Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 14, 2022; 10(2): 725-732
Published online Jan 14, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.725
Published online Jan 14, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.725
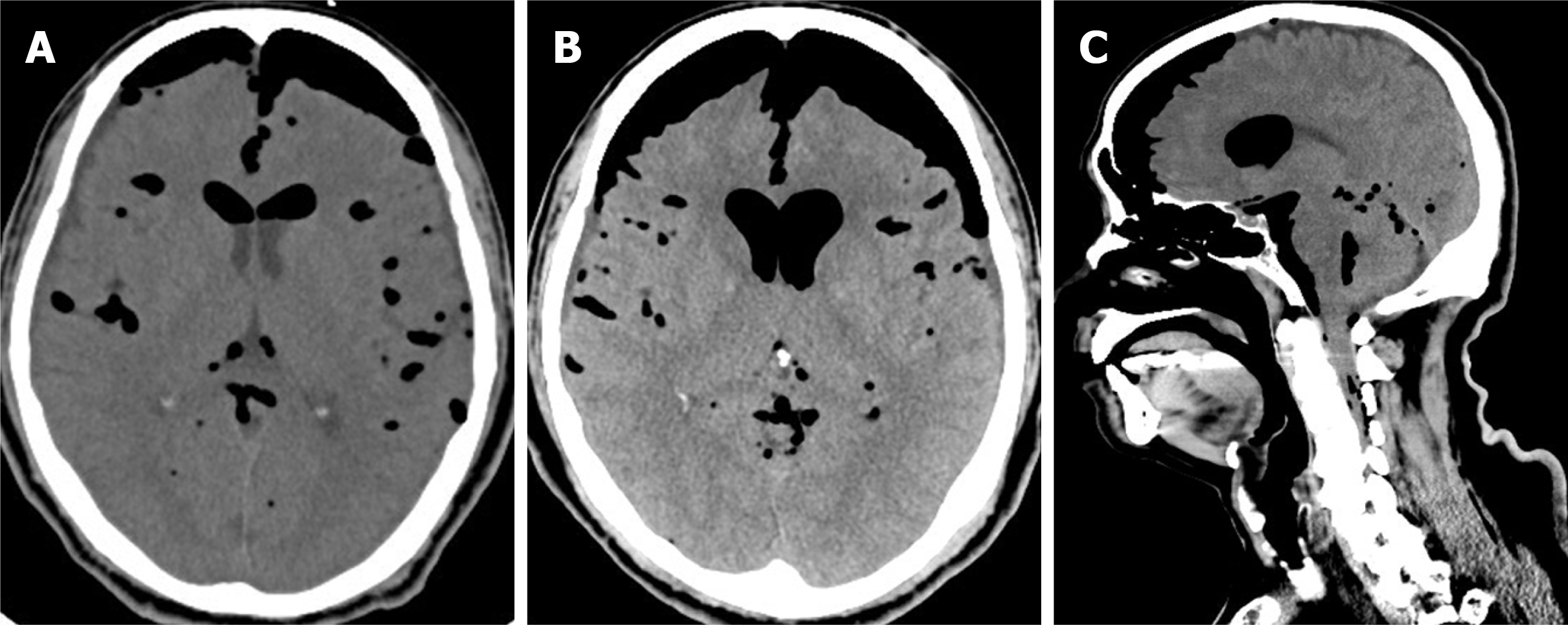
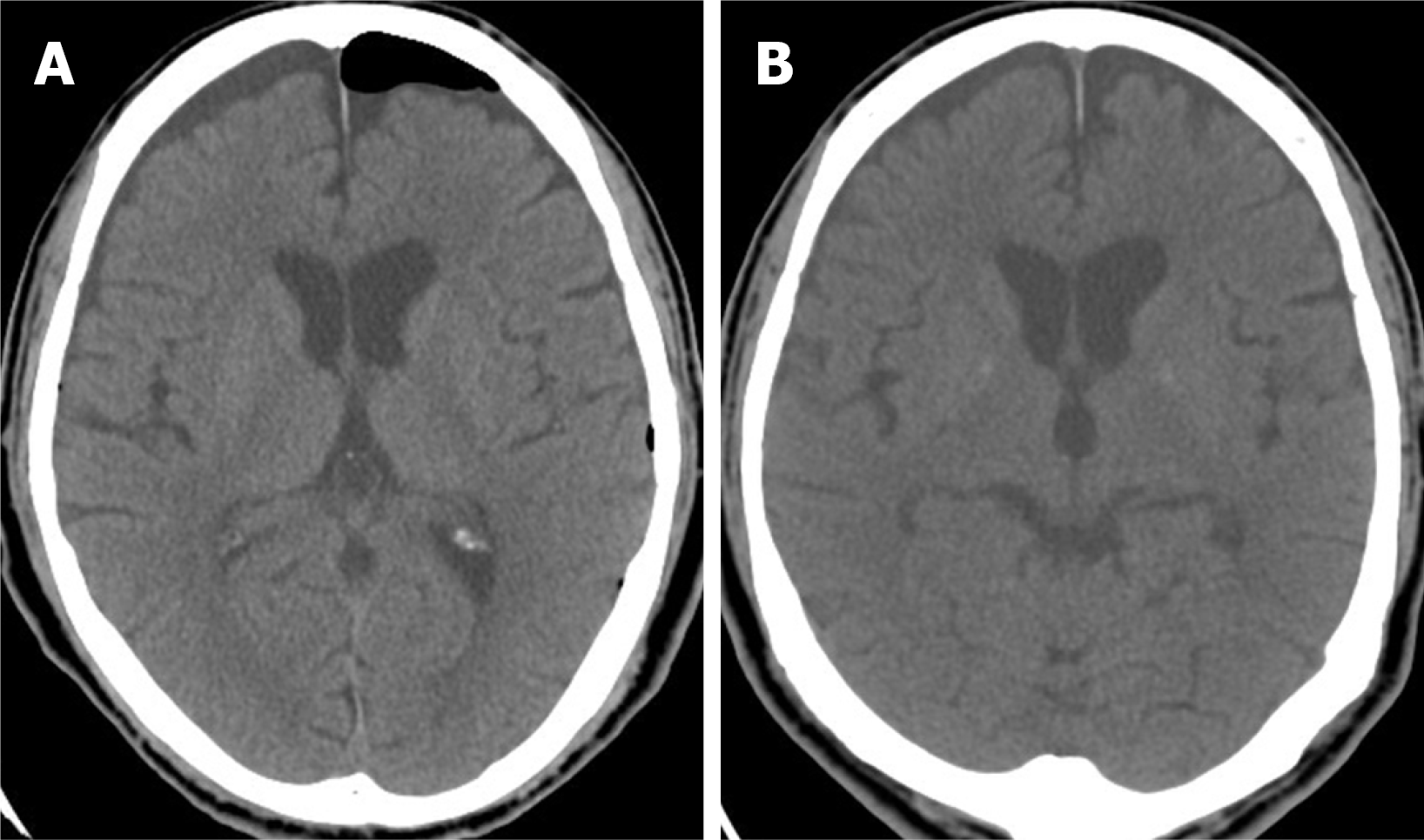
Figure 1 Computed tomography scans of the patient’s brain showing tension pneumocephalus.
A: Non-contrast views of preoperative brain computed tomography images; B-C: Images of axial (B) and sagittal view (C) show progressive tension pneumocephalus, pneumoventricle, and air leak in the spinal canal.
