Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 16, 2022; 10(20): 6811-6824
Published online Jul 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i20.6811
Published online Jul 16, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i20.6811
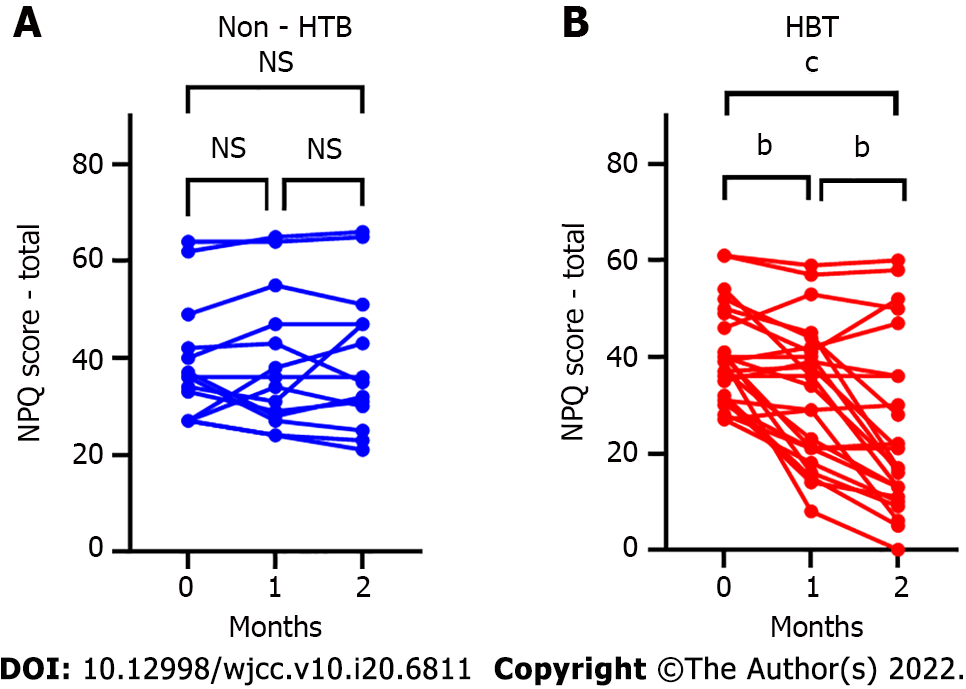
Figure 1 Niigata persistent postural-perceptual dizziness questionnaire score changes after hangebyakujutsutemmato treatment for persistent postural-perceptual dizziness.
A: No statistically significant changes in Niigata persistent postural-perceptual dizziness questionnaire (NPQ) scores were seen in the non-hangebyakujutsutemmato (HBT) group (baseline vs 1 mo, P = 0.98; 1 mo vs 2 mo, P = 0.94; baseline vs 2 mo, P = 0.92); B: In the HBT group, NPQ scores showed a statistically significant decrease (baseline vs 1 mo, P = 0.002; 1 mo vs 2 mo, P = 0.003; baseline vs 2 mo, P < 0.001). bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. NS: Not significant; NPQ: Niigata PPPD questionnaire; HBT: Hangebyakujutsutemmato; PPPD: Persistent postural-perceptual dizziness.
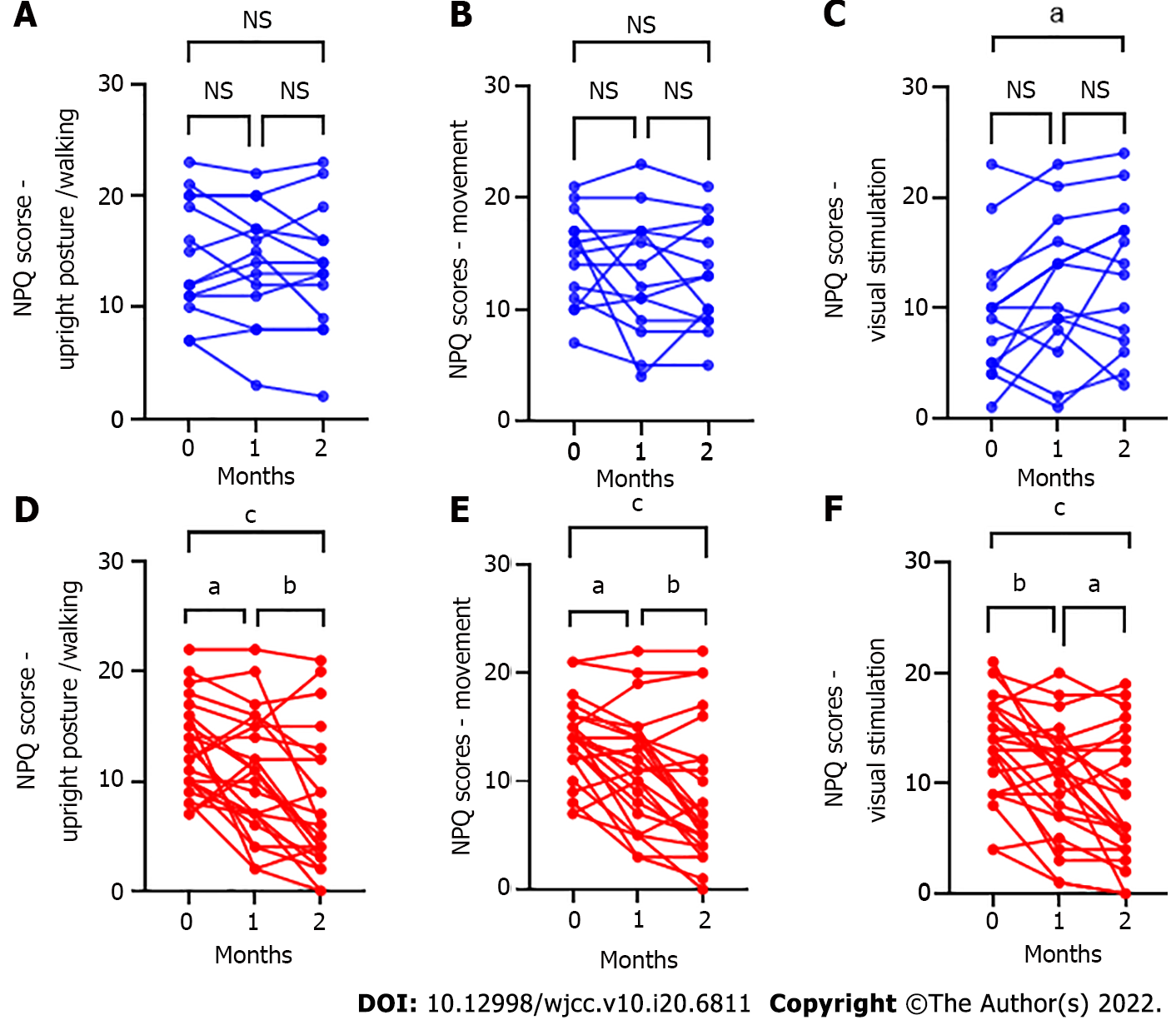
Figure 2 Niigata persistent postural-perceptual dizziness questionnaire subcategory score changes after hangebyakujutsutemmato treatment for persistent postural-perceptual dizziness.
