Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 21, 2022; 10(3): 1116-1121
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.1116
Published online Jan 21, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.1116
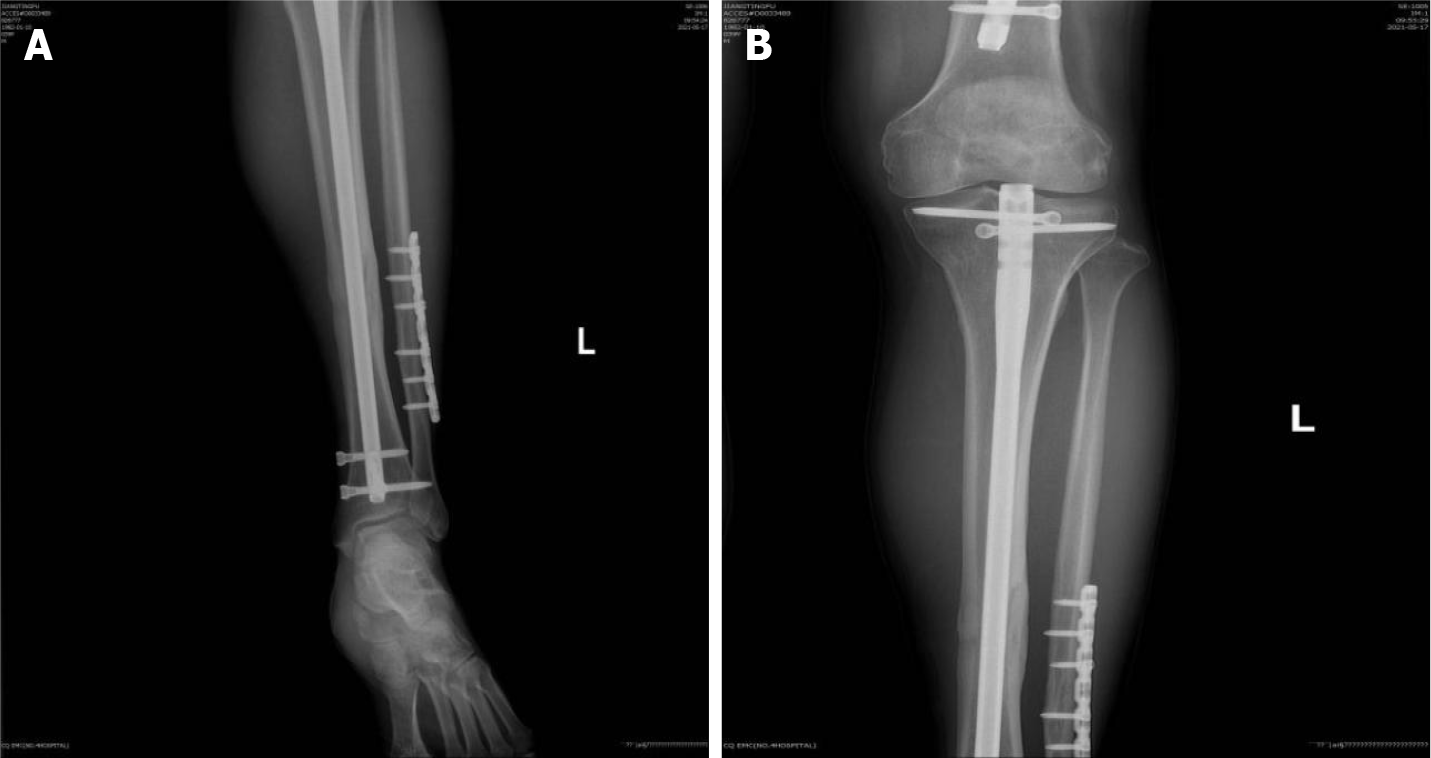
Figure 1 X-ray images of the patient’s left proximal tibia.
A: Antero-posterior X-ray view of the left proximal tibia showing complete bony union; B: Antero-posterior X-ray view of the left distal tibia showing complete bony union.
