Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2022; 10(31): 11226-11239
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11226
Published online Nov 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11226
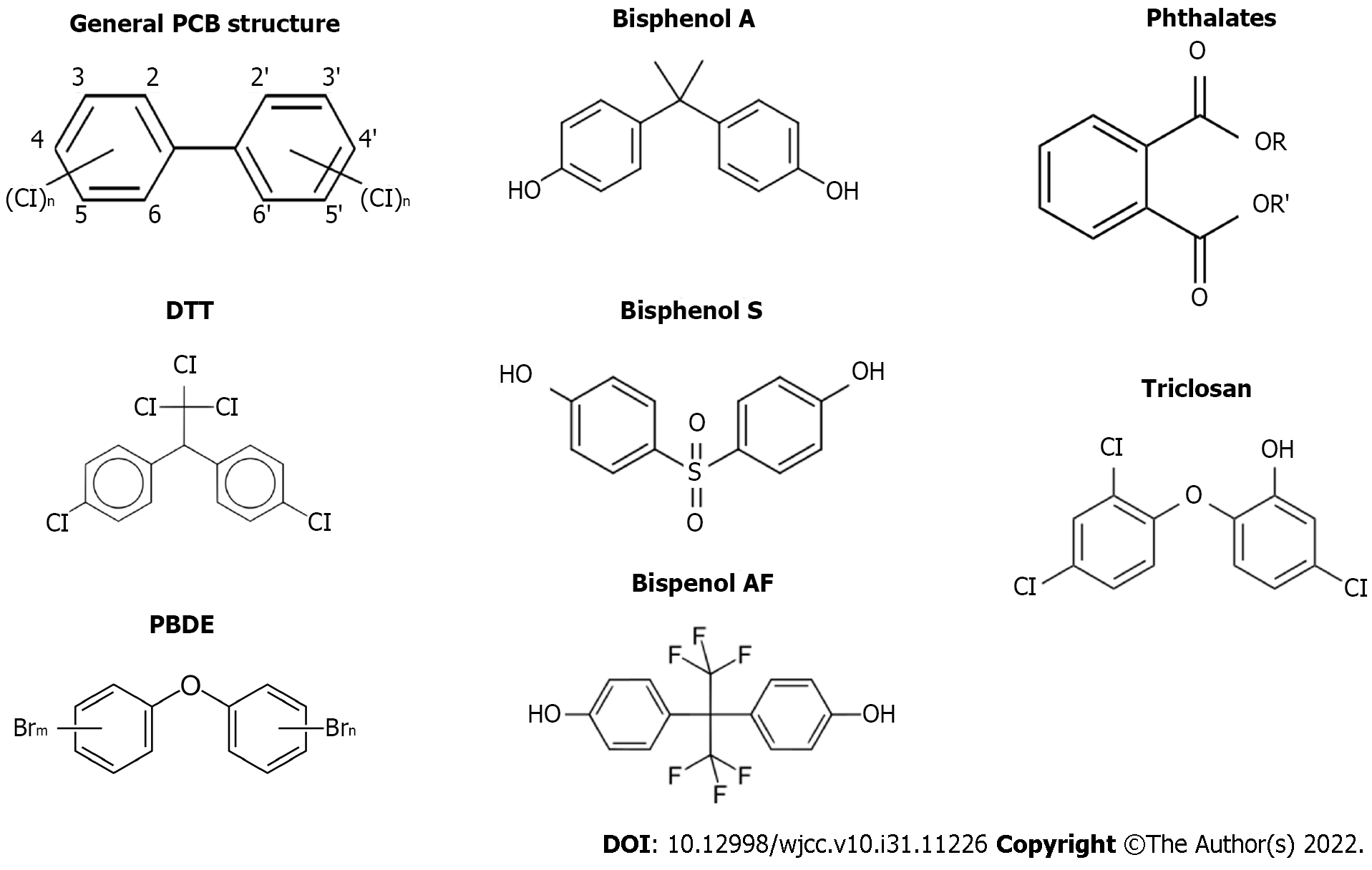
Figure 1 General chemical structure of endocrine disruptors.
PCB: Polychlorinated bisphenol; PBDE: Polybrominated diphenyl ether.
