Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 14, 2022; 10(2): 625-630
Published online Jan 14, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.625
Published online Jan 14, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.625
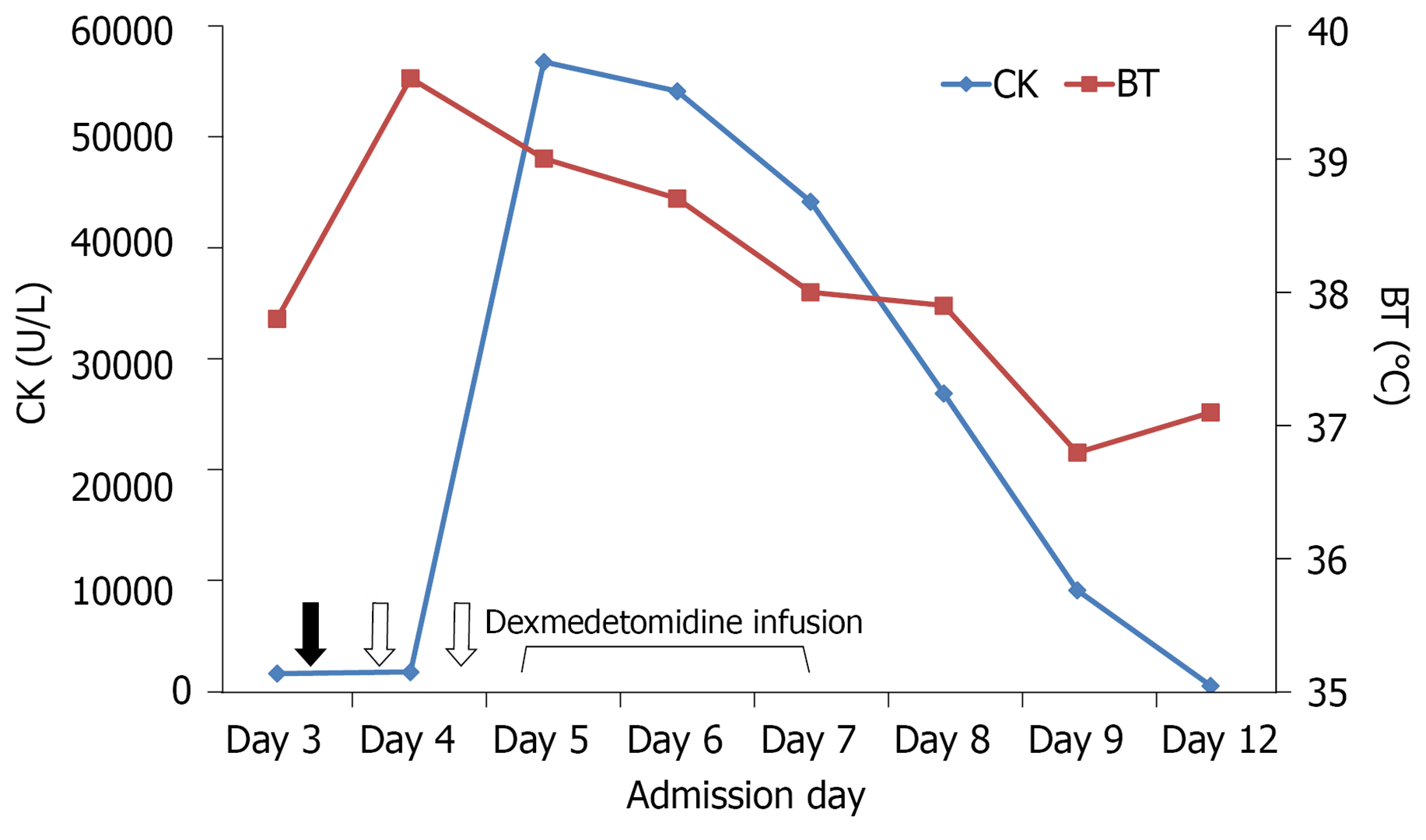
Figure 1 Time course of haloperidol administration (Black arrow: 15 mg; white arrow: 10 mg) and dexmedetomidine infusion in relation to changes in BT and serum CK levels.
BT: Body temperature; CK: Creatine kinase.