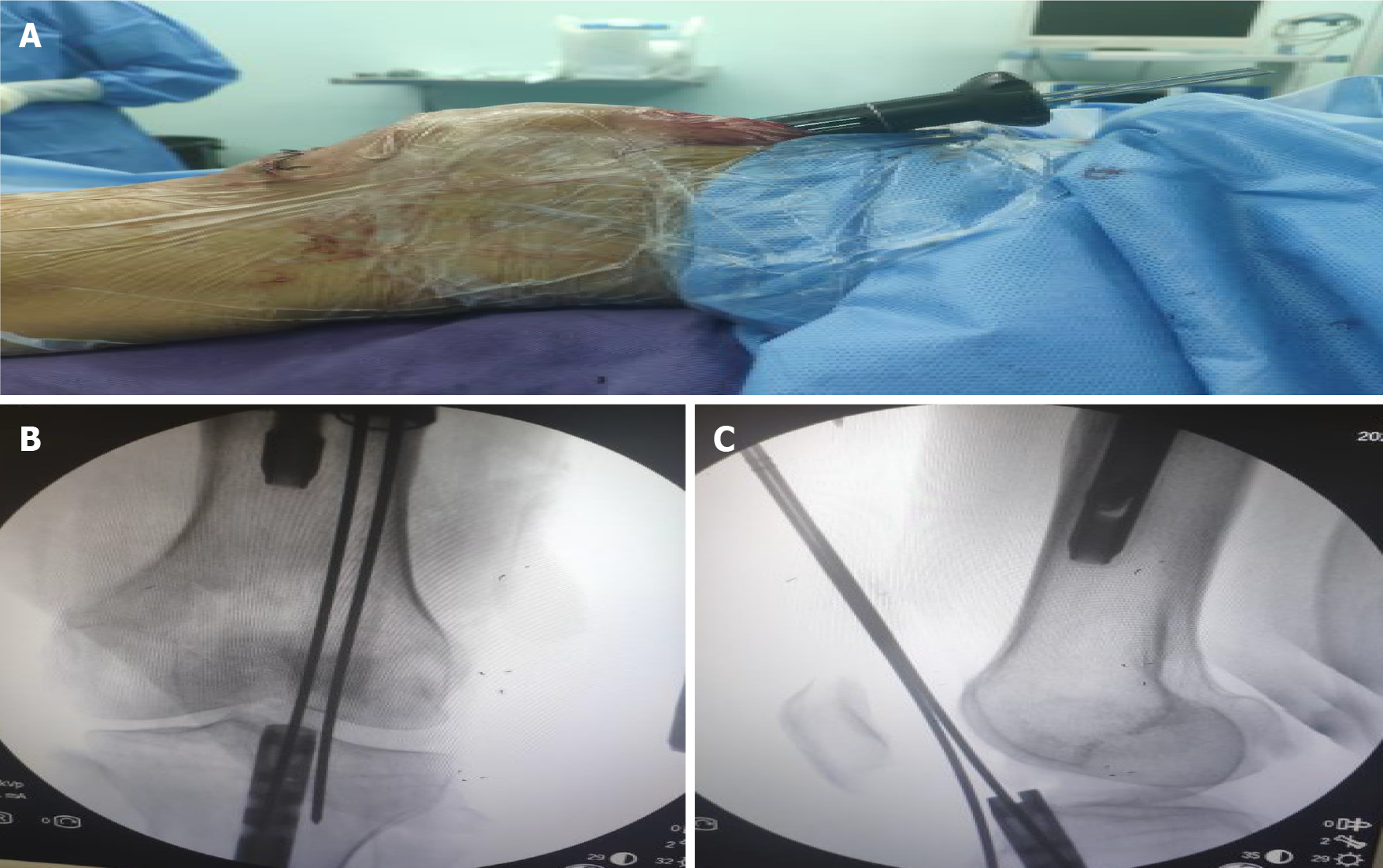
Figure 2 Insertion of the guide needle through the nail.
A: The guide needle was inserted through the nail via the suprapatellar approach and was assisted by a multi-holed guide pin sleeve; B: Antero-posterior X-ray view showing insertion of the guide needle into the cavity of the intramedullary nail; C: Lateral X-ray view showing insertion of the guide needle into the cavity of the intramedullary nail.