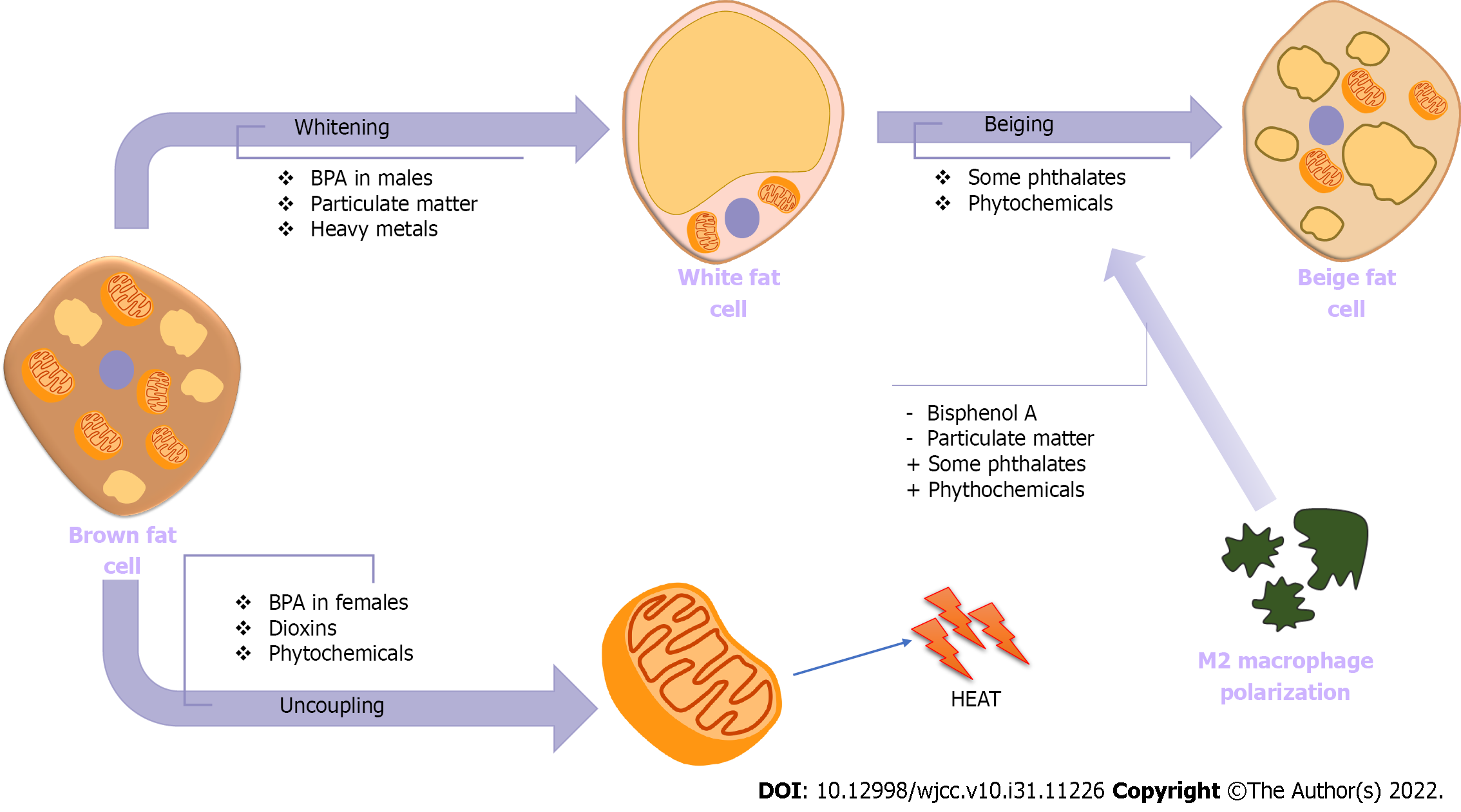
Figure 2 Potential effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on brown and beige adipogenesis.
BPA: Bisphenol A.