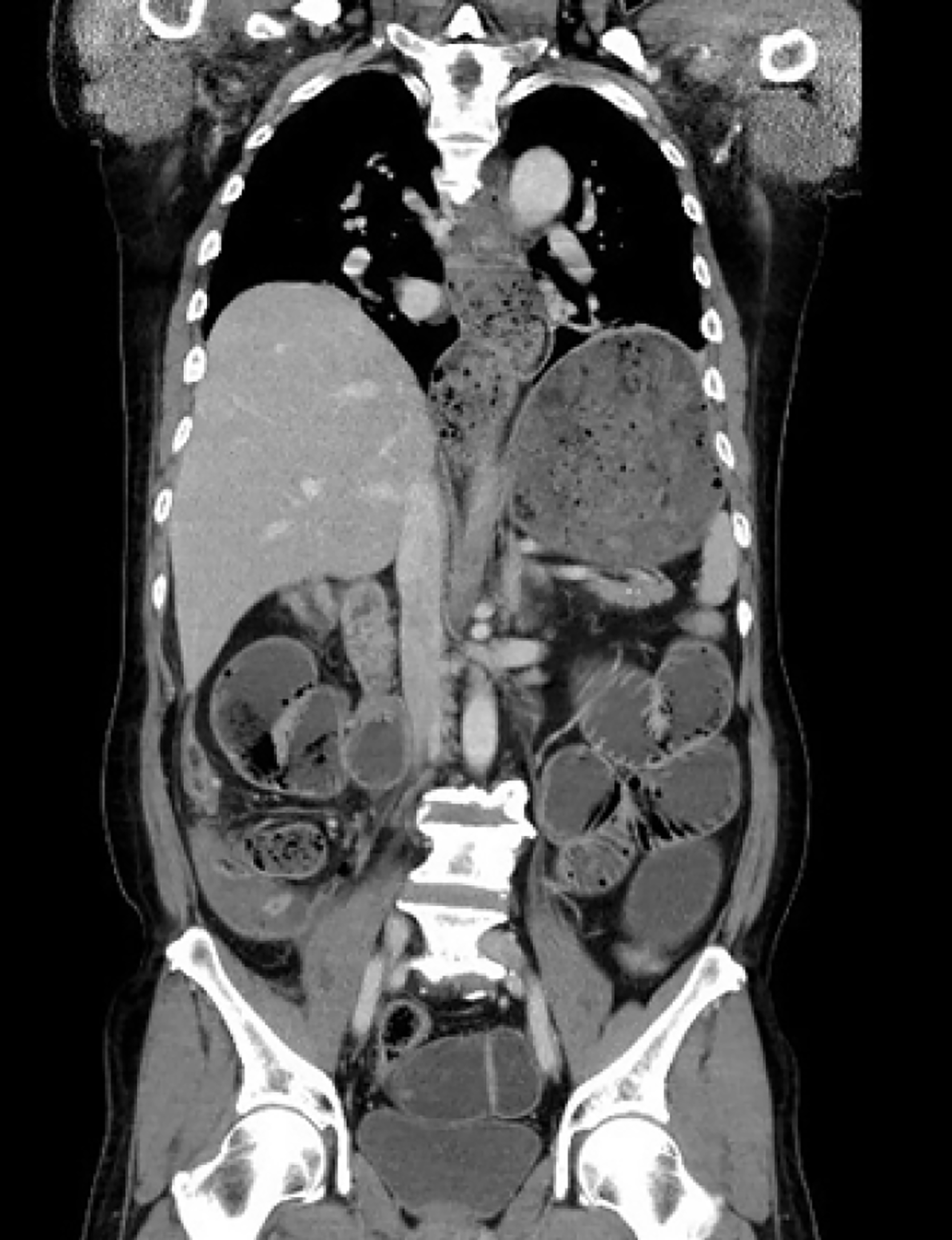
Figure 2 Abdominal computed tomography findings.
Digestive tract distension was shown from the esophagus to the small bowel.
