Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2022; 10(31): 11381-11390
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11381
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11381
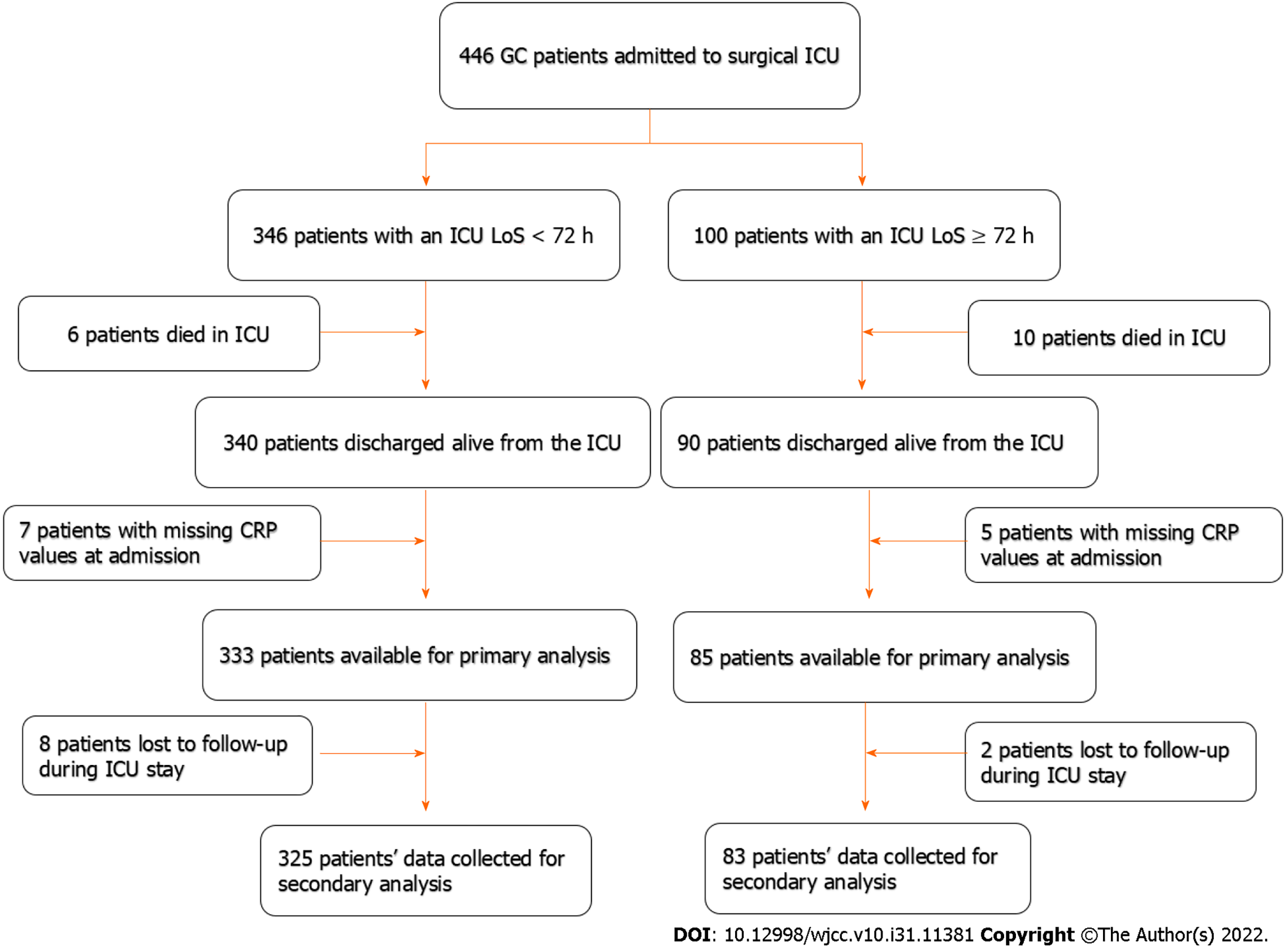
Figure 1 Flowchart for patient enrollment.
