Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2022; 10(34): 12734-12741
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12734
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12734
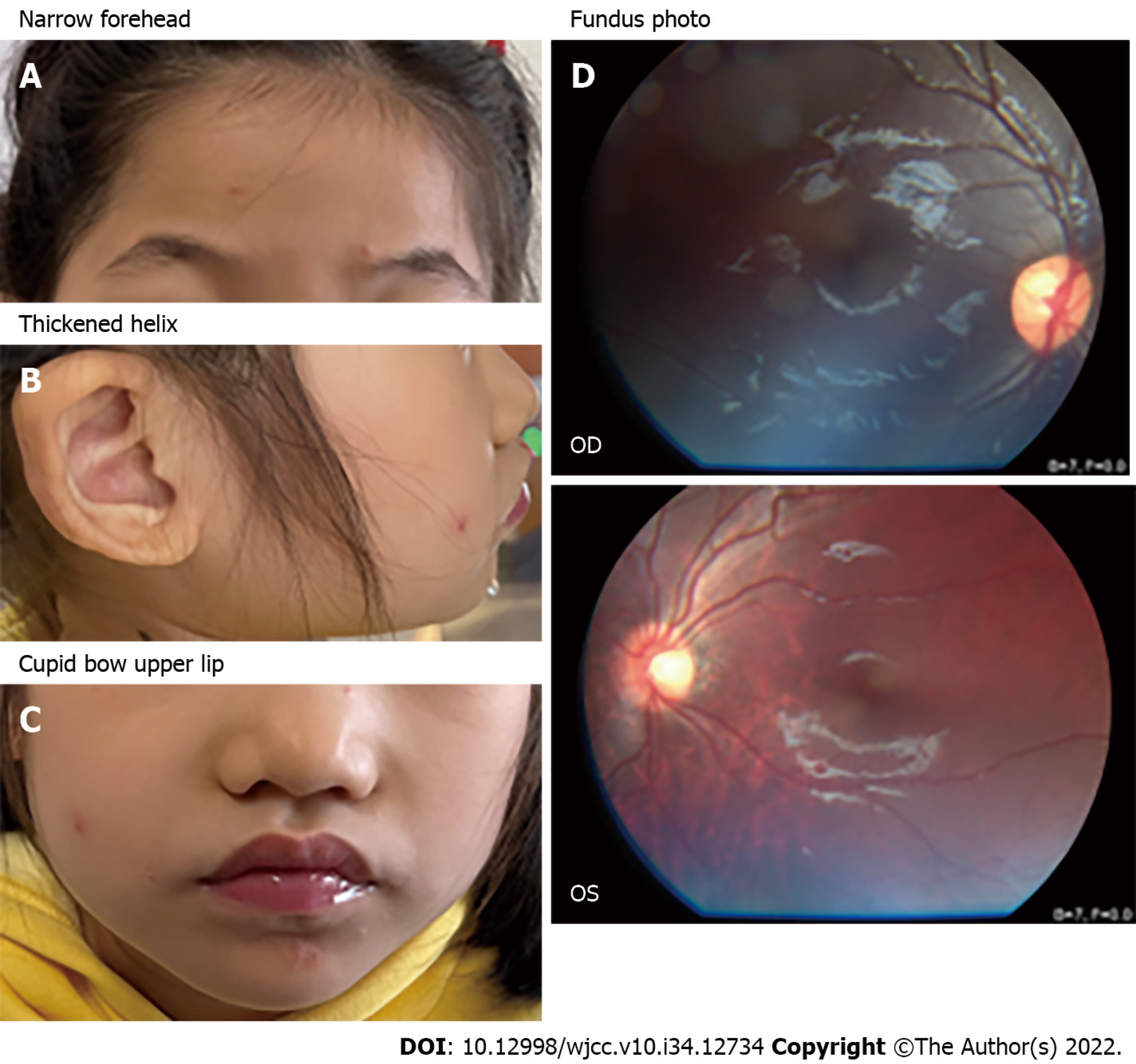
Figure 1 Image of patient 1.
A-C: Facial abnormalities included narrow forehead, thickened helix, wide mouth and cupid bow upper lip; D: Fundus photos in both eyes of the patient, the left eye (oculus sinister) revealed a slight fundus tessellation. OD: Oculus dexter; OS: Oculus sinister.
