Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2022; 10(21): 7539-7544
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7539
Published online Jul 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7539
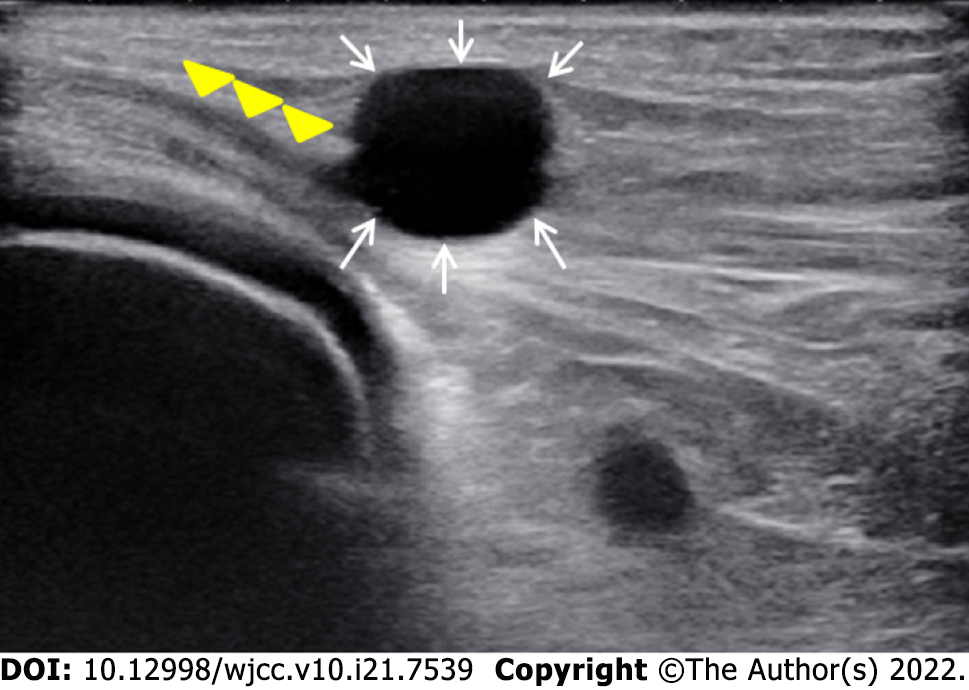
Figure 1 Ultrasound examination showed the compressed common peroneal nerve (yellow arrowheads) and a hypoechoic cystic lesion (white arrows).
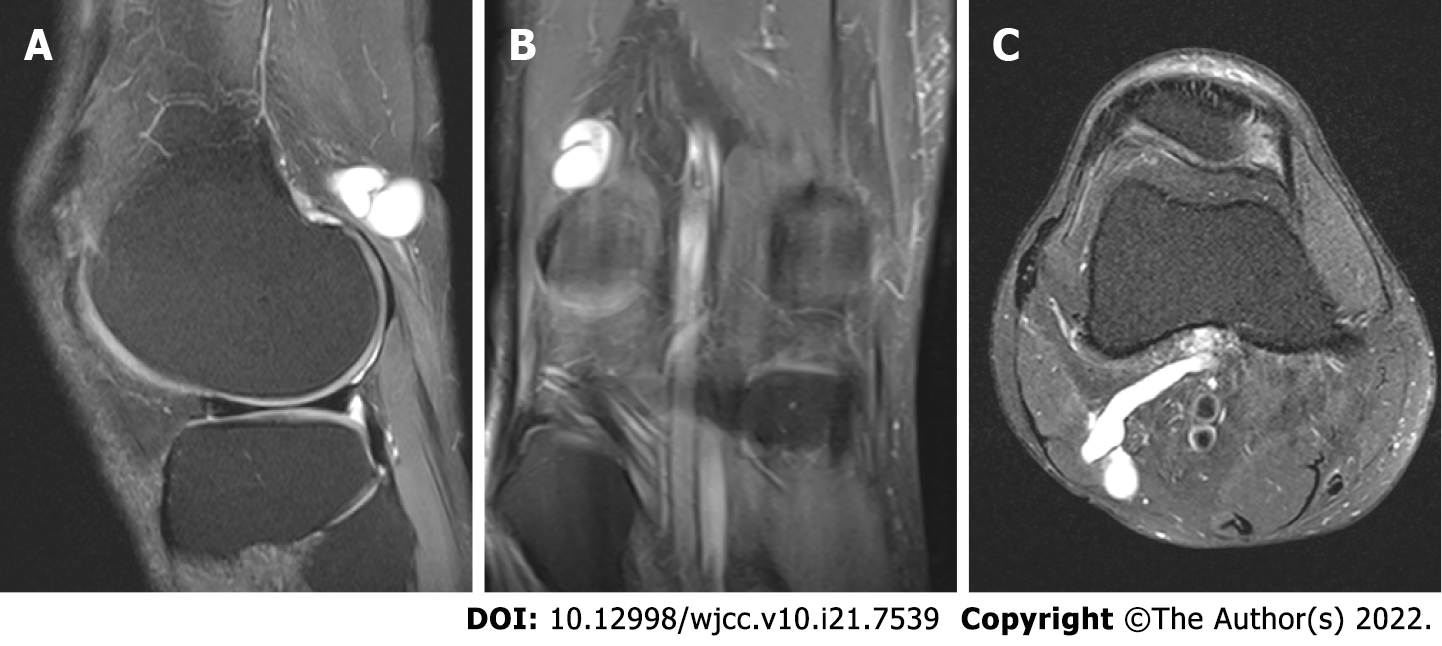
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging views (sagittal, coronal, and axial) of the right knee revealing a