Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 26, 2022; 10(6): 1883-1888
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1883
Published online Feb 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1883
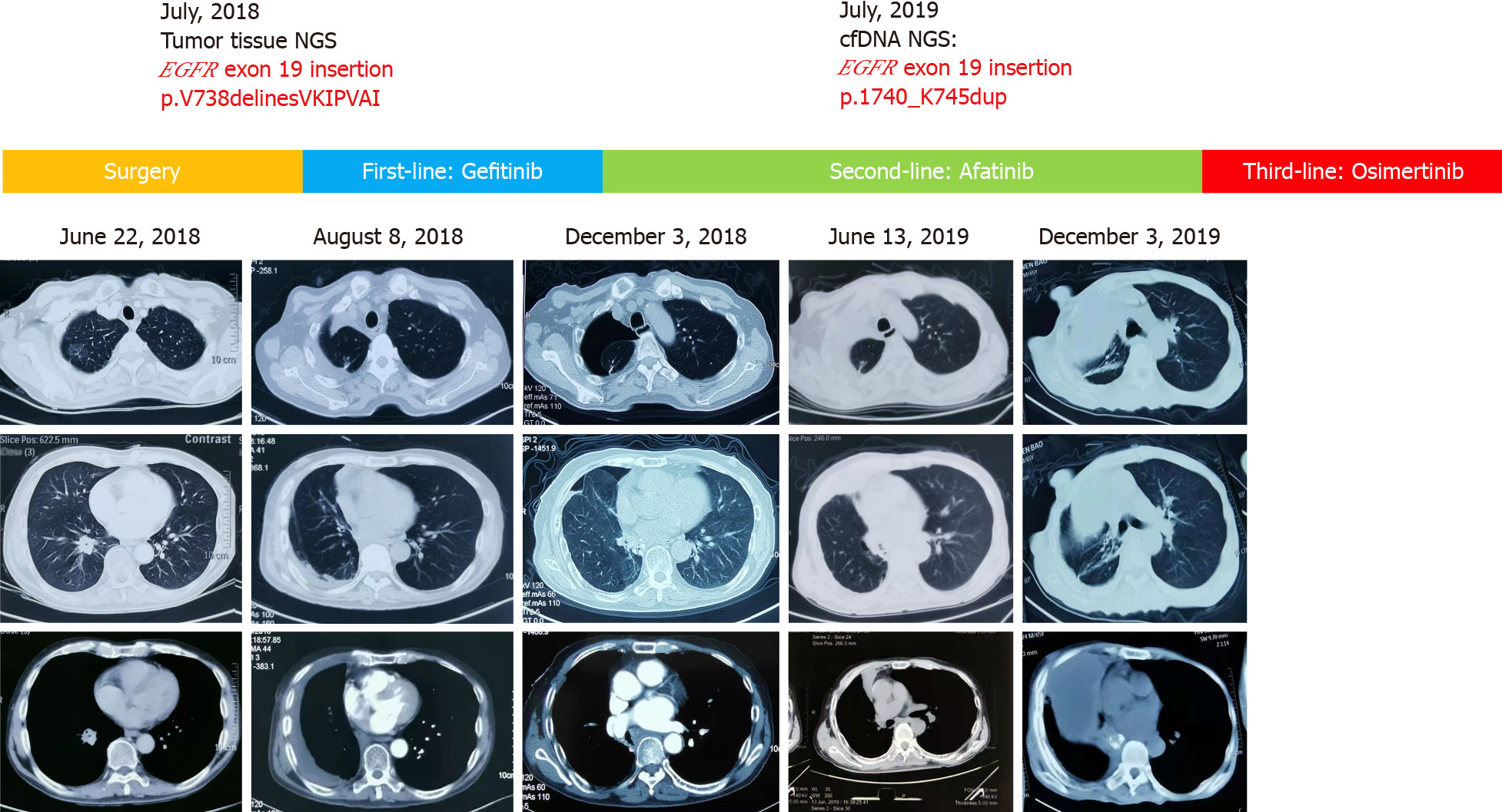
Figure 1 Treatment course of non-small cell lung cancer with sequential epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor regimen with serial chest computed tomography scanning.
June 22, 2018, a nodular density shadow in the lower lobe of the right lung, approximately 2.0 cm × 2.7 cm in size, and a ground-glass shadow in the upper right lung lobe, approximately 2 cm × 1.5 cm in size; August 8, 2018, postoperative changes and pleural effusion in the right lung; December 3, 2018, pleural effusion absorbed in the right lung after targeted therapy; June 13, 2019, encapsulated effusion in the right pleural cavity; December 3, 2019, encapsulated effusion increasing in the right pleural cavity. EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; TKI: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor; cfDNA: cell free DNA; NGS: Next-generation sequencing.
Figure 2
Next-generation sequencing showed EGFR exon 19 insertion.
- Citation: Shan BB, Li Y, Zhao C, An XQ, Zhang QM. Efficacy of EGFR-TKI sequential therapy in patients with EGFR exon 19 insertion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(6): 1883-1888
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i6/1883.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i6.1883