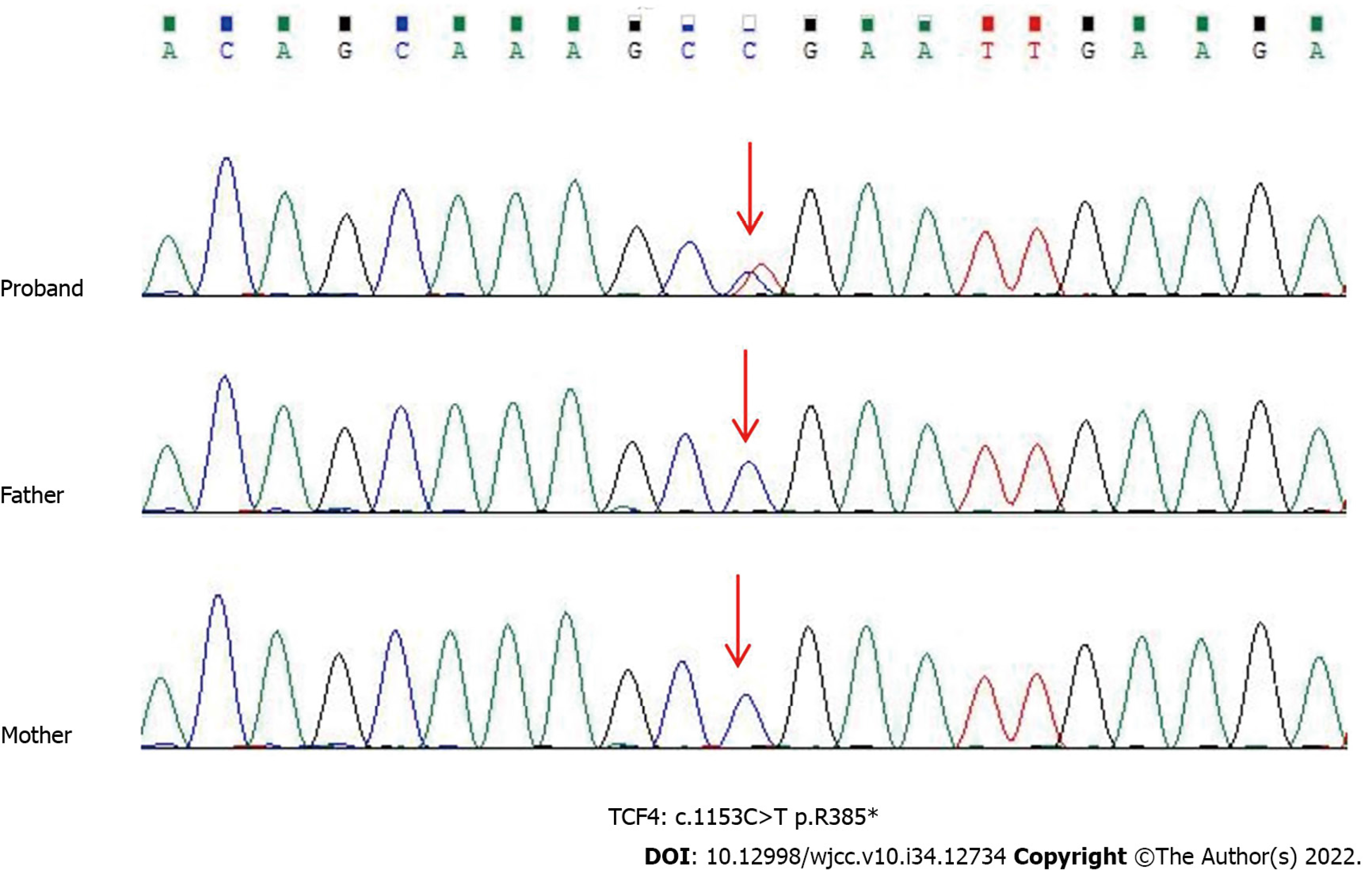
Figure 2 Sanger sequencing showed a heterozygous nonsense mutation (c.
1153C>T:p.R385* in exon 15) in the patient 2. Her parents were normal. Red arrows point to the mutant bases. TCF4: Transcription factor 4.