hyperintense cystic mass with narrow and long stalk stretching out posterolaterally from middle popliteal fossa in supracondylar area.
A: Fat suppressed proton density sagittal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image; B: Fat suppressed proton density coronal MRI image; C: T2 pronton density axial MRI image.
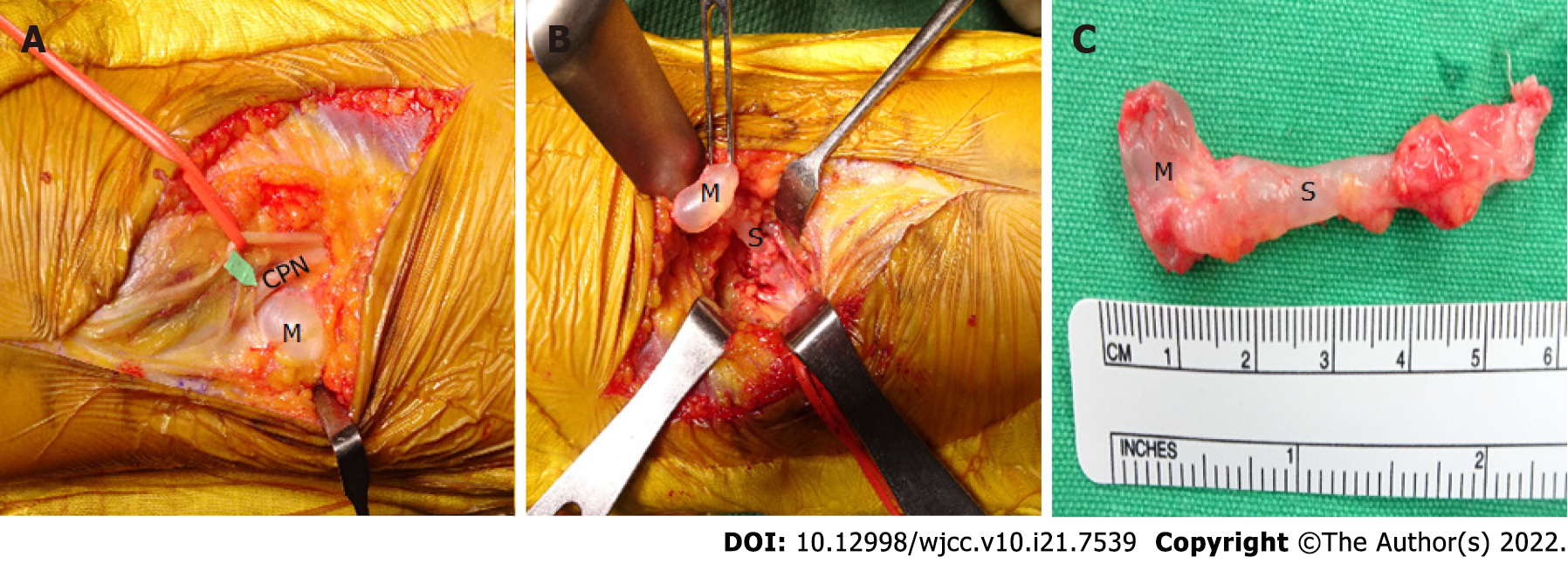
Figure 3 The common peroneal nerve compressed by an adjacent cystic mass with stalk identified following incision of skin and fascia of right popliteal fossa.