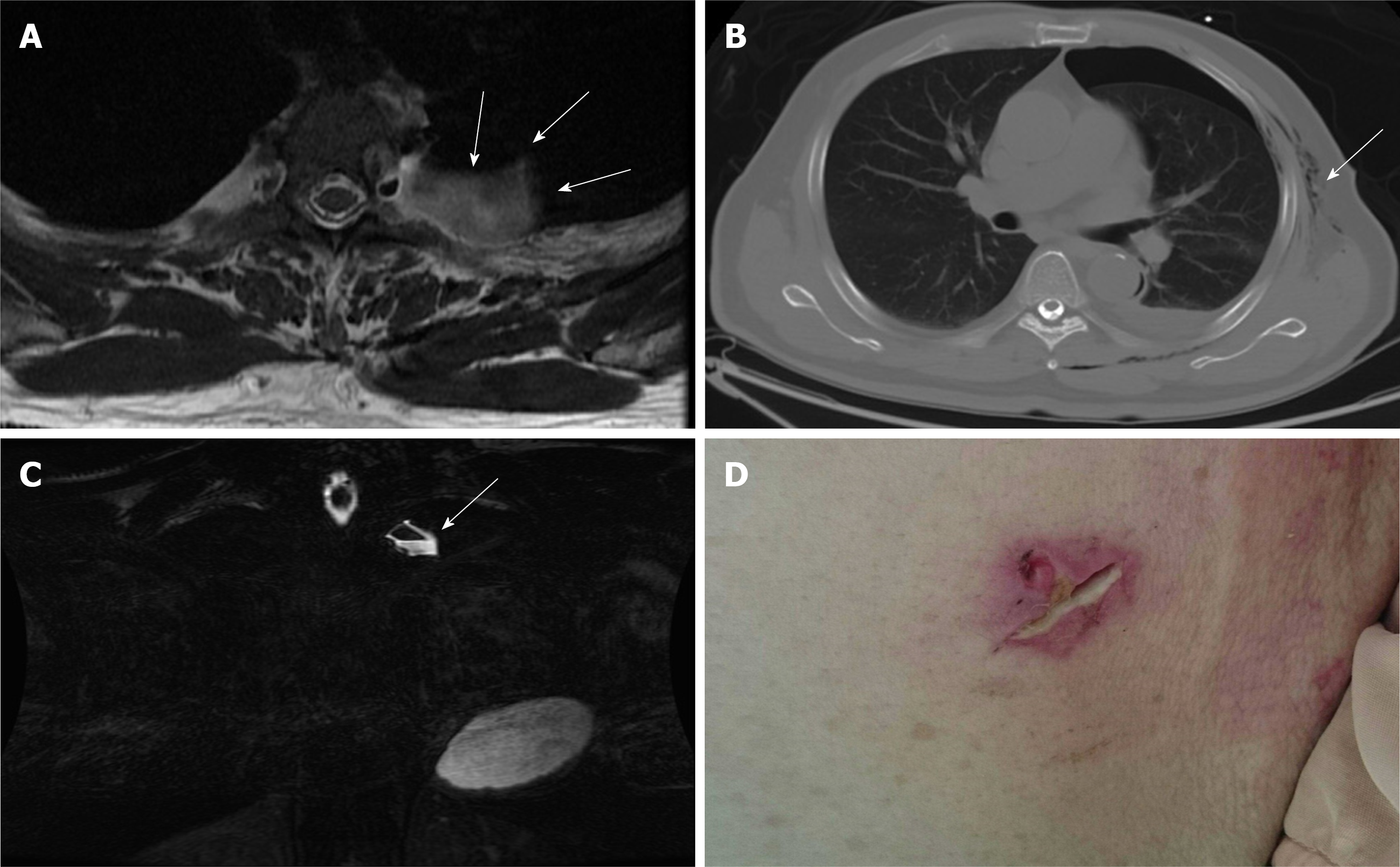
Figure 2 Pre-operative evaluations.
A-B: T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in axial view (A) and fast spin echo, fat-suppression coronal view (B) showing a cystic pouch laterally surrounding the spinal nerve root at left T3 level (arrow), which may be derived from the neural foramen of the L3 level. The air-fluid level was also demonstrated (arrow); C) Axial view of chest computed tomography showing pneumothorax and subcutaneous emphysema (arrow); D) Poorly healing previous thoracoscopic access wound.
