Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2022; 10(34): 12470-12483
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12470
Published online Dec 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12470
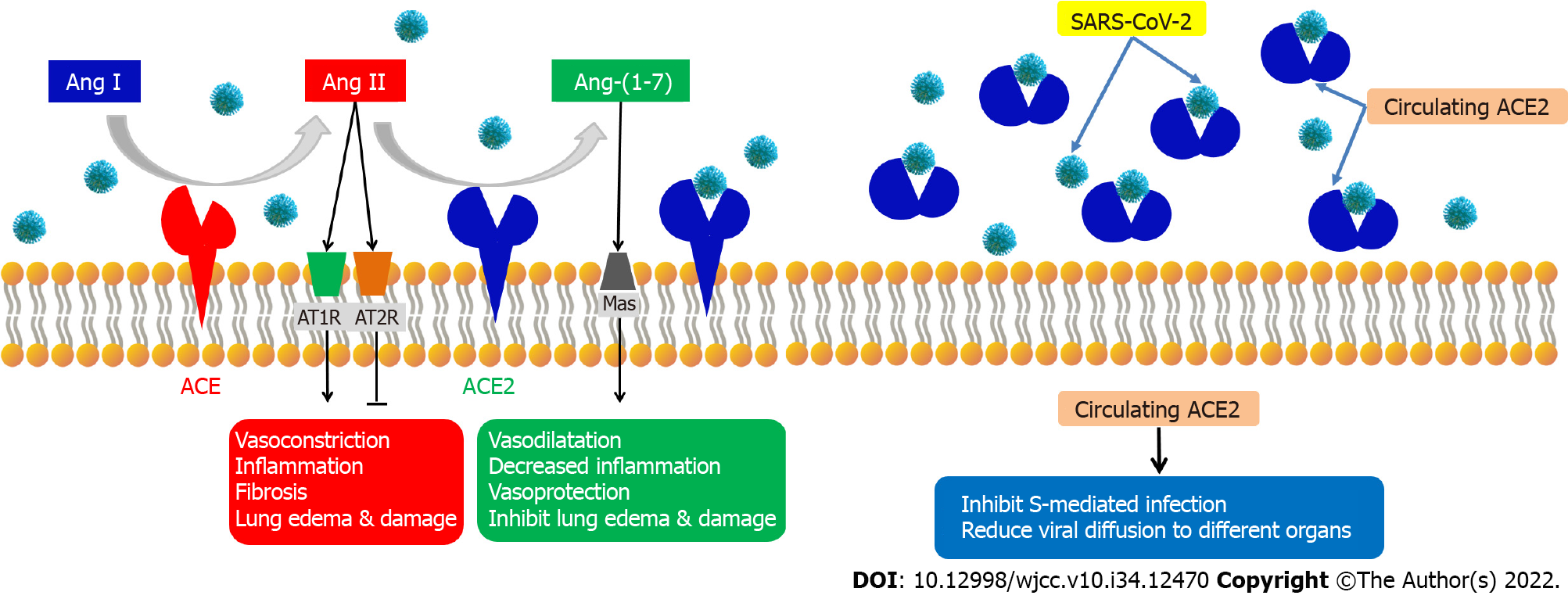
Figure 1 Mechanism of action of angiotensin converting enzyme 2.
The angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) metabolizes angiotensin (Ang) I to Ang II, which activates Ang II type 1 receptors (AT1R) and Ang II type 2 receptors (AT2R), leading to increased vasoconstriction, inflammation, fibrosis, lung damage, and edema. Conversely, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE 2) counteracts Ang I by generating angiotensin 1-7 [Ang-(1-7)], which then interacts with the G-protein-coupled receptor Mas to exert vasoprotective actions. Circulating ACE2 (cACE2) inhibits S-mediate infection and reduces viral diffusion to different organs.
- Citation: Leowattana W, Leowattana T, Leowattana P. Circulating angiotensin converting enzyme 2 and COVID-19. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(34): 12470-12483
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i34/12470.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i34.12470