Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2022; 10(34): 12484-12493
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12484
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12484
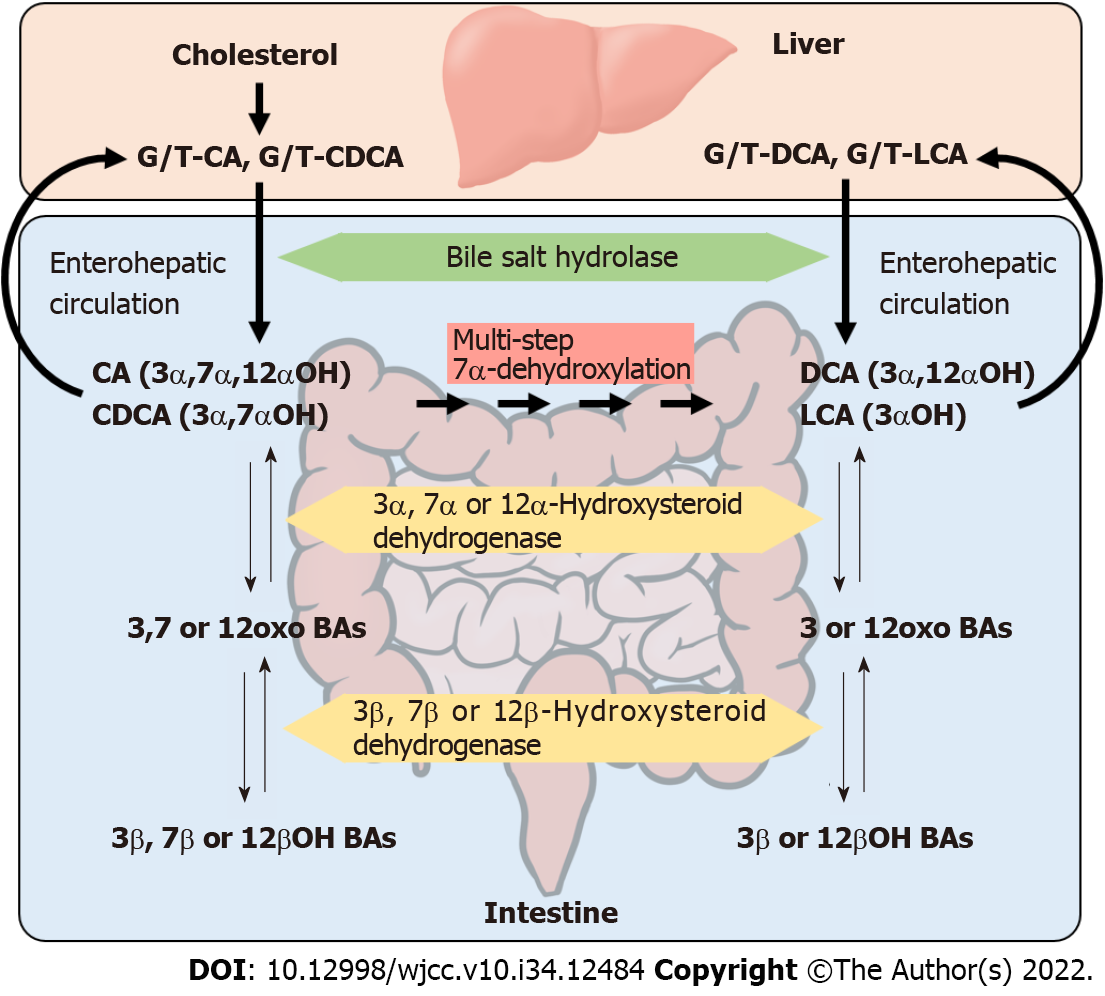
Figure 1 Metabolism of amino acid (glycine or taurine)-conjugated primary bile acids by human intestinal microbiota.
