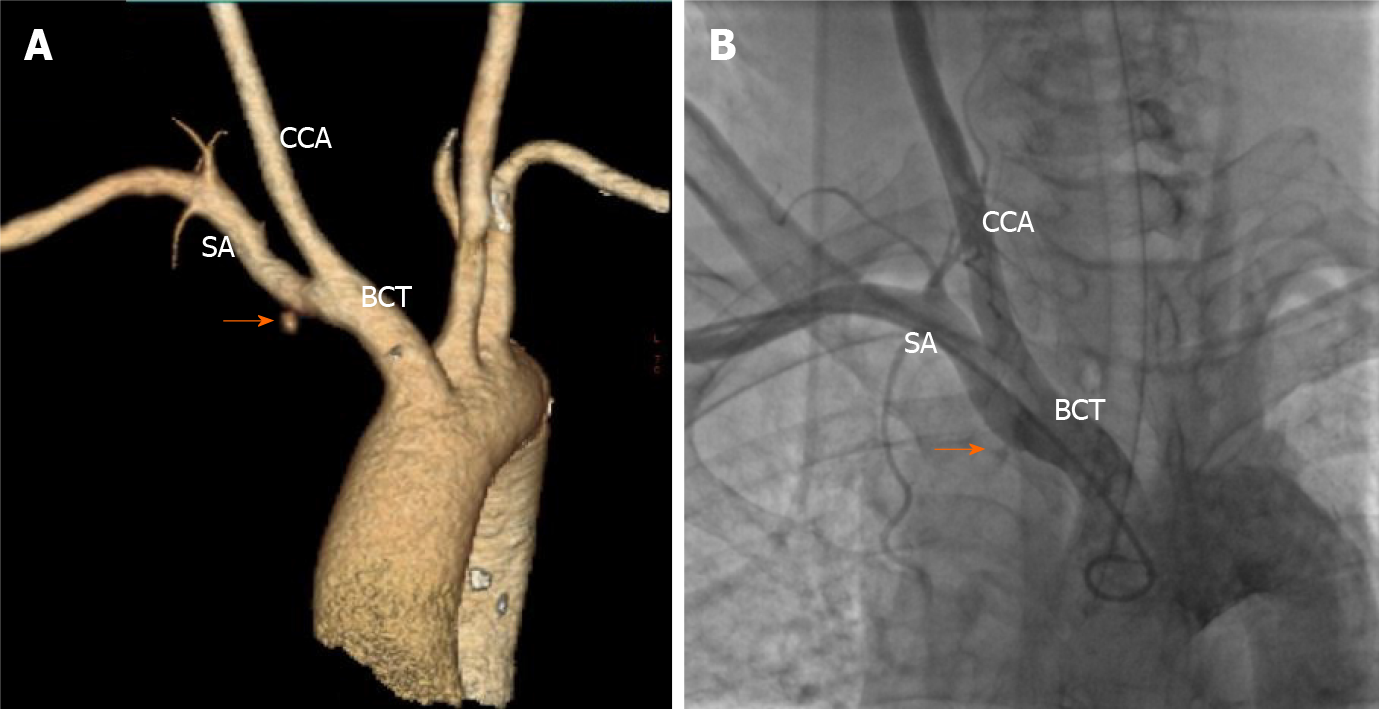
Figure 3 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography and brachiocephalic angiography.
A: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography showing contrast extravasation surrounding the proximal subclavian artery (SA) (orange arrow); B: Brachiocephalic angiography revealing the site of bleeding at the root of the right SA at the intersection of the right common carotid artery (orange arrow). SA: Subclavian artery; CCA: Common carotid artery; BCT: Brachiocephalic trunk.
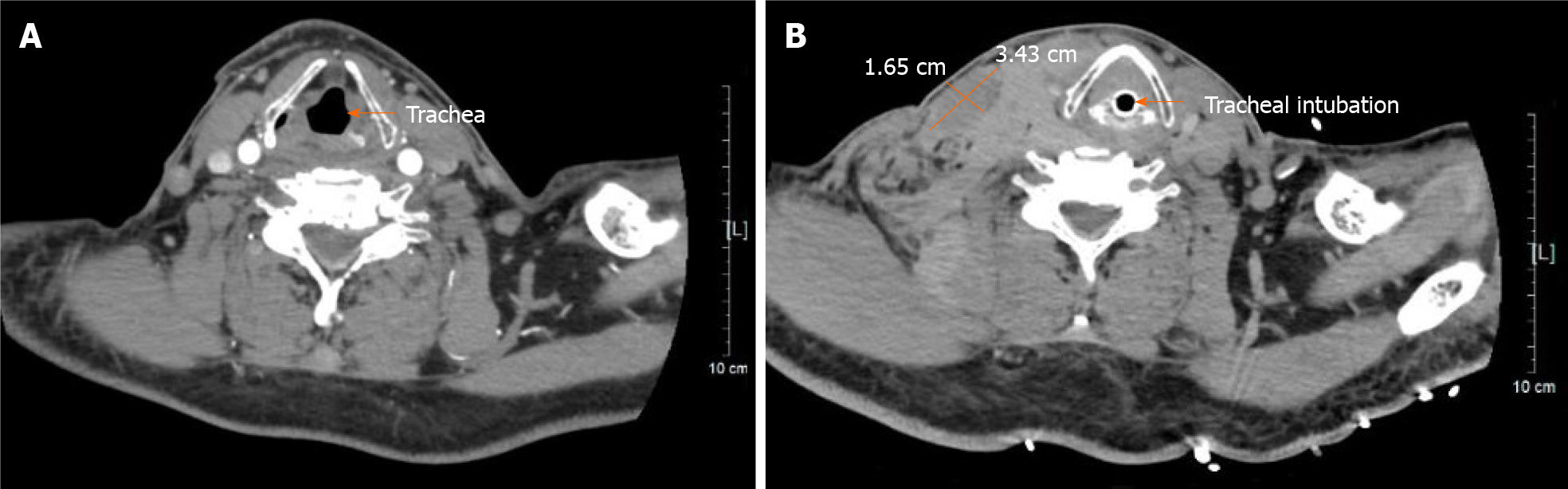
Figure 4 Cervical computed tomography.
