Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2022; 10(33): 12240-12246
Published online Nov 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i33.12240
Published online Nov 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i33.12240
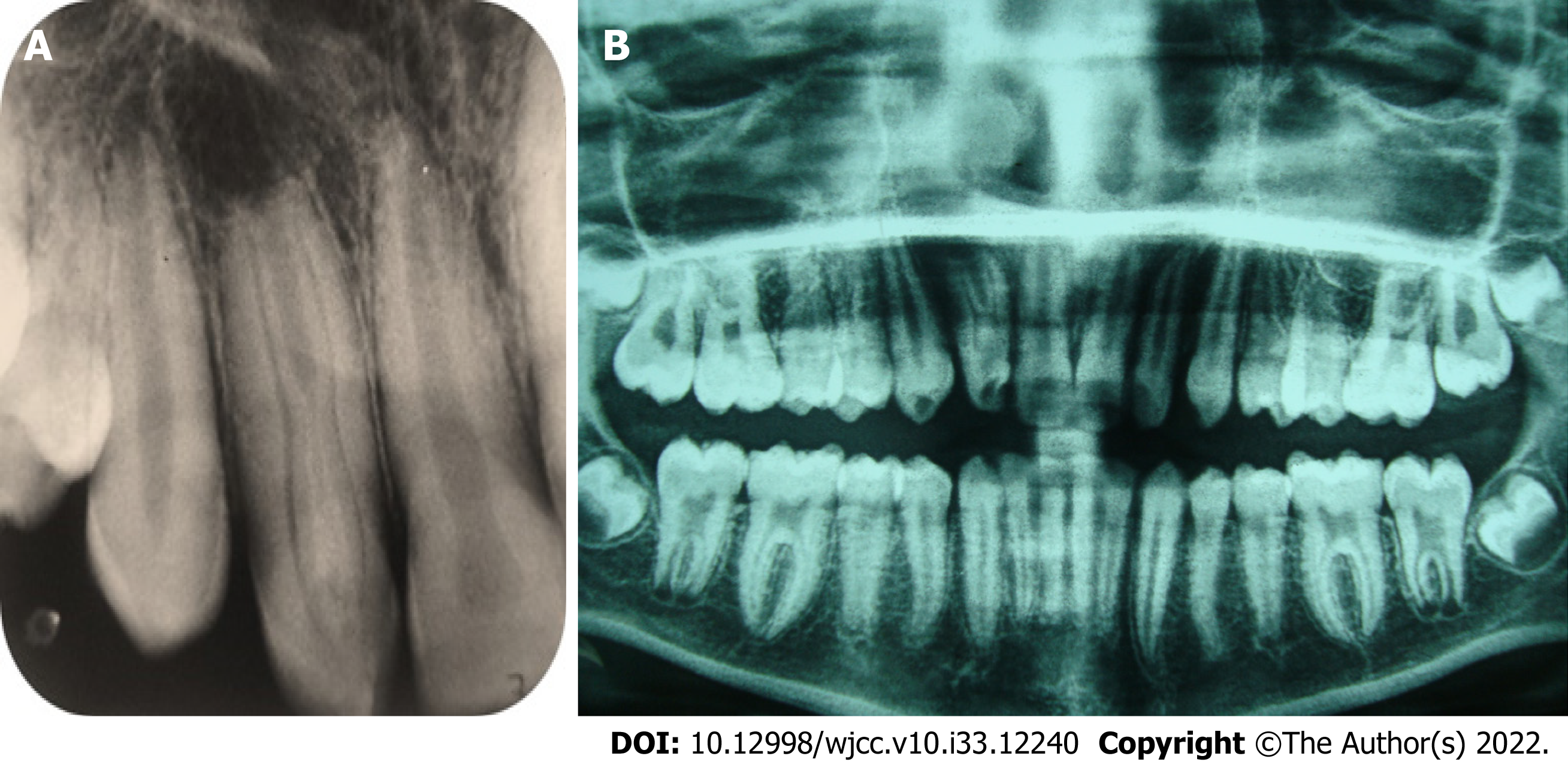
Figure 1 Radiographic diagnosis and interpretation.
A: Periapical radiograph of tooth #7 displays dens invaginatus Oehler’s type IIIB, along with wider dimension mesiodistally, complex internal anatomy, and periapical radiolucency; B: Panoramic radiograph displays that tooth #10 and other teeth have normal root canal configuration.
