Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 6, 2022; 10(28): 10220-10226
Published online Oct 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.10220
Published online Oct 6, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.10220
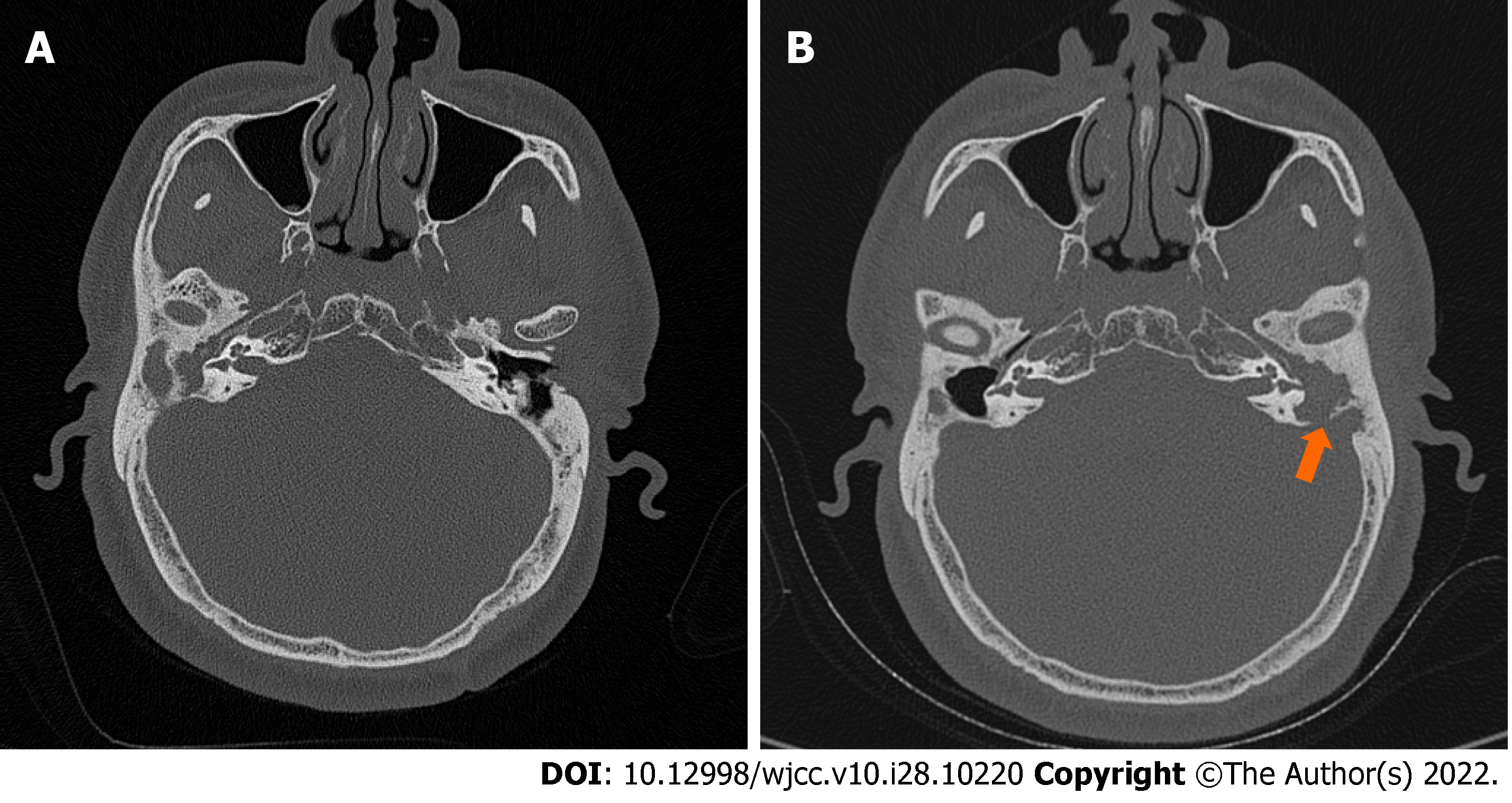
Figure 1 Axial computed tomography scans showed cholesteatoma.
