Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Feb 6, 2022; 10(4): 1320-1325
Published online Feb 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i4.1320
Published online Feb 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i4.1320
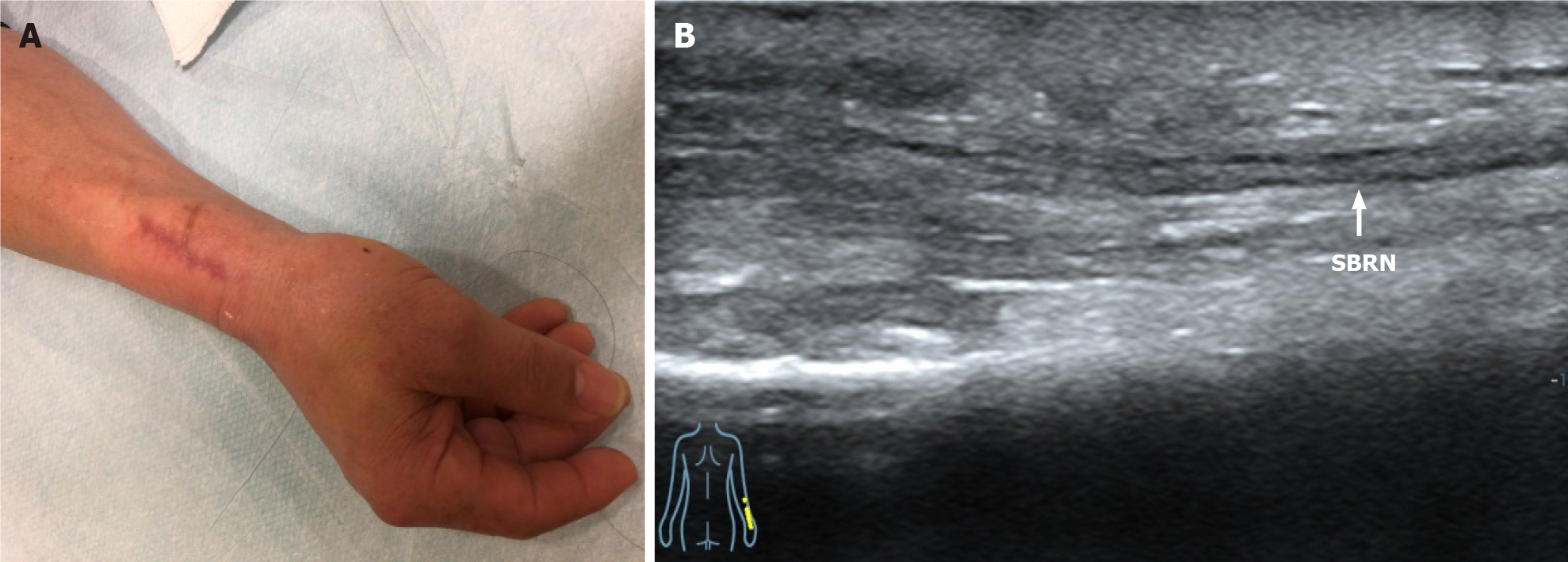
Figure 1 Three months after resection of traumatic neuroma.
A: Appearance; B: Ultrasound image shows the long-axis view of the superficial branch of radial nerve adhered to the surrounding tissues (white line). SBRN: Superficial branch of radial nerve.
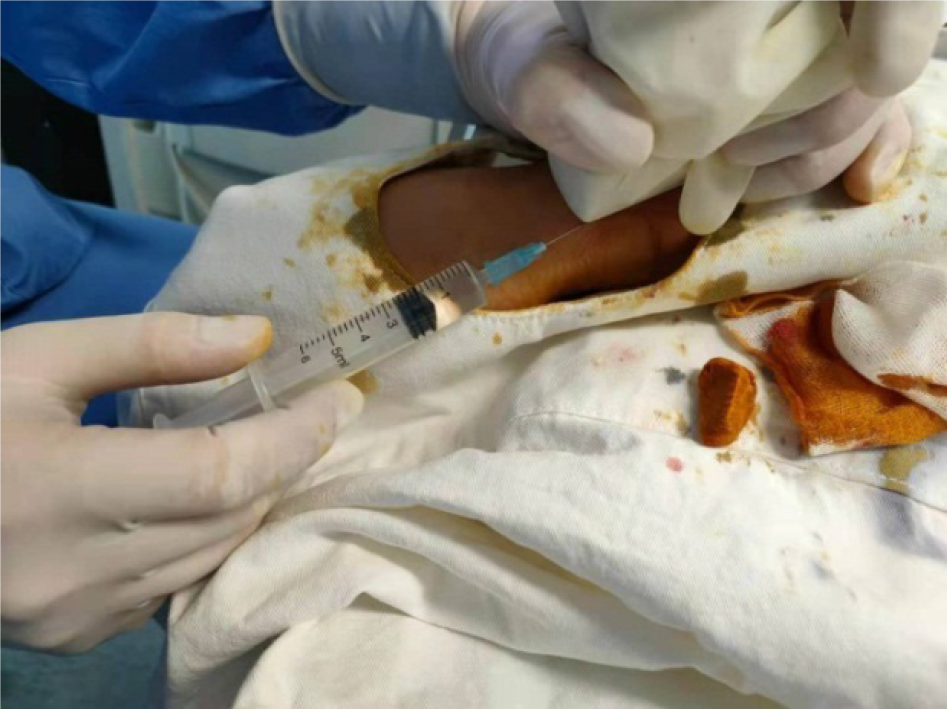
Figure 2
Sonographer held the probe covered with surgical gloves with one hand and did needle release of the superficial branch of radial nerve continuously under continuous guidance of ultrasound.