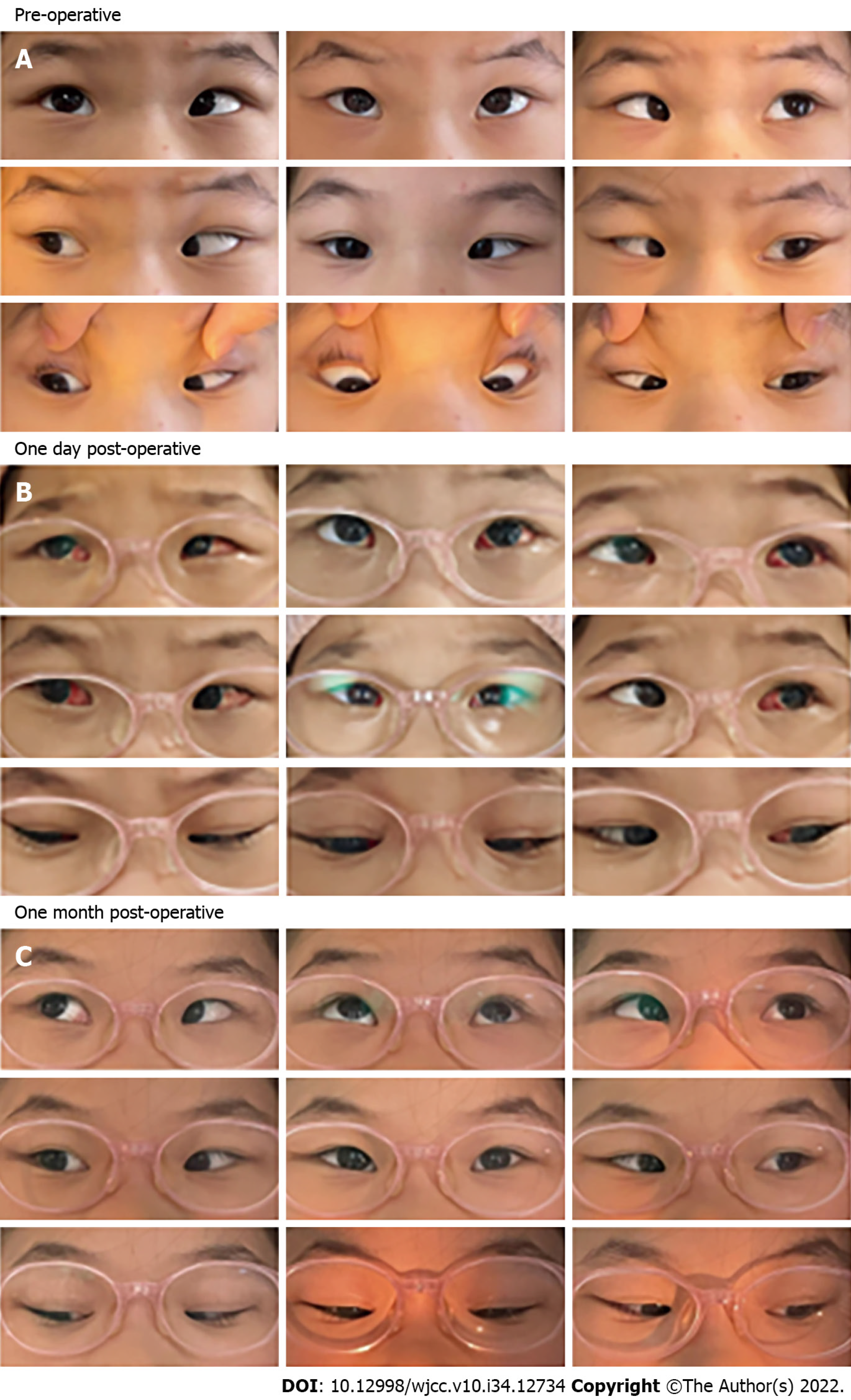
Figure 3 Pre-operative, one day post-operative and one month post-operative alignment of patient 1.
A: Case 1 had +40 prism diopter in the primary position before the surgery; B and C: After bilateral medial rectus recession combined with posterior scleral reinforcement surgery, the patient’s esotropia was significantly relieved on the secondary day of surgery. Conjunctival congestion and edema were observed in this patient at an early stage, and both conditions were completely alleviated after 1 mo.
