Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 14, 2022; 10(2): 518-527
Published online Jan 14, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.518
Published online Jan 14, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.518
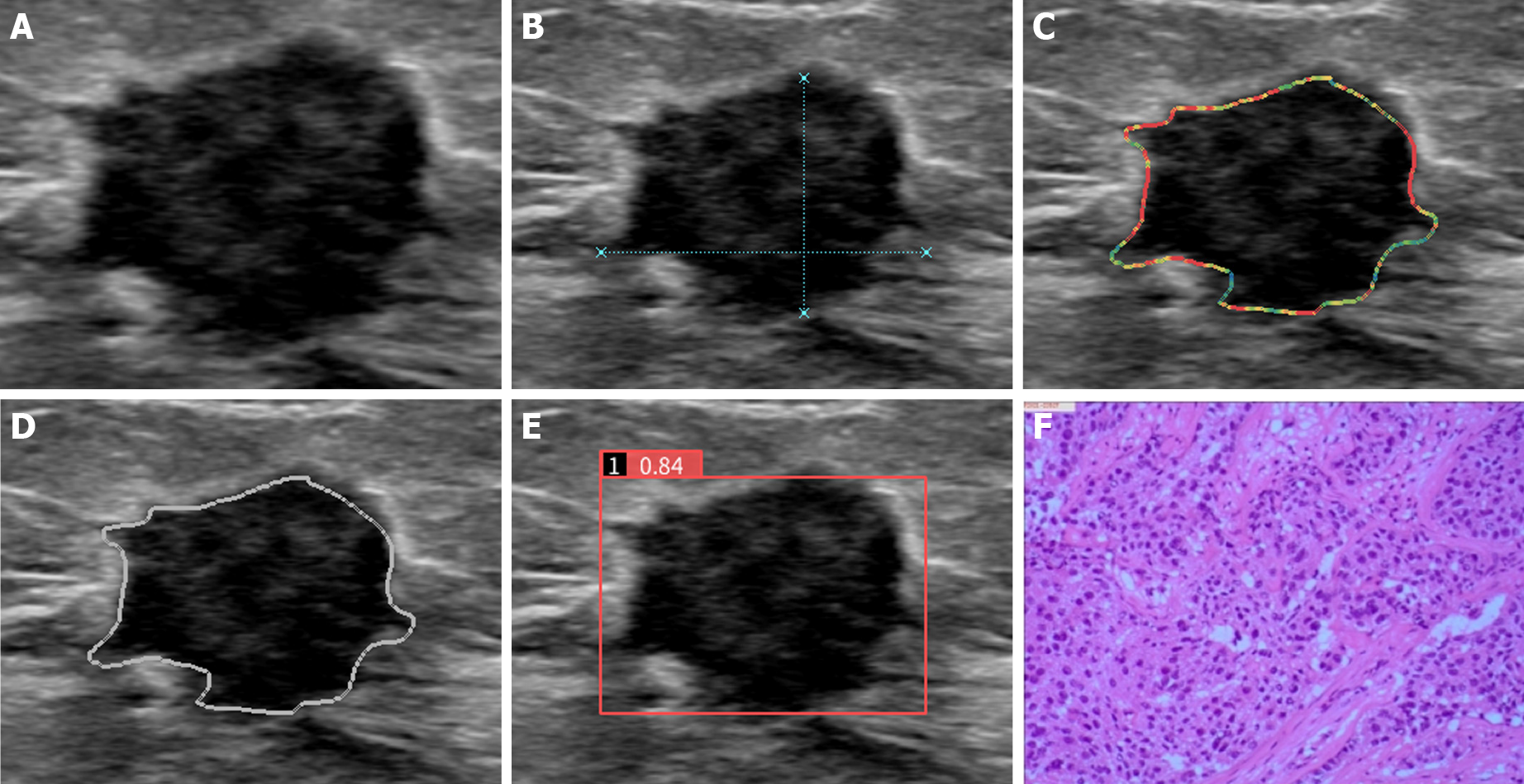
Figure 1 AI-SONIC breast system automatically recognizes markers and quantifies breast nodule characteristics.
BI-RADS 4C, breast invasive ductal carcinoma confirmed by pathological findings. A: Conventional ultrasound BI-RADS classification suggests BI-RADS 4C; B: Automatic measurement and display of the growth direction; C: Edge feature analysis: the color changes from blue, green, yellow and red in turn to clear to blur; D: The dotted red line represents a strong echo; E: Based on the longitudinal section of the right breast nodule, the benign and. malignancy probability of this lesion was 0.84, as detected by artificial intelligence; F: The pathological diagnosis was invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast.
