Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2022; 10(18): 6325-6332
Published online Jun 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6325
Published online Jun 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6325
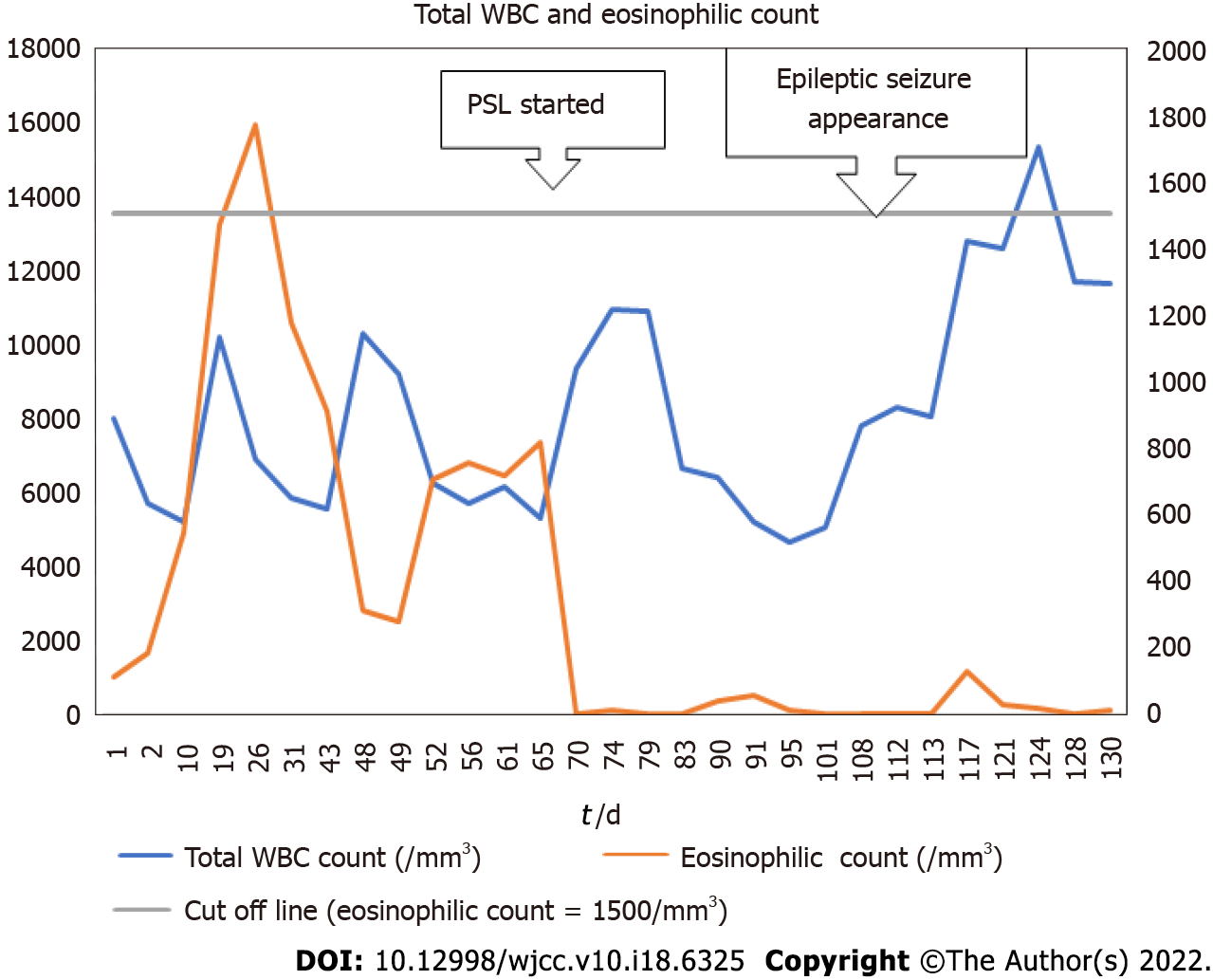
Figure 1 The patient’s serial blood test results showing changes in total white blood cells and eosinophil count.
The eosinophil count was automatically calculated from the ratio of eosinophils to total white blood cells. When the ratio was less than 0.1%, it was counted as 0. WBC: White blood cells; PSL: Prednisolone.