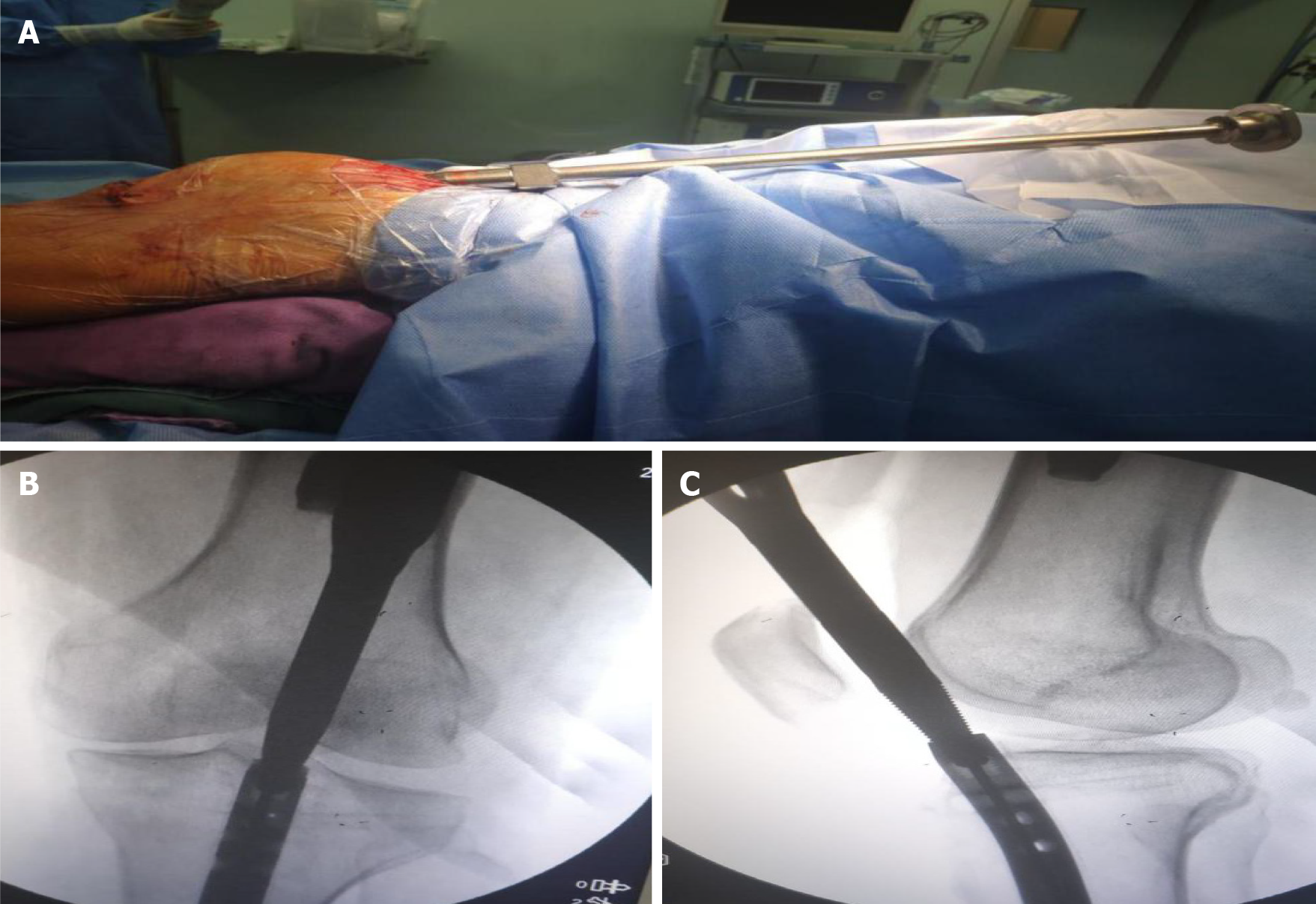
Figure 3 A jig was screwed into the tail of the nail.