CRP: C-reactive protein; ICU: Intensive care unit.
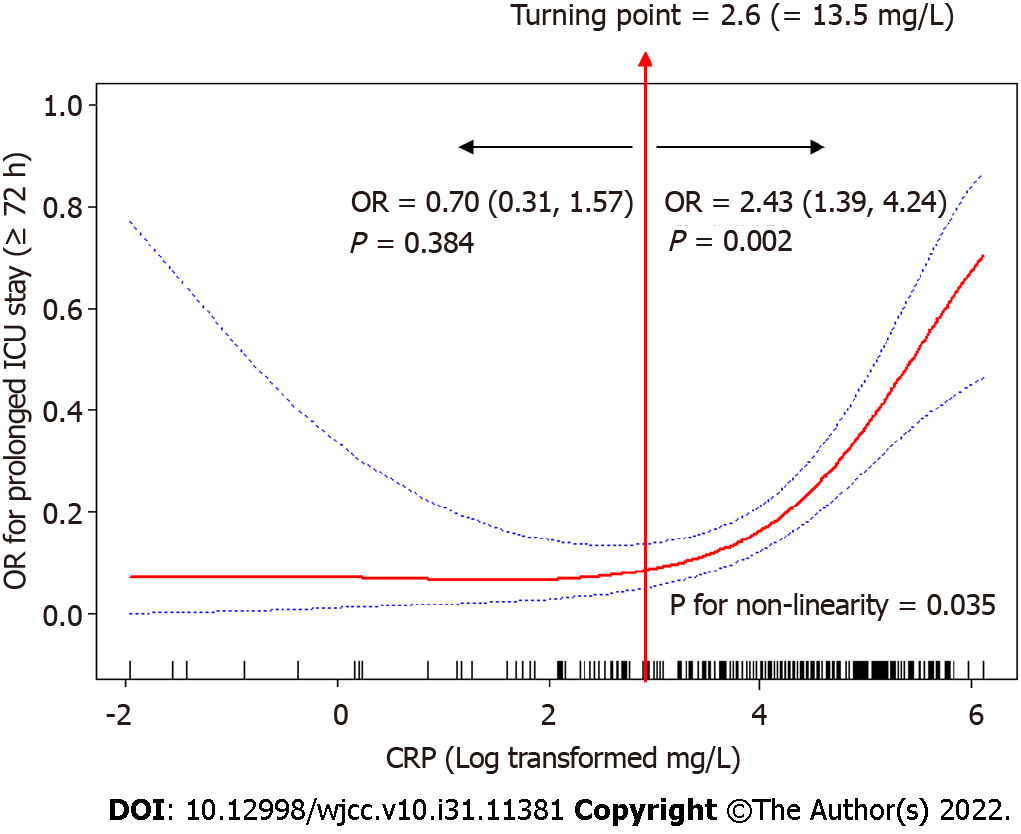
Figure 2 Non-linear relationship between C-reactive protein levels and log odds ratio of prolonged intensive care unit length of stay after controlling for potential confounding variables (age, gender, laparoscopic surgery, emergency surgery, cancer site, intensive care unit readmission, tracheotomy, continuous renal replacement therapy, and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II.
) (multivariate odds ratio, 95% confidence intervals and P values are shown). CRP: C-reactive protein; OR: Odds ratio; ICU: Intensive care unit.