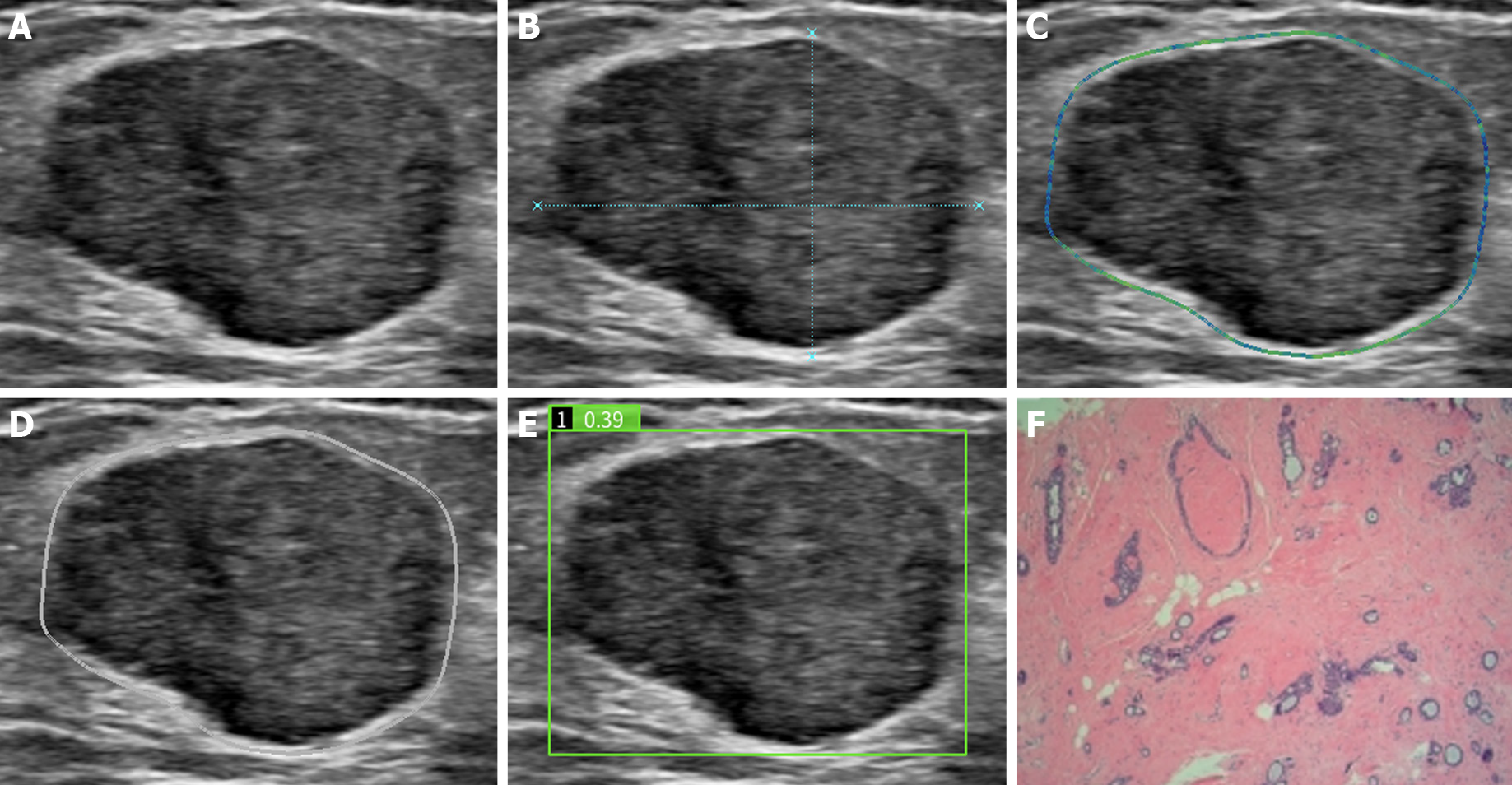
Figure 2 AI-SONIC breast system automatically recognizes markers and quantifies breast nodule characteristics.
BI-RADS 4A, breast fibroadenoma confirmed by pathological findings. A: Conventional ultrasound BI-RADS classification suggests BI-RADS 4A; B: Automatic measurement and display of the growth direction; C: Edge feature analysis: the color changes from blue, green, yellow and red in turn to clear to blur; D: The dotted red line represents a strong echo; E: Based on the longitudinal section of the right breast nodule, the benign and malignancy probability of this lesion was 0.39, as detected by artificial intelligence; F: The pathological diagnosis was fibroadenoma of the breast.
- Citation: Lyu SY, Zhang Y, Zhang MW, Zhang BS, Gao LB, Bai LT, Wang J. Diagnostic value of artificial intelligence automatic detection systems for breast BI-RADS 4 nodules. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(2): 518-527
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i2/518.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.518