A: A hollow jig was rotated along the guide needle and screwed into the tail of the nail; B: Antero-posterior X-ray view showing that the clamp was screwed into the end of the intramedullary nail and tightened; C: Lateral X-ray view showing that the clamp was screwed into the end of the intramedullary nail and tightened.
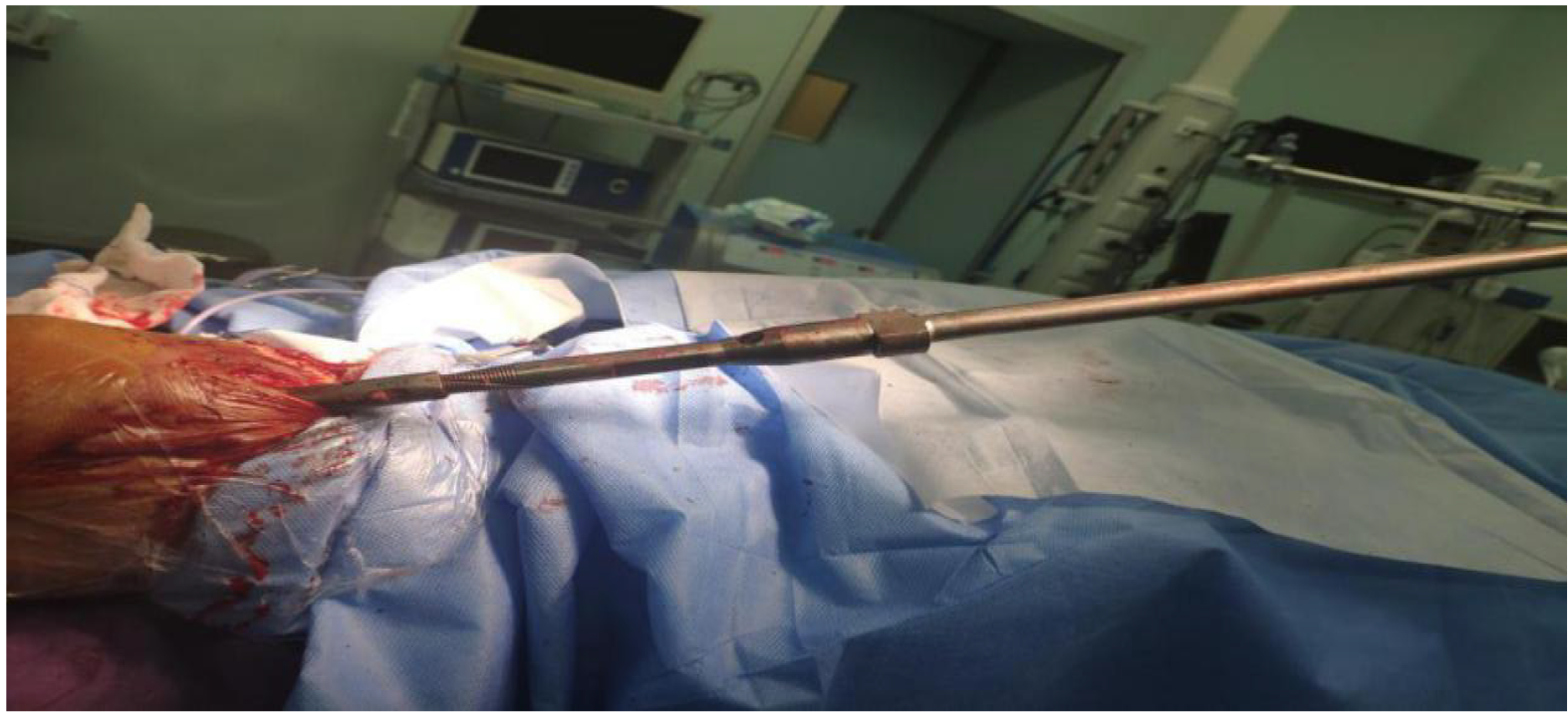
Figure 4 The intramedullary nail was struck out of the tibia using a mallet through the suprapatellar approach.