A: After incision in the surgery; B: After dissection around the extraneual ganglion cyst; C: The ganglion cyst size. CPN: Common peroneal nerve; M: Mass; S: Stalk.
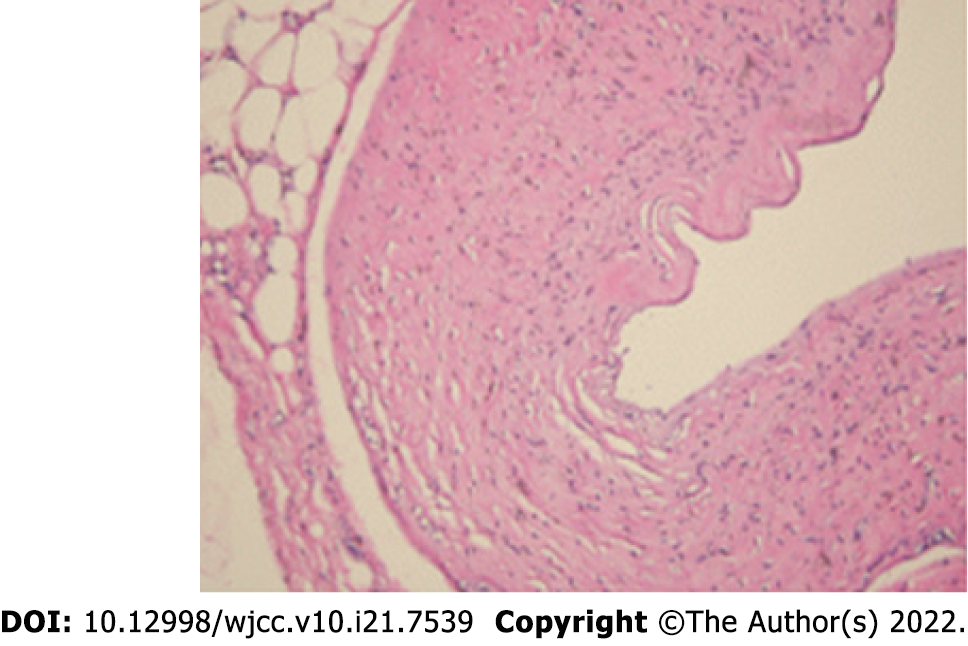
Figure 4 Histology photomicrograph.
The resected cyst was diagnosed as a ganglion cyst.
- Citation: Won KH, Kang EY. Differential diagnosis and treatment of foot drop caused by an extraneural ganglion cyst above the knee: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(21): 7539-7544
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i21/7539.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7539