Bile salt hydrolase deconjugates amino acid to form free cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. The free (deconjugated) cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid are then transformed to deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, respectively, by multi-step 7α-dehydroxylation. Hydroxyl groups at the 3α, 7α, and 12α positions can be metabolized to carbonyl groups by 3α-, 7α-, and 12α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases, respectively. In addition, the carbonyl groups at the 3, 7, and 12 positions can be metabolized to hydroxyl groups at the 3β, 7β, and 12β positions by the reverse reactions of 3β-, 7β-, and 12β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases, respectively. G: Glycine; T: Taurine; DCA: Deoxycholic acid; CA: Cholic acid; CDCA: Chenodeoxycholic acid; LCA: Lithocholic acid; BA: Bile acid. This figure was adapted from a previous study[25].
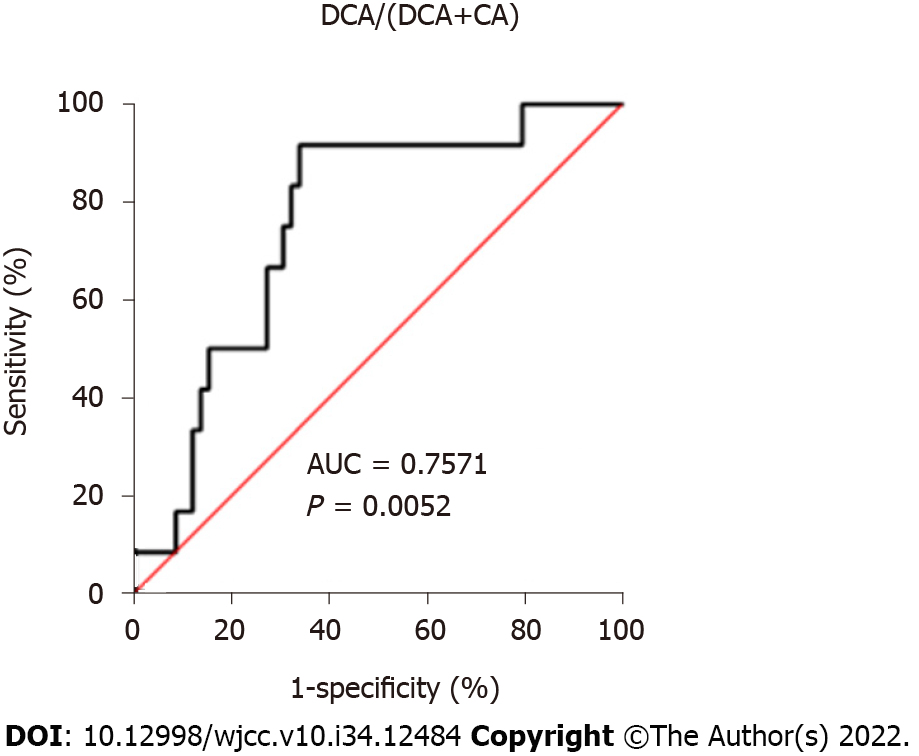
Figure 2 Receiver operating characteristic analysis for the prediction of Clostridium difficile infection development in relation to the serum deoxycholic acid (DCA)/(DCA + cholic acid) ratio.
AUC: Area under the curve. Sensitivity = true-positive number/(true-positive number + false-negative number); specificity = true-negative number/(true-negative number + false-positive number). The minimum distance from the upper left corner (0, 1) was considered the optimal cut-off value. The cut-off value of DCA/(DCA+CA) was < 0.349 in discriminating high-risk patients with Clostridium difficile infection before treatment with antibiotics. At this value, the sensitivity was 91.67% and the specificity was 66.10%. This figure was adapted from a previously published study[25].
- Citation: Monma T, Iwamoto J, Ueda H, Tamamushi M, Kakizaki F, Konishi N, Yara S, Miyazaki T, Hirayama T, Ikegami T, Honda A. Evaluation of gut dysbiosis using serum and fecal bile acid profiles. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(34): 12484-12493
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i34/12484.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12484