Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2022; 10(33): 12164-12174
Published online Nov 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i33.12164
Published online Nov 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i33.12164
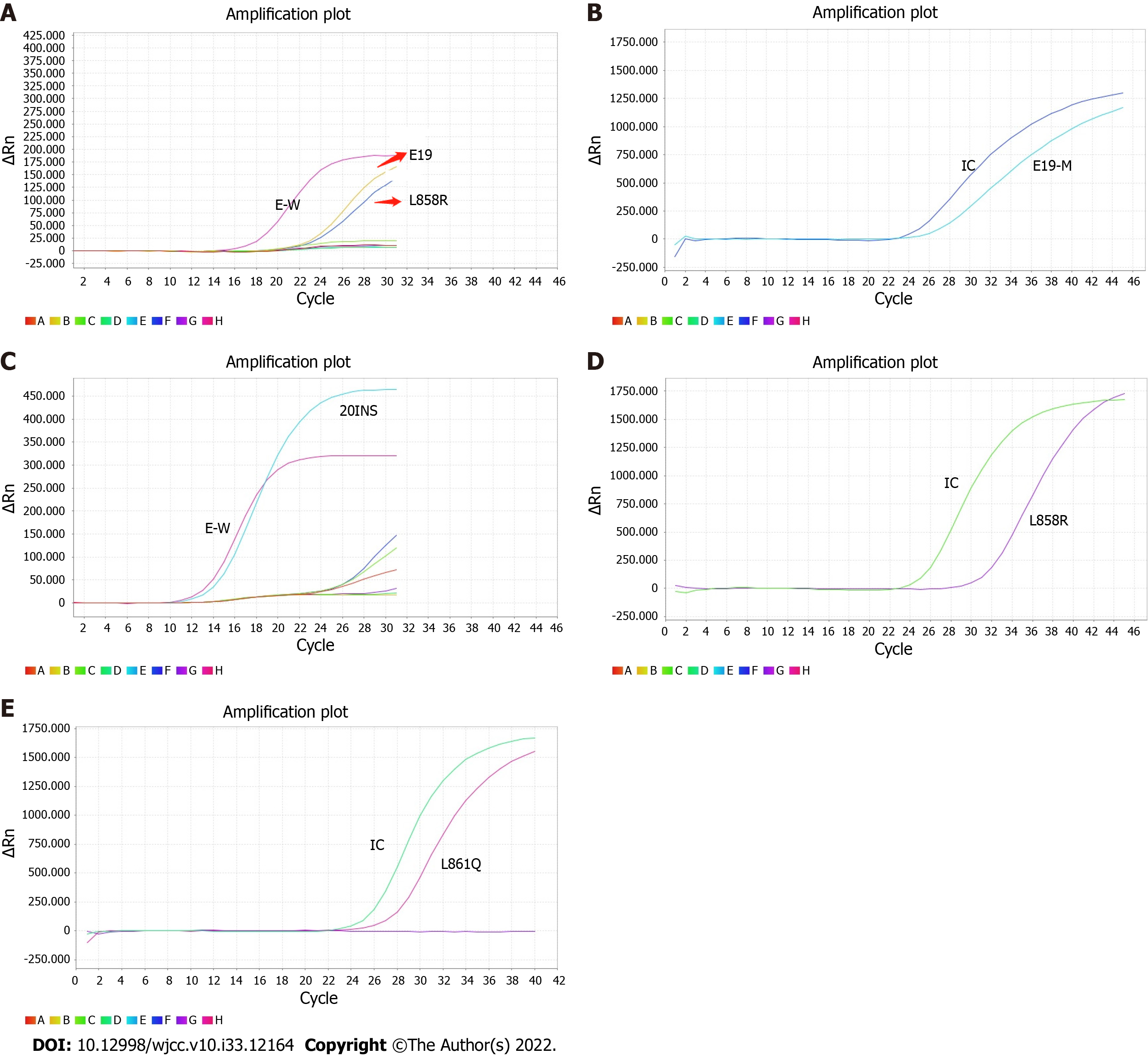
Figure 1 Real-time polymerase chain reaction amplification plots of six cases with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation.
A: Case 1#; B: Case 2#; C: Case 3#; D: Cases 4# and 5#; E: Case 6#. E-W: Wild type in exons; IC: Internal control; E19: Deletion mutation in exon19; L858R: L858R mutation in exon21; 20INS: Insert mutation in exon20; L861Q: L861Q mutation in exon21.
