Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2022; 10(18): 6021-6031
Published online Jun 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6021
Published online Jun 26, 2022. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6021
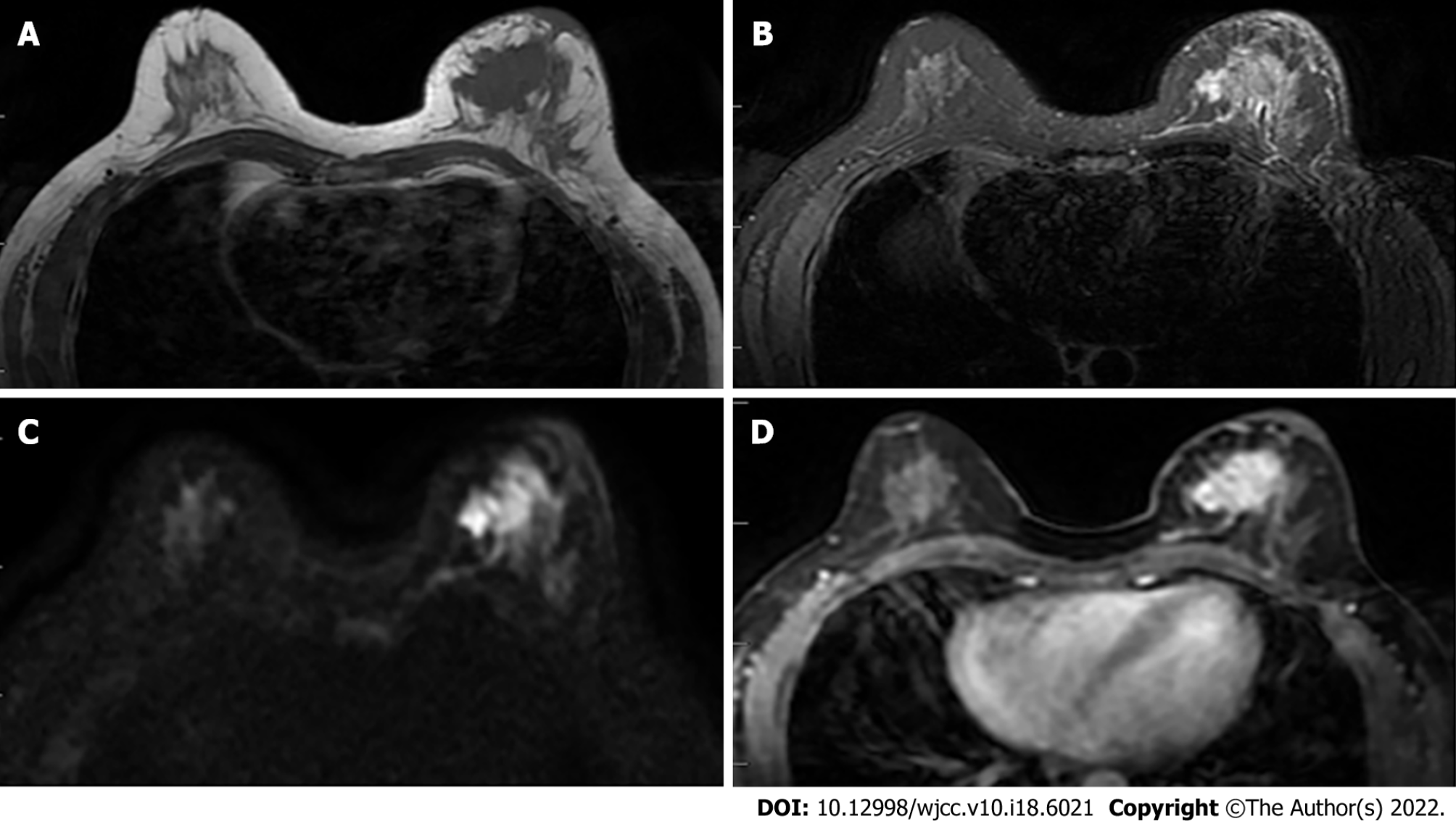
Figure 1 Female, 52 years old, breast carcinoma.
A and B: The left breast mass in T1WI and T2WI fat-saturated sequence is shown as a long T1 and long T2 signal shadow; C: The left breast mass is shown as a high signal in the diffusion-weighted imaging image; D: Obvious enhancement of the tumor in the transverse section of the enhanced scan.