A: Cervical computed tomography showing a normal trachea (orange arrow); B: Cervical computed tomography showing a cervical hematoma (3.43 cm × 1.65 cm) (orange cross) and tracheal compression (orange arrow).
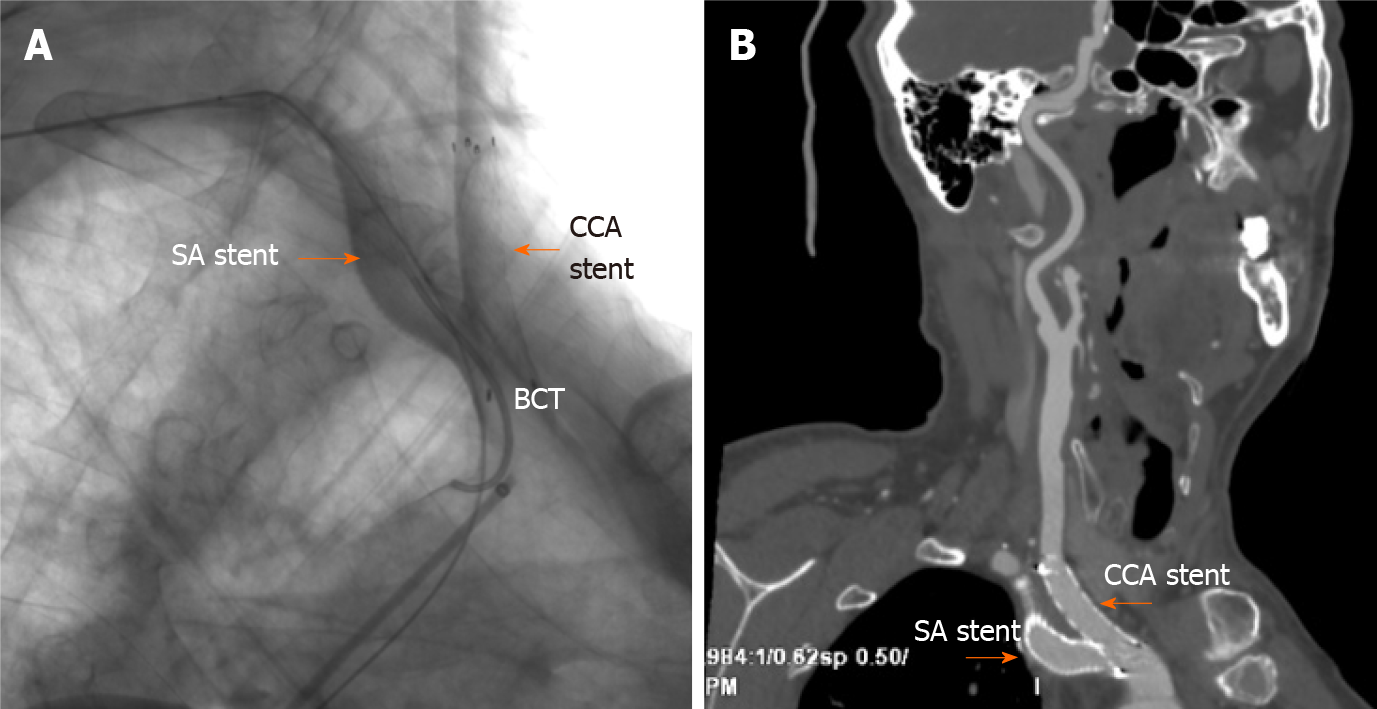
Figure 5 Immediate postoperative angiography and contrast-enhanced computed tomography at the 1.
5-mo follow-up. A: Immediate postoperative angiography showing deployment of a covered stent in the right subclavian artery and a bare stent in the junction of the right common carotid artery and brachiocephalic trunk (orange arrow); B: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography showing the two stents in a satisfactory position and unobstructed at the 1.5-mo follow-up (orange arrow). SA: Subclavian artery; CCA: Common carotid artery; BCT: Brachiocephalic trunk.
- Citation: Shi F, Zhang Y, Sun LX, Long S. Life-threatening subclavian artery bleeding following percutaneous coronary intervention with stent implantation: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(6): 1937-1945
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i6/1937.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1937