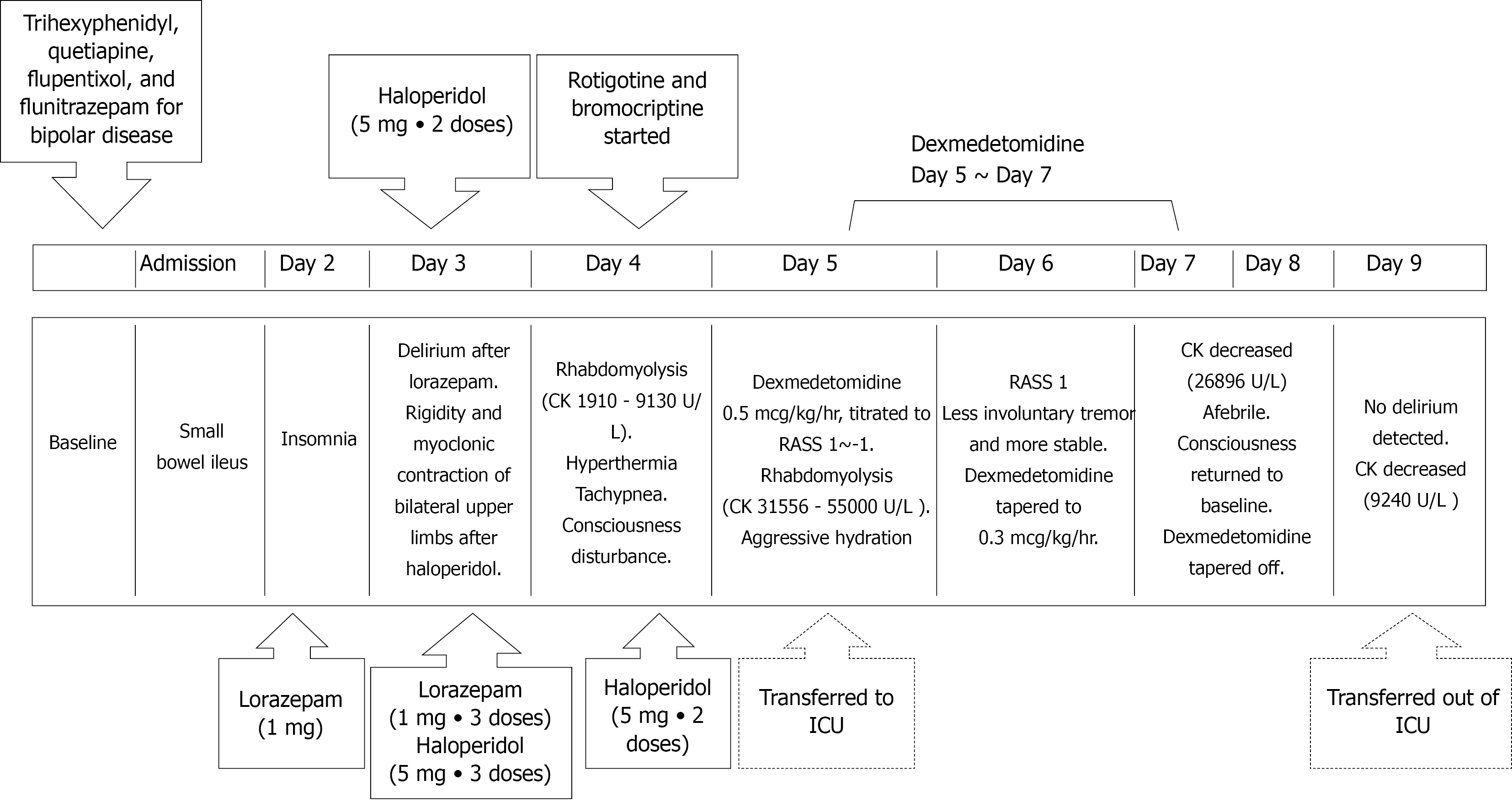
Figure 3 Timeline depicting the onset of lorazepam-induced delirium followed by the development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
CK: Creatine kinase; RASS: Richmond agitation-sedation scale; ICU: Intensive care unit.
- Citation: Yang CJ, Chiu CT, Yeh YC, Chao A. Successful management of delirium with dexmedetomidine in a patient with haloperidol-induced neuroleptic malignant syndrome: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(2): 625-630
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i2/625.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.625