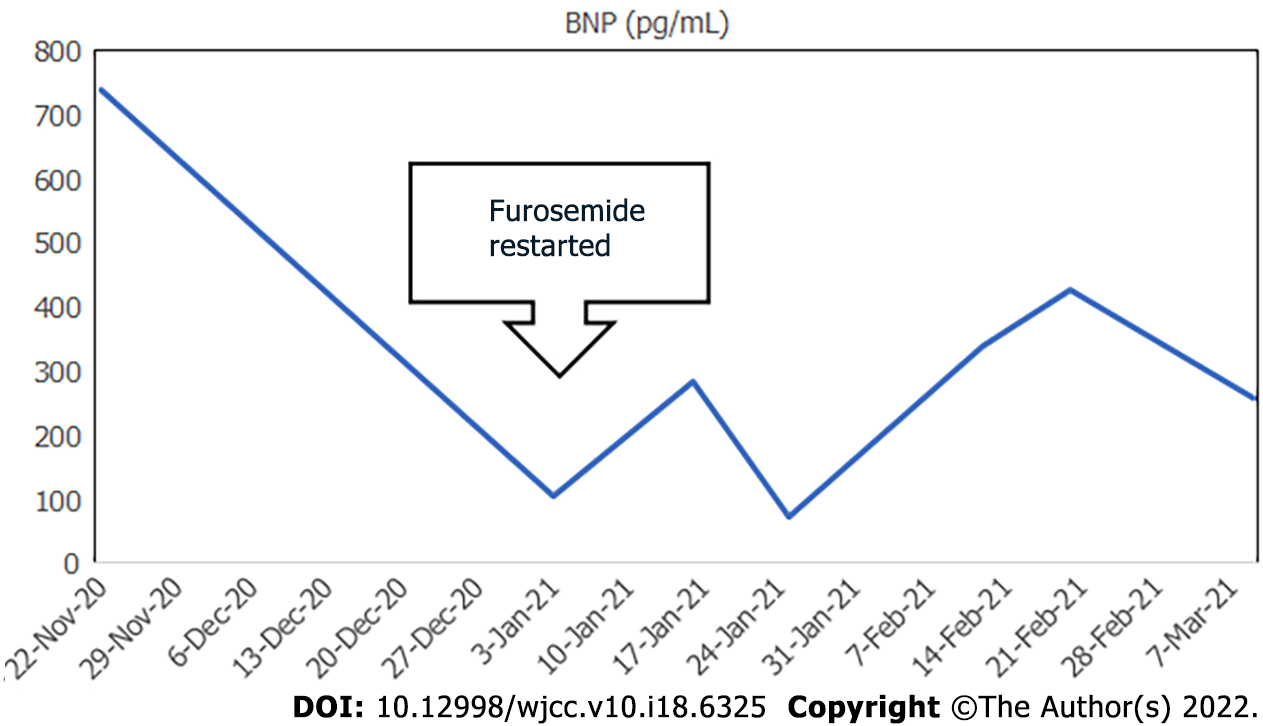
Figure 2 Serial changes in the patient’s brain natriuretic peptide values.
BNP: Brain natriuretic peptide.
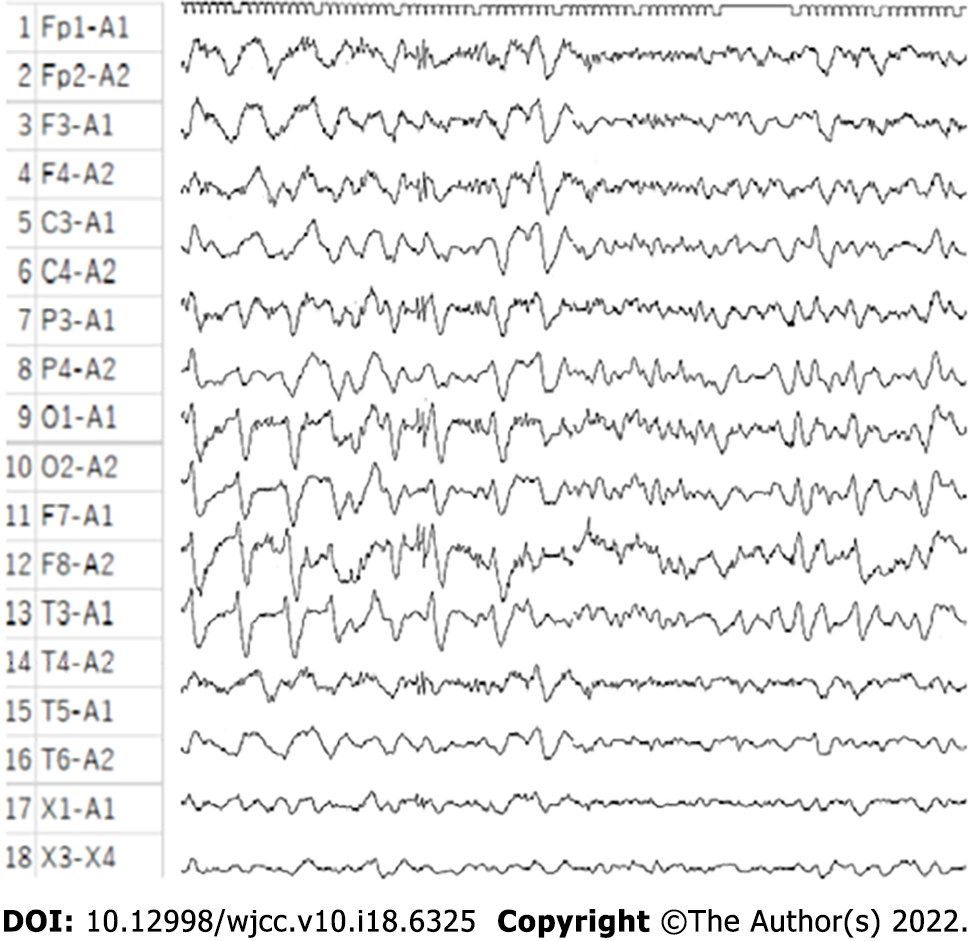
Figure 3 The patient’s post loss of consciousness electroencephalogram showing a slow wave indicative of a clinical epileptic seizure.