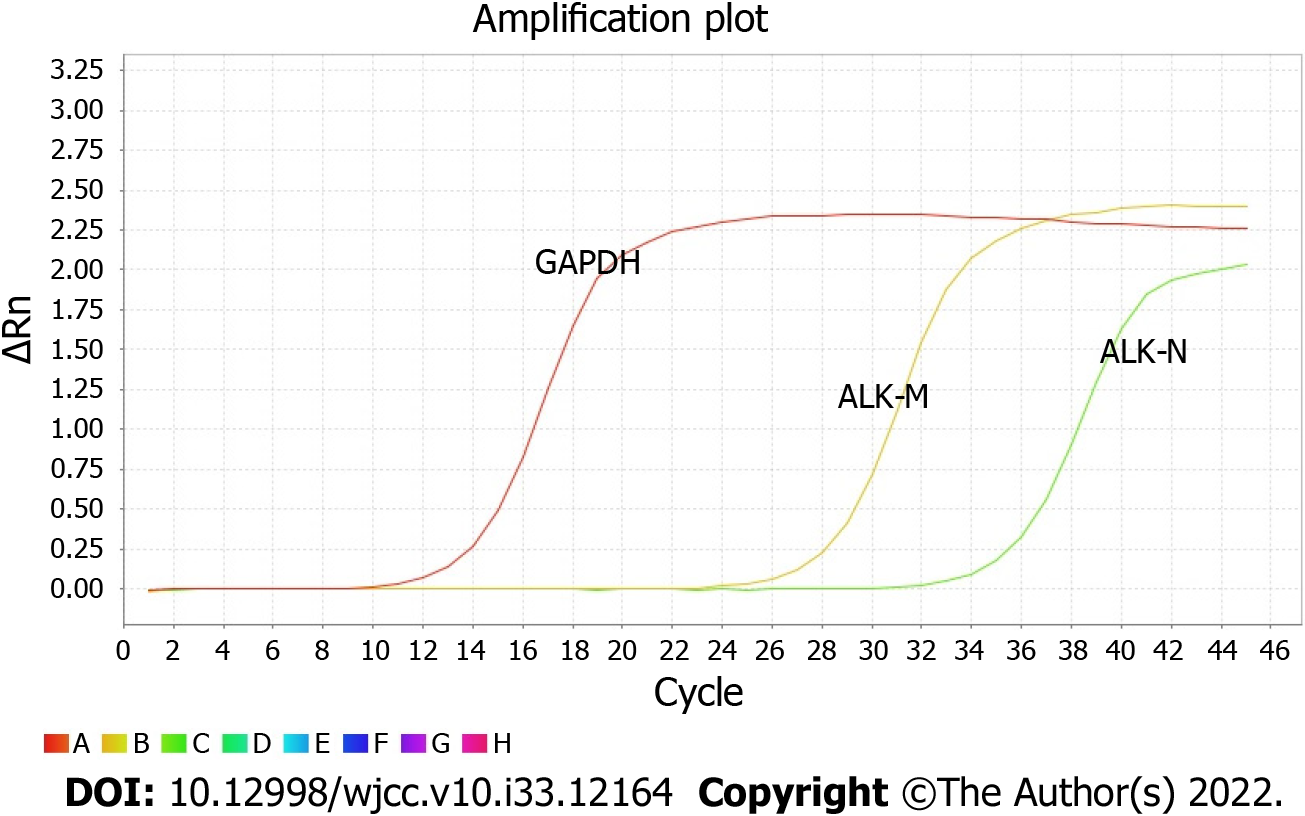
Figure 2 Real-time polymerase chain reaction amplification plots of six patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement.
GAPDH: Reference gene; ALK-M/N: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement.