A-C: There was no significant difference in the Niigata persistent postural-perceptual dizziness questionnaire (NPQ) subcategory scores in the non-hangebyakujutsutemmato (HBT) group except for the NPQ visual subcategory; A: Upright posture/walking: Baseline vs 1 mo, P = 0.67; 1 mo vs 2 mo, P = 0.73; baseline vs 2 mo, P = 0.41; B: Movement: Baseline vs 1 mo, P = 0.50; 1 mo vs 2 mo, P > 0.99; baseline vs 2 mo, P = 0.38; C: Visual stimulation: Baseline vs 1 mo, P = 0.11; 1 mo vs 2 mo, P = 0.53; baseline vs 2 mo, P = 0.02); D-F: In the HBT group, NPQ subcategory scores showed statistically significant differences; D: Upright posture/walking: Baseline vs 1 mo, P = 0.04; 1 mo vs 2 mo, P = 0.005; baseline vs 2 mo, P < 0.001; E: Movement: Baseline vs 1 mo, P = 0.01; 1 mo vs 2 mo, P = 0.006; baseline vs 2 mo, P < 0.001; F: Visual stimulation, baseline vs 1 mo, P = 0.002; 1 mo vs 2 mo, P = 0.03; baseline vs 2 mo, P < 0.001. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. NS: Not significant; NPQ: Niigata PPPD questionnaire; HBT: Hangebyakujutsutemmato; PPPD: Persistent postural-perceptual dizziness.