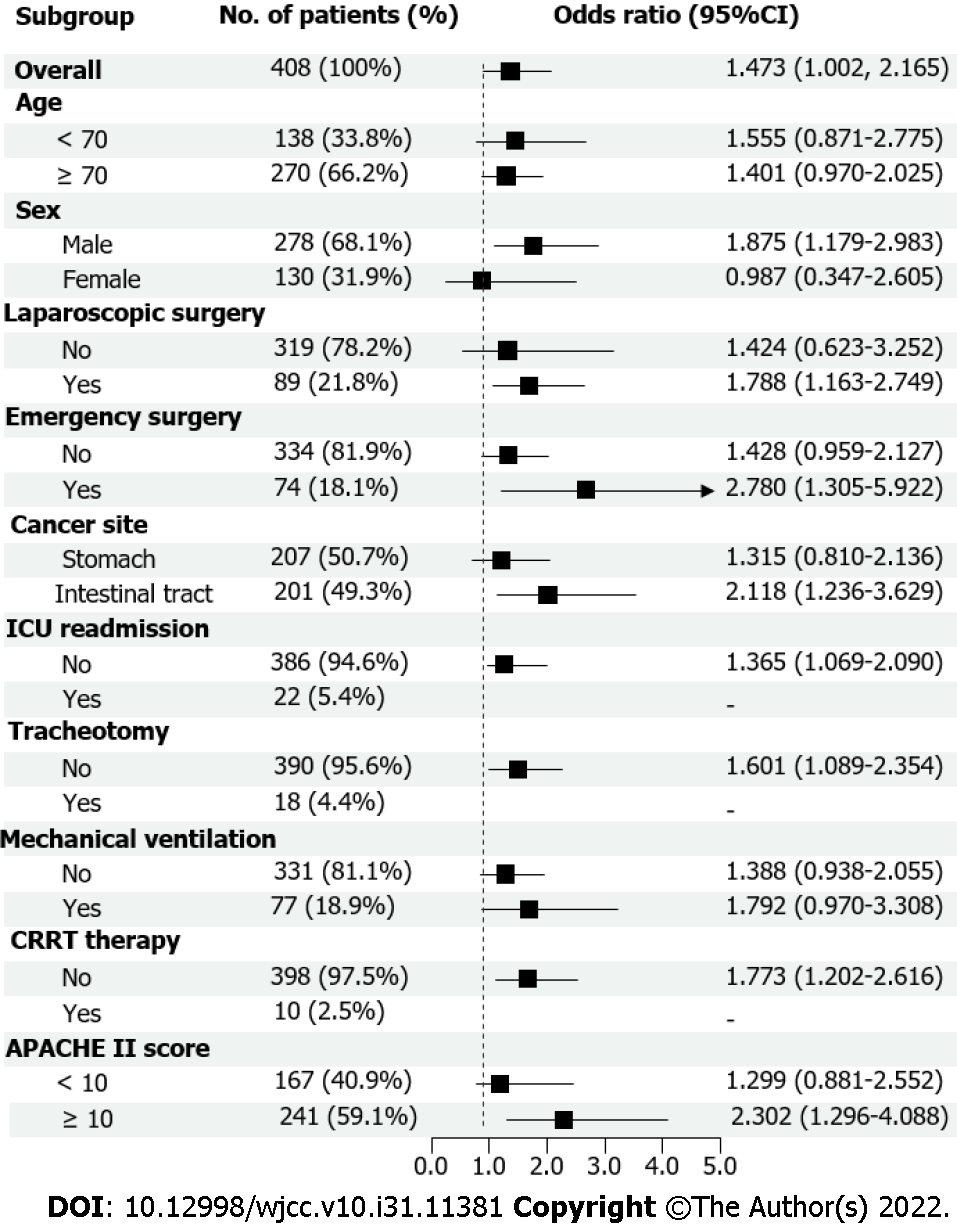
Figure 3 Subgroup analysis of effect of C-reactive protein levels on predicting prolonged intensive care unit length of stay after gastrointestinal cancer surgery.
CRRT: Continuous renal replacement therapy; APACHE: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation.
- Citation: Yan YM, Gao J, Jin PL, Lu JJ, Yu ZH, Hu Y. C-reactive protein as a non-linear predictor of prolonged length of intensive care unit stay after gastrointestinal cancer surgery. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(31): 11381-11390
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i31/11381.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11381