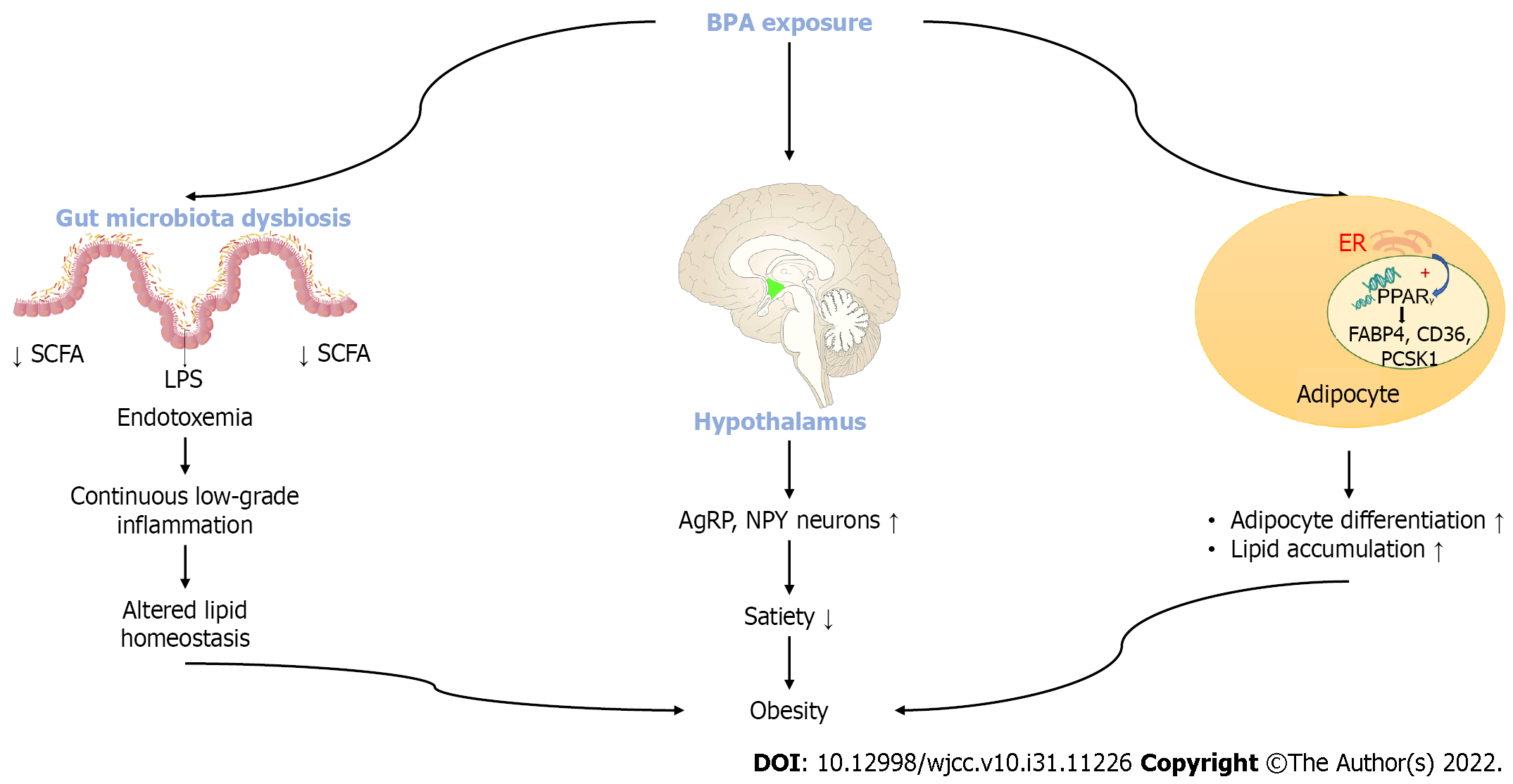
Figure 3 Changes in the hypothalamus, adipocyte and gut microbiota caused by bisphenol A exposure in favor of obesity.
BPA: Bisphenol A; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; SCFA: Small chain fatty acid; NPY: Neuropeptide Y; AgRP: Agouti related peptide; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; FABP4: Fatty acid binding protein 4; CD36: Cluster of differentiation 36.