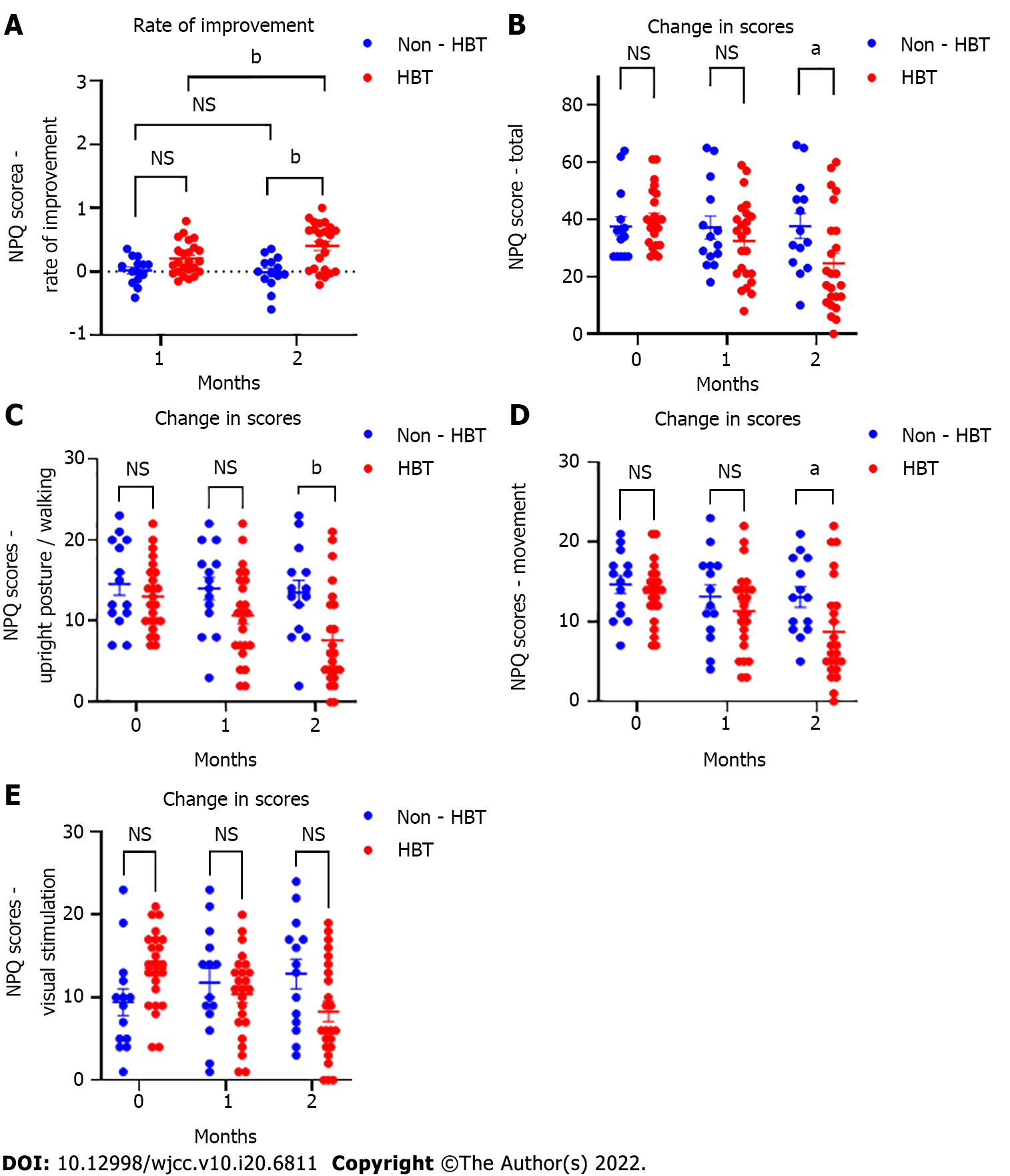
Figure 3 Comparison of rate of improvement and Niigata persistent postural-perceptual dizziness questionnaire scores between groups.
A: Comparisons between groups revealed significant differences in the rate of Niigata persistent postural-perceptual dizziness questionnaire (NPQ) improvement (1 mo, P = 0.16; 2 mo, P = 0.009); B-E: There were significant differences in NPQ total scores, upright posture/walking scores, and movement scores at 2 mo between groups; B: Total score: Baseline, P > 0.99; 1 mo, P = 0.89; 2 mo, P = 0.02; C: Upright posture/walking: Baseline, P > 0.99; 1 mo, P = 0.21; 2 mo, P = 0.005; D: Movement: Baseline, P > 0.99; 1 mo, P = 0.87; 2 mo, P = 0.03; E: Visual stimulation: Baseline, P = 0.11; 1 mo, P > 0.99; 2 mo, P = 0.06. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. Data represent mean and standard error (vertical bars). NPQ: Niigata PPPD questionnaire; HBT: Hangebyakujutsutemmato; PPPD: Persistent postural-perceptual dizziness; NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Miwa T, Kanemaru SI. Effects of Kampo medicine hangebyakujutsutemmato on persistent postural-perceptual dizziness: A retrospective pilot study. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(20): 6811-6824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i20/6811.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i20.6811