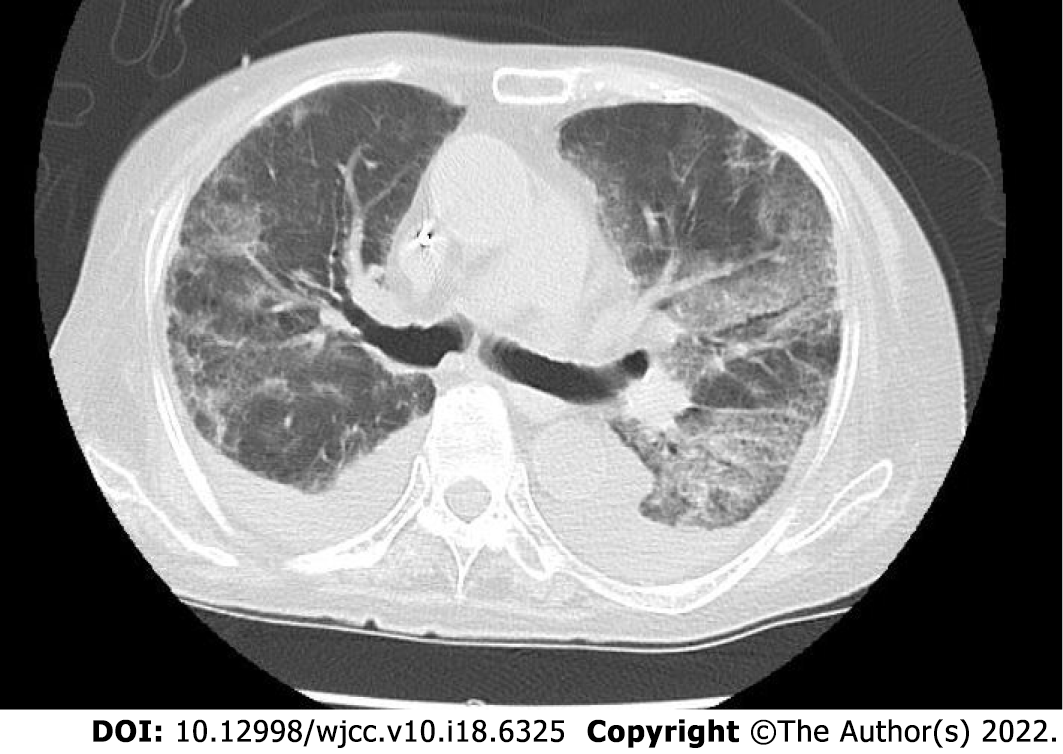
Figure 4 Non-contrast computed tomography image of the patient’s chest showing bilateral pleural effusions and infiltrative shadows.