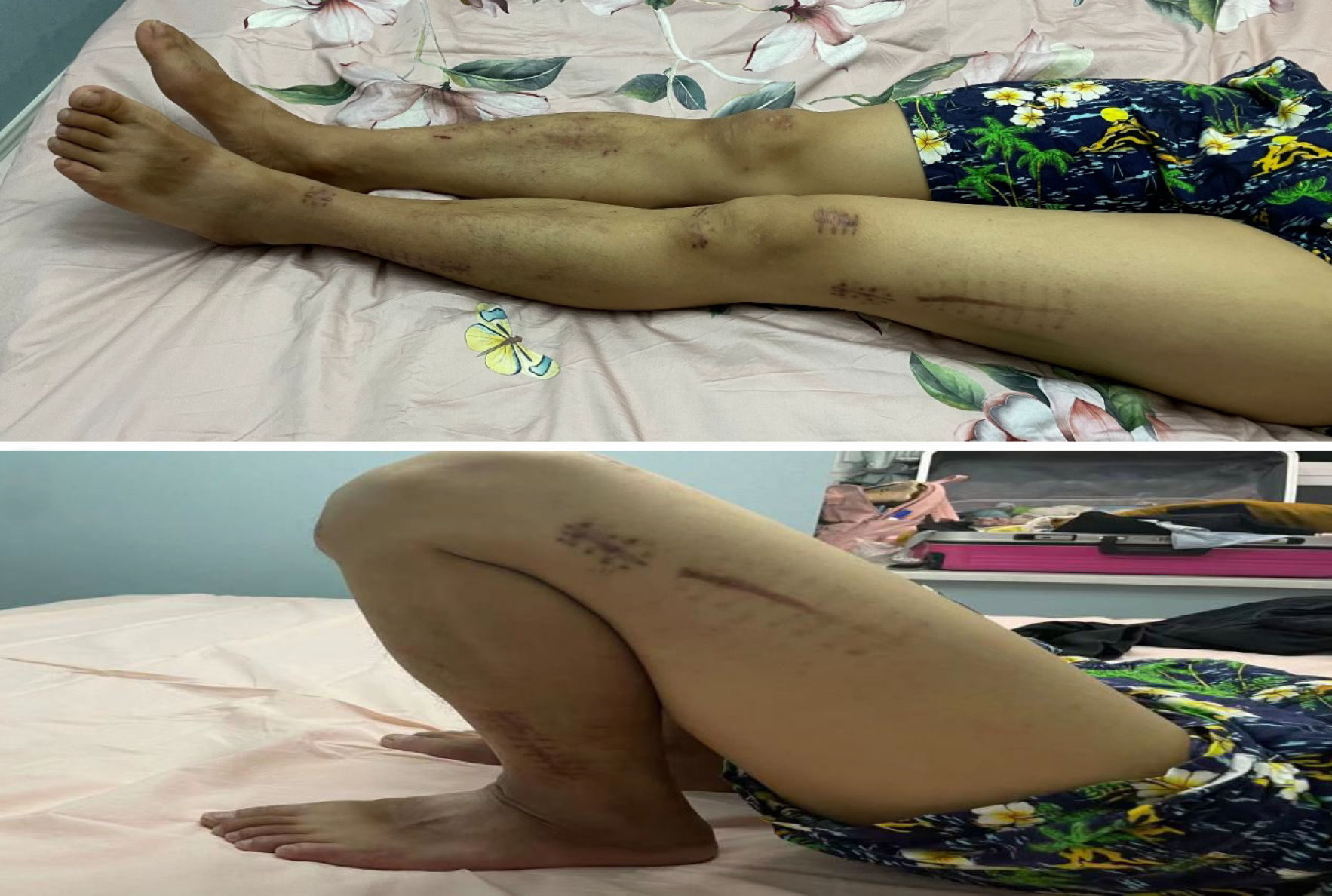
Figure 5 Knee range of motion at the 4-mo follow-up.
- Citation: He M, Li J. New method to remove tibial intramedullary nail through original suprapatellar incision: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(3): 1116-1121
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i3/1116.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i3.1116