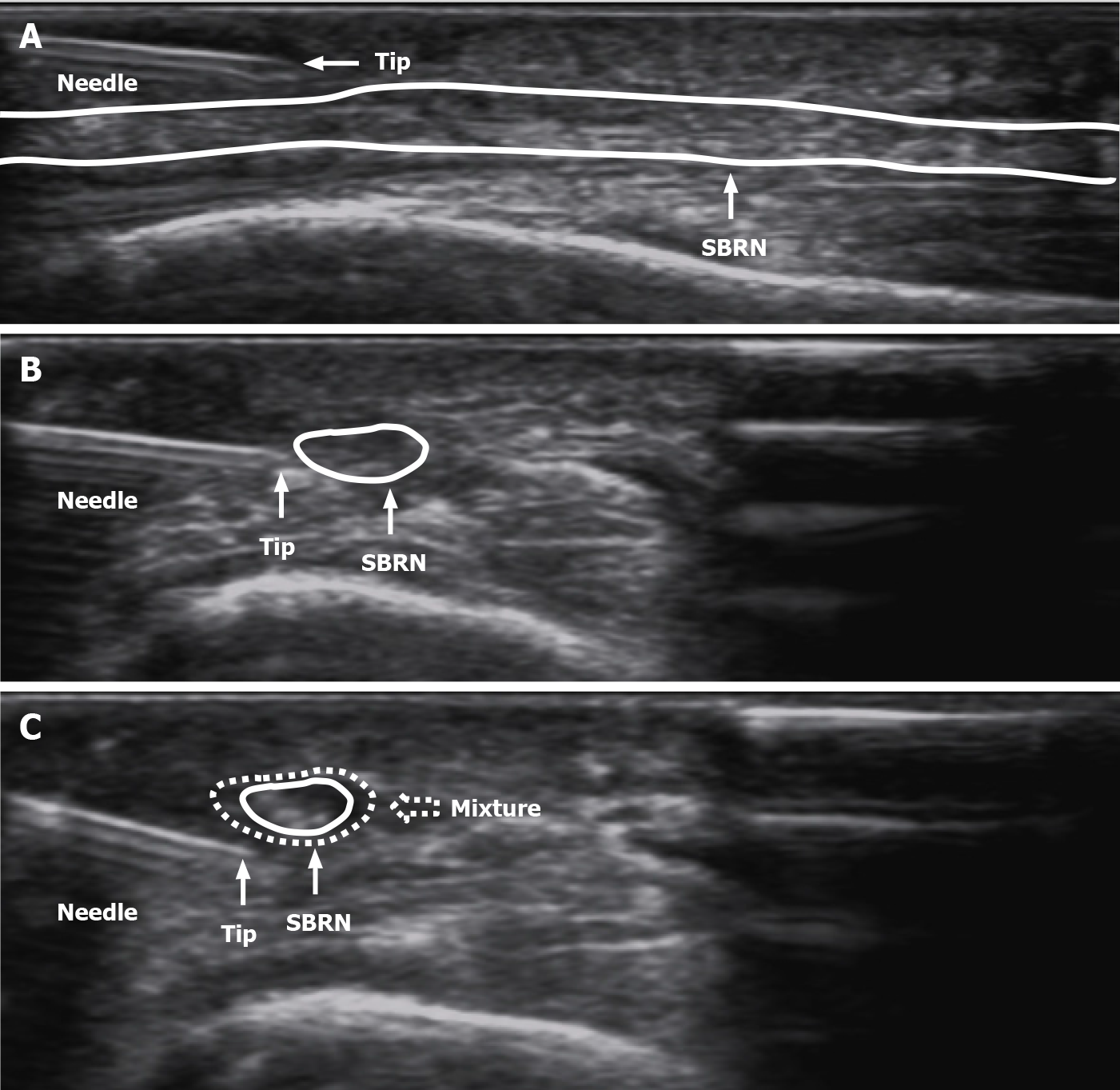
Figure 3 Procedures of ultrasound-guided needle release plus corticosteroid injection of superficial radial nerve.
A: The superficial adhesion of superficial branch of radial nerve (SBRN) was separated by needle release; B: The deep adhesion of SBRN was separated by needle release; C: Injected the mixture (1 mL betamethasone and 2 mL 2% lidocaine) (white dotted arrow) around the SBRN. SBRN: Superficial branch of radial nerve.
- Citation: Zeng Z, Chen CX. Ultrasound-guided needle release plus corticosteroid injection of superficial radial nerve: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(4): 1320-1325
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i4/1320.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i4.1320