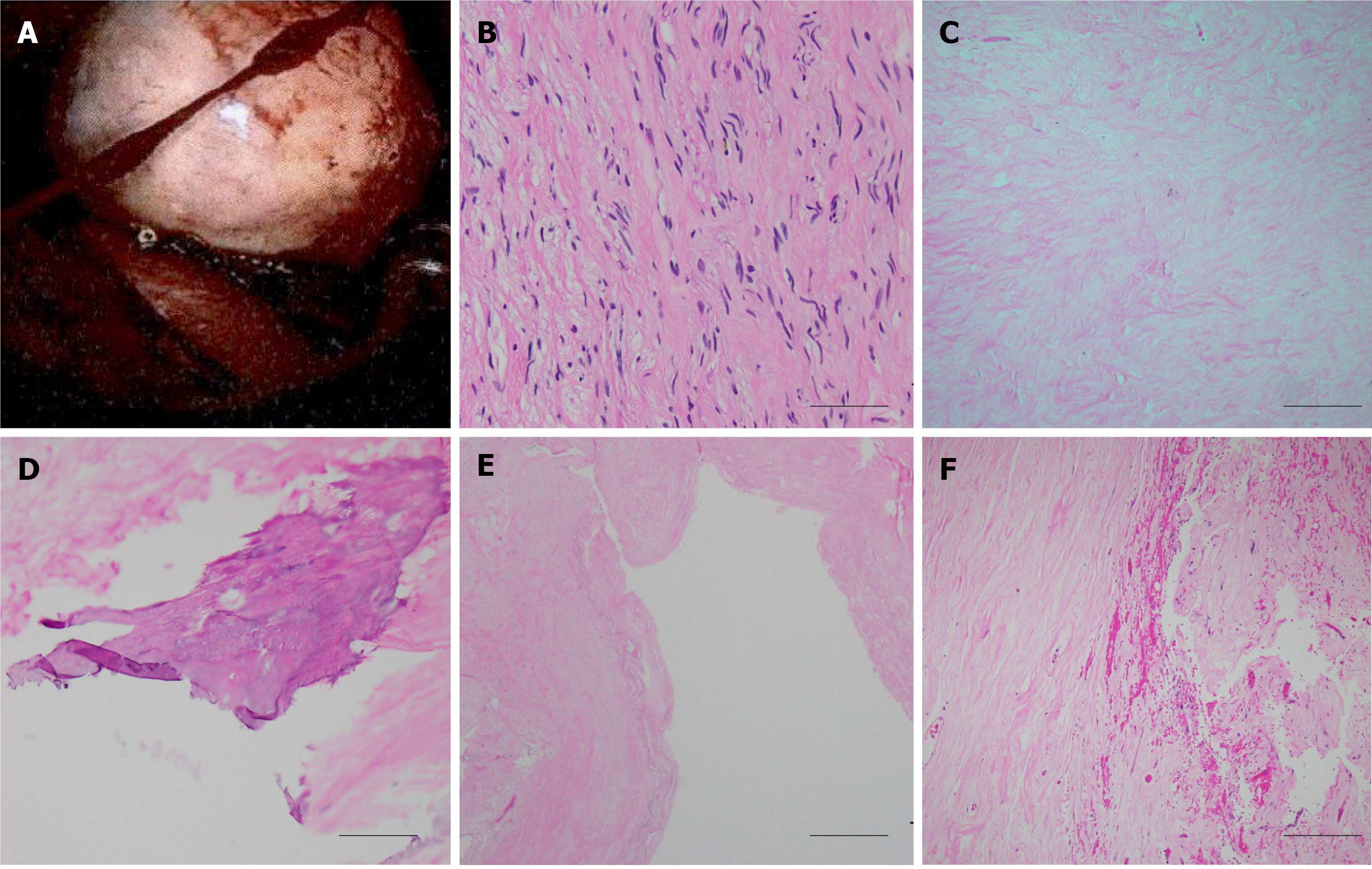
Figure 3 Histological examination of the spinal tumor.
A: Intraoperative image of the posterior mediastinal tumor demonstrated well-defined border, which was pathologically proved to be neurogenic tumor; B-F: A histological image of the neurofibroma showing bland spindle cells with wavy nuclei and pale eosinophilic cytoplasm (scale bar 50 μm) (B), secondary degeneration of hyalinization (scale bar 200 μm) (C), calcification (scale bar 100 μm) (D), cyst (scale bar 500 μm) (E), and hemorrhage (scale bar 200 μm) (F).