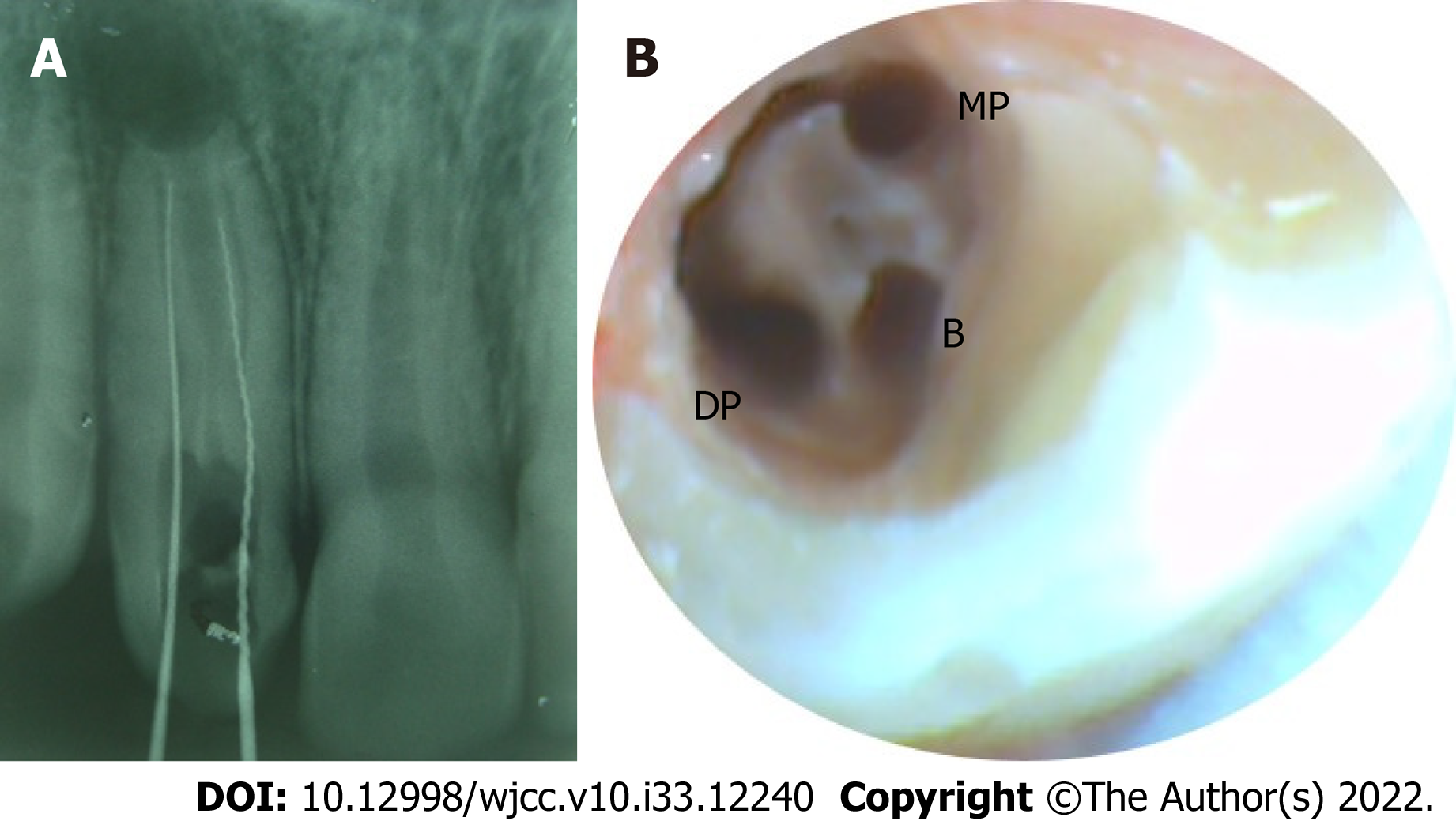
Figure 2 Initial access and exploration radiographically and final access cavity clinically.
A: Periapical radiograph of tooth #7 displaying the initial access into the two regular root canals on the palatal side: mesio-palatal (MP) and disto-palatal (DP); B: Magnified view under dental operating microscope depicting the regular palatal canals (MP and DP) joined by a C-shaped groove along the palatal surface and the invaginated buccal canal near the buccal surface.