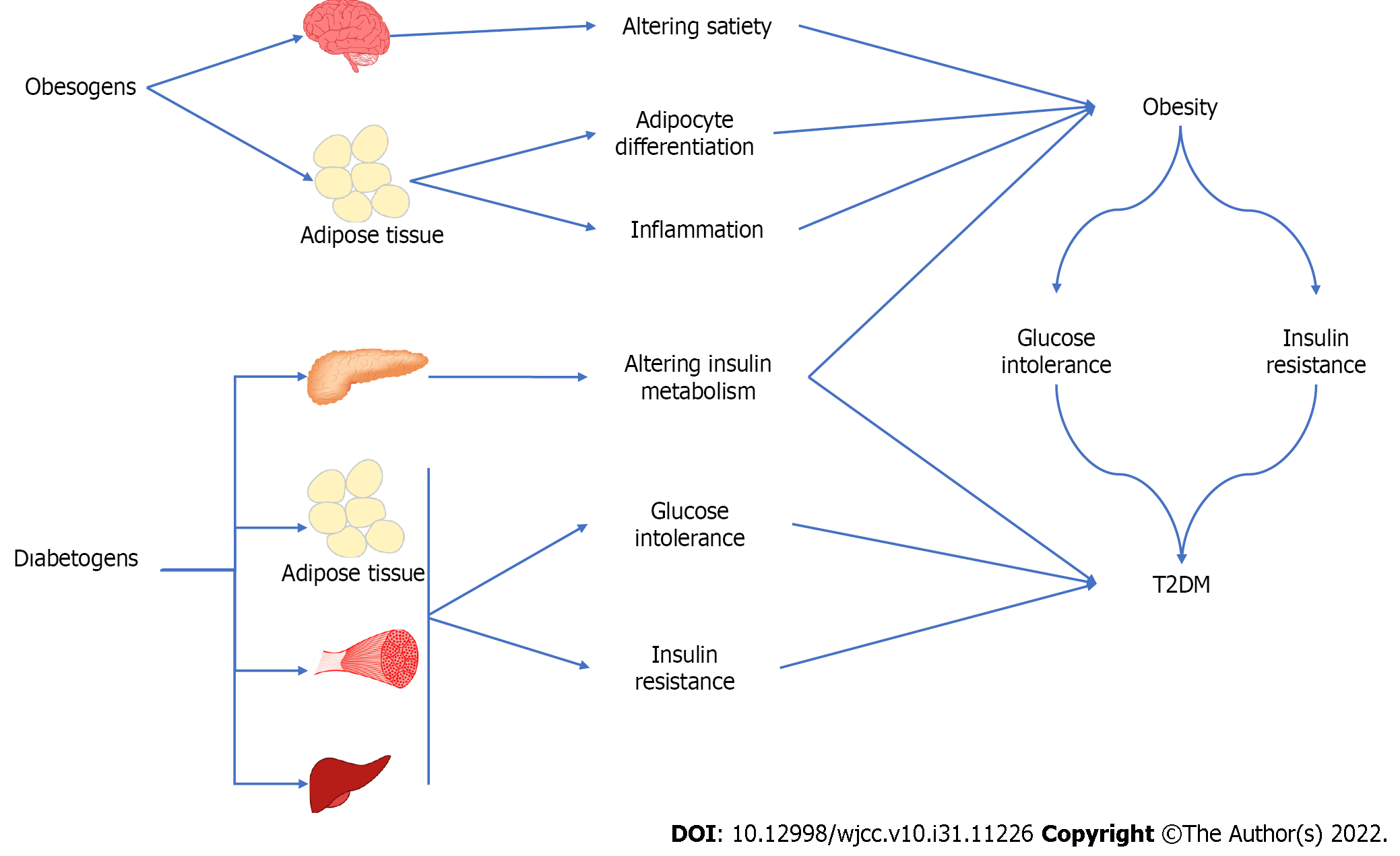
Figure 4 Summary of the effects of obesogen and diabetogen on tissues and the relationship of these effects with obesity and diabetes.
T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Citation: Kurşunoğlu NE, Sarer Yurekli BP. Endocrine disruptor chemicals as obesogen and diabetogen: Clinical and mechanistic evidence. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(31): 11226-11239
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i31/11226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11226