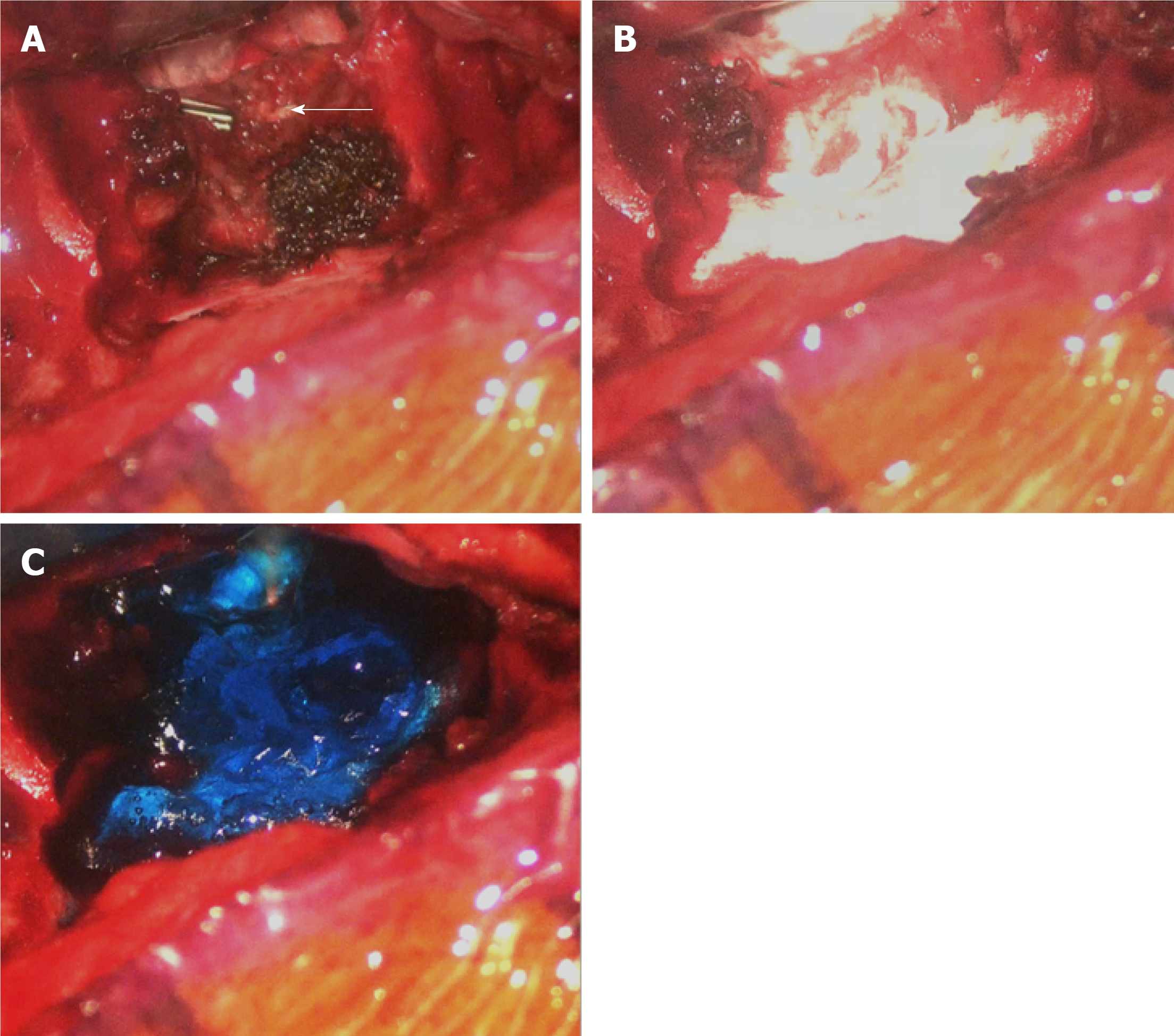
Figure 4 Intraoperative images of the surgical repair.
A: Cerebrospinal fluid leakage might derive from the previous endoscopic clipped tumor stump near the dural sac of the T3 level (arrow); B-C: Repairing of the leakage sites with tissue glue, gelfoam, and dural seal.
Figure 5 Post-operative computed tomography images demonstrate successful repair.
A-B: Axial view of brain computed tomography on the 5th (A) and 15th postoperative day (B) showing resolution of pneumocephalus and pneumoventricle though subdural effusion accumulation without brain parenchymal compression.
- Citation: Chang CY, Hung CC, Liu JM, Chiu CD. Tension pneumocephalus following endoscopic resection of a mediastinal thoracic spinal tumor: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(2): 725-732
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i2/725.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.725