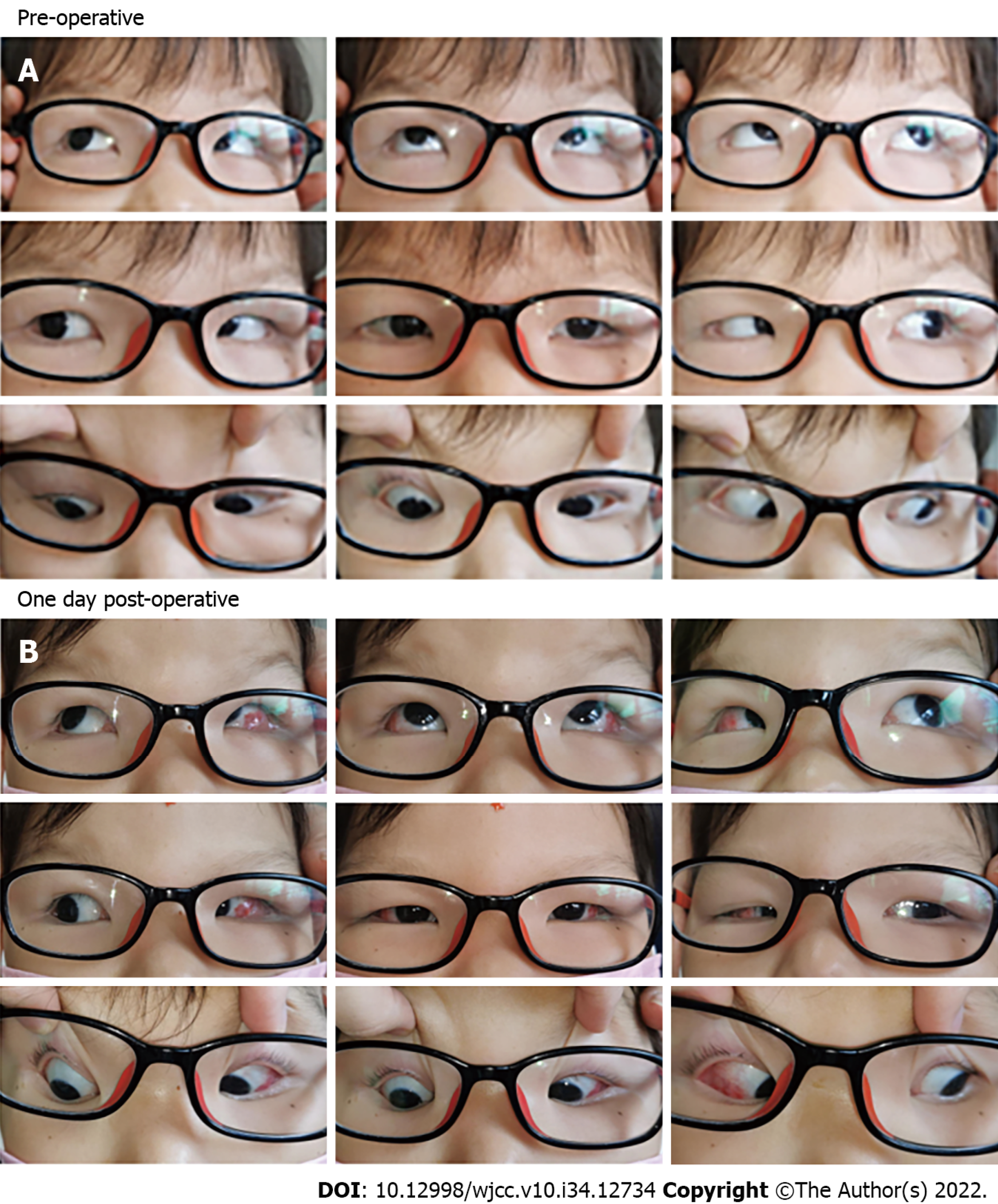
Figure 4 Pre-operative and one day post-operative alignment of patient 2.
A: Case 2 had -50 prism diopter in the primary position before the surgery; B: After bilateral lateral rectus recession surgery, the patient’s exotropia was significantly relieved on the secondary day of surgery.
- Citation: Huang Y, Di Y, Zhang XX, Li XY, Fang WY, Qiao T. Surgical treatment of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome associated with strabismus and early-onset myopia: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(34): 12734-12741
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i34/12734.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12734