A: The presence of soft tissue density in the right middle ear in 2018; B: A reduced soft tissue shadow in the mastoid cavity of the right ear and an increased soft tissue shadow in the mastoid cavity of the left ear with a bony defect of the temporal bone (arrow) in 2021.
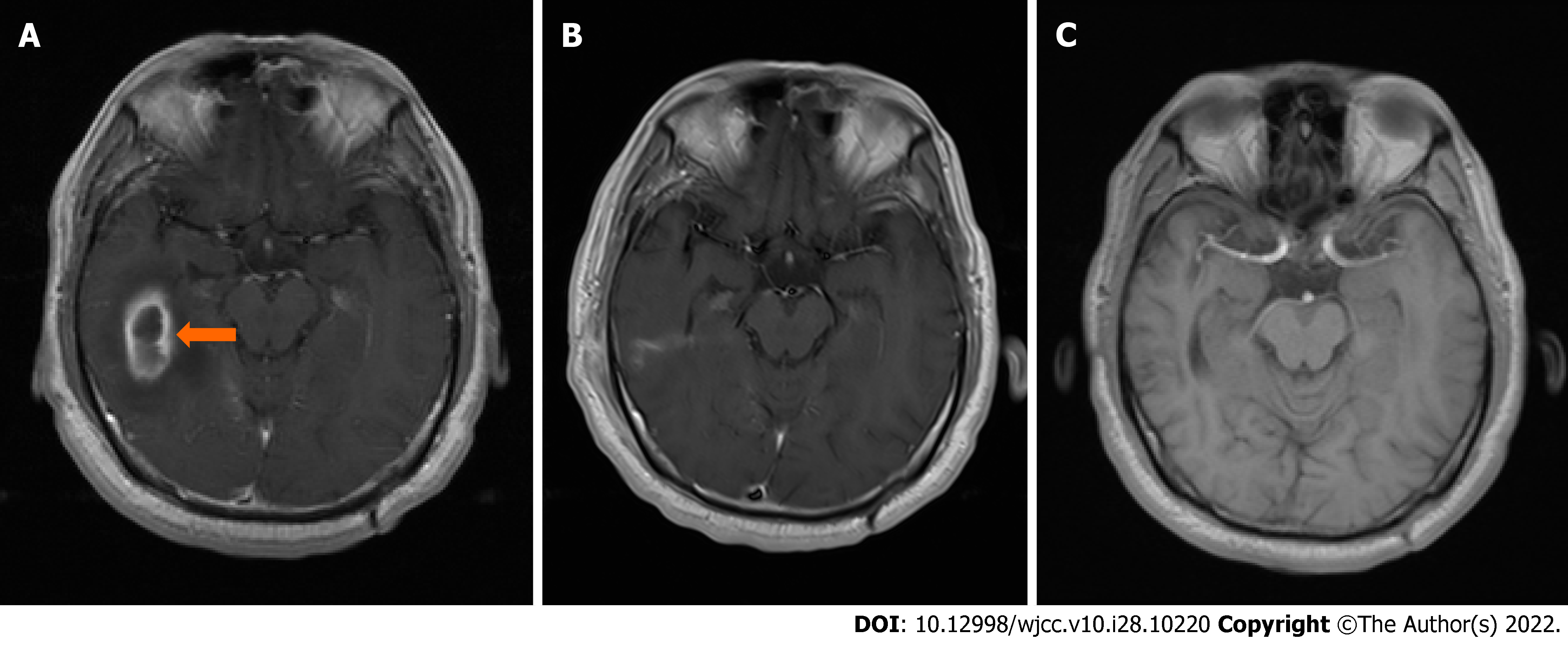
Figure 2 Axial magnetic resonance imaging shows brain abscess.
A: A low-intensity area encapsulated by the tan area, i.e., a high-intensity area, in the right temporal region (arrow) on April 30, 2018; B: No brain abscess was showed on June 7, 2018; C: No brain abscess was found on October 24, 2021.
- Citation: Zhang L, Niu X, Zhang K, He T, Sun Y. Potential otogenic complications caused by cholesteatoma of the contralateral ear in patients with otogenic abscess secondary to middle ear cholesteatoma of one ear: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(28): 10220-10226
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i28/10220.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i28.10220