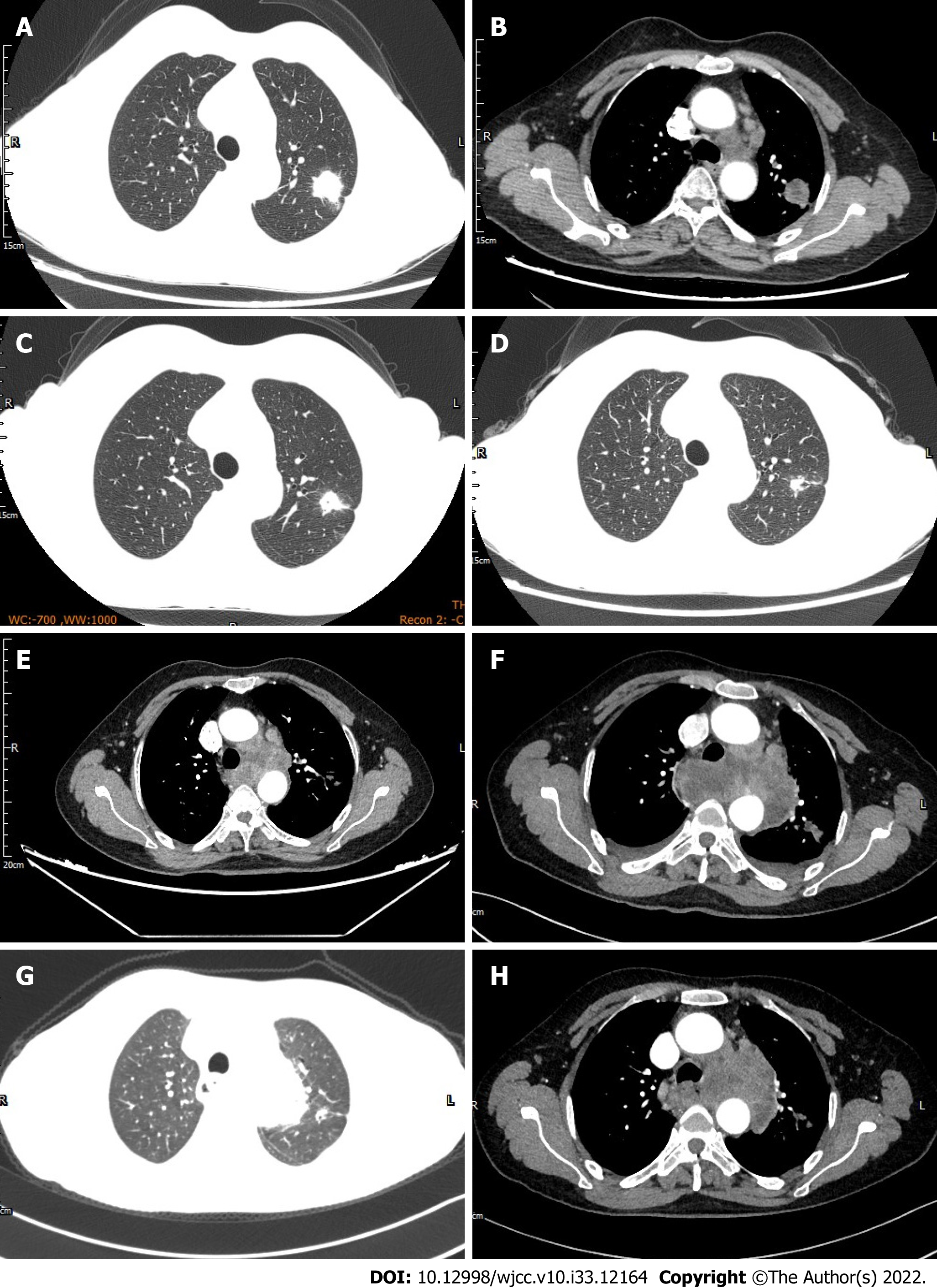
Figure 3 The chest computed tomography scan findings (A-H) of case 6#.
A: Left upper lung lesion before therapy; B: Left hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes before therapy; C: One month after erlotinib treatment; D: Three months after erlotinib treatment; E: Four months after erlotinib treatment; F: Fifteen days after erlotinib combined with crizotinib treatment; G: The shrinkage of left upper lung lesion after 2 courses of bevacizumab plus pemetrexed combined with carboplatin regimen; H: The shrinkage of left hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes after 2 courses of bevacizumab plus pemetrexed combined with carboplatin regimen.
- Citation: Zhong WX, Wei XF. Coexistence of anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement in lung adenocarcinoma harbouring epidermal growth factor receptor mutation: A single-center study. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(33): 12164-12174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i33/12164.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i33.12164