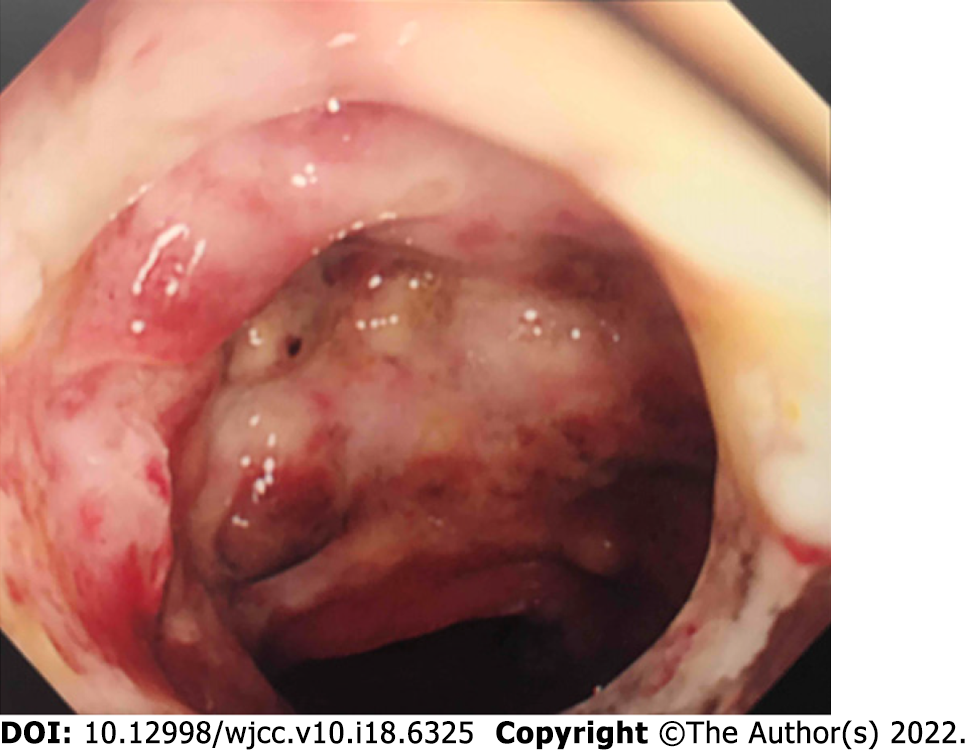
Figure 5 Gastrointestinal endoscopy image showing multiple mucosal ulcers in the sigmoid colon.
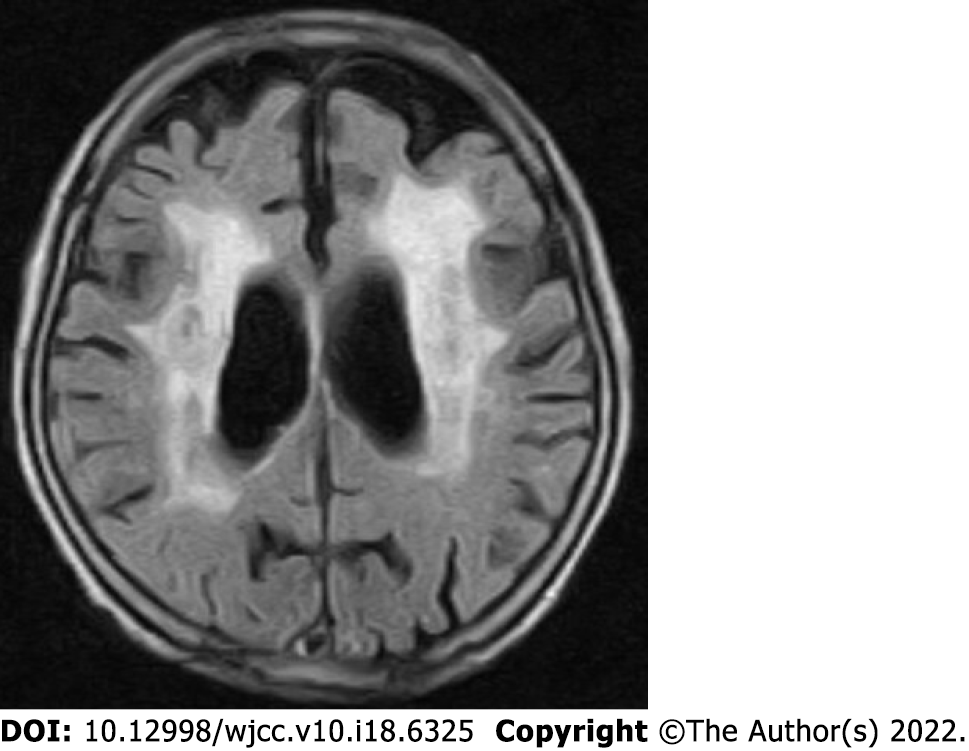
Figure 6 Non-contrast magnetic resonance imaging of the patient’s head showing extensive periventricular hyperintensity.
- Citation: Ishida T, Murayama T, Kobayashi S. Pneumonia and seizures due to hypereosinophilic syndrome—organ damage and eosinophilia without synchronisation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(18): 6325-6332
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i18/6325.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6325