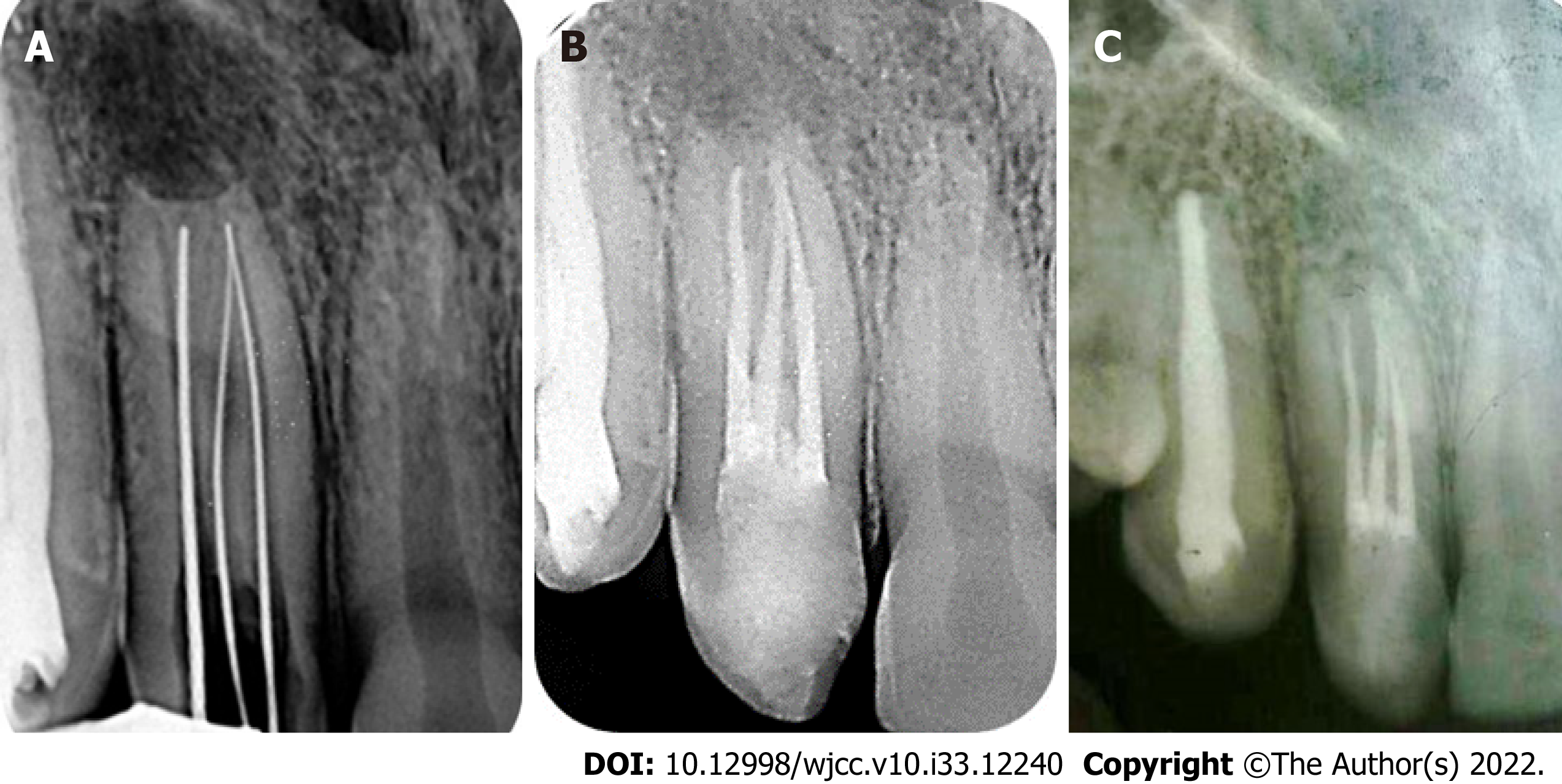
Figure 3 Radiography displaying working length determination and obturation at two different times.
A: Periapical radiograph of tooth #7 to confirm the working length; B: Periapical radiograph of tooth #7 immediately after obturation; C: Periapical radiograph of tooth #7 at 6-year follow-up, displaying significant periapical healing.
- Citation: Arora S, Gill GS, Saquib SA, Saluja P, Baba SM, Khateeb SU, Abdulla AM, Bavabeedu SS, Ali ABM, Elagib MFA. Non-surgical management of dens invaginatus type IIIB in maxillary lateral incisor with three root canals and 6-year follow-up: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(33): 12240-12246
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i33/12240.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i33.12240