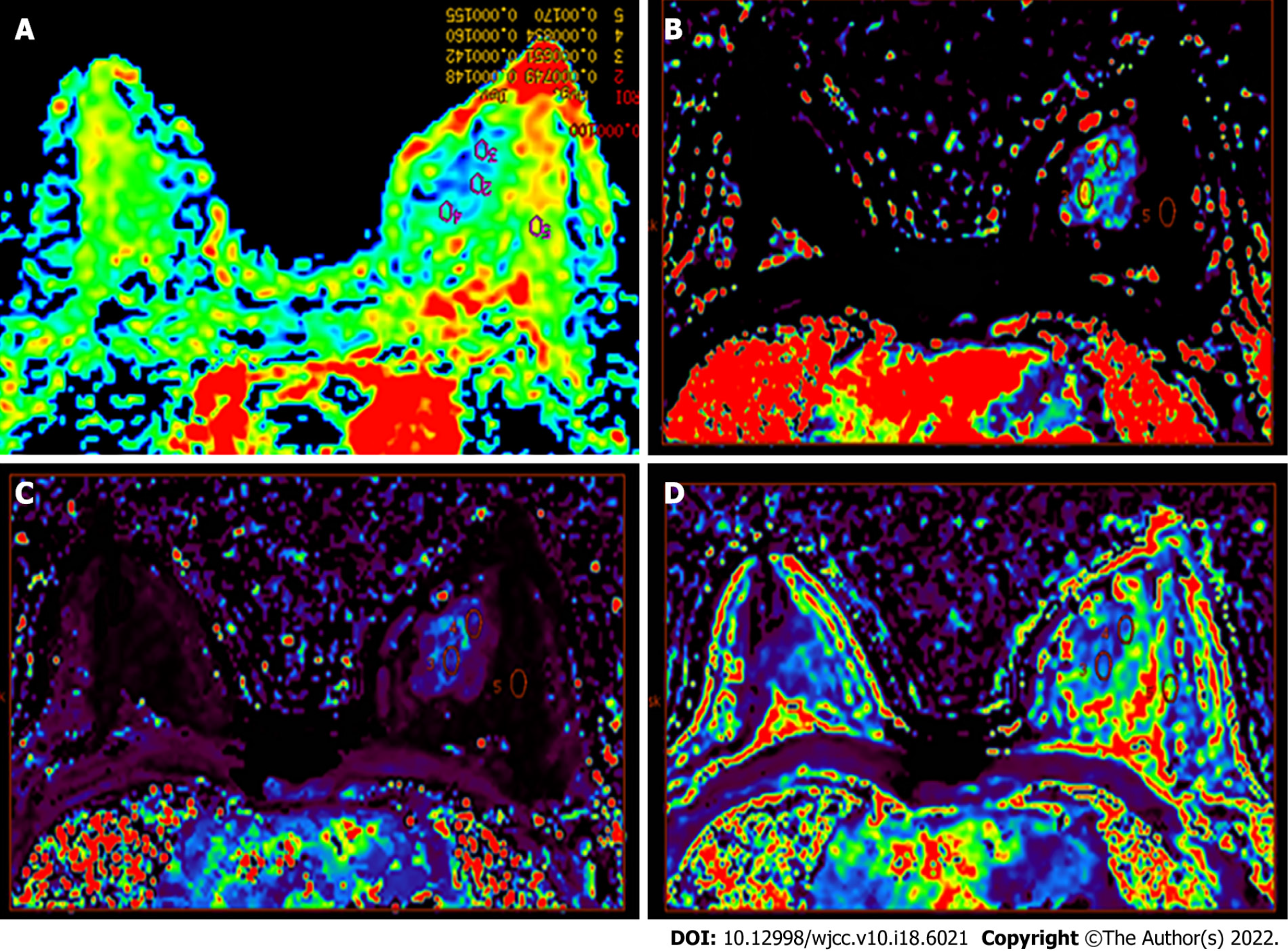
Figure 2 Color image.
A: The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) color image allows the multipoint measurement of the ADC value; B-D: Multipoint measurement of olume transfer constant (Ktrans) (B), rate constant (Kep) (C), and extravascular extracellular volume fraction (Ve) (D) of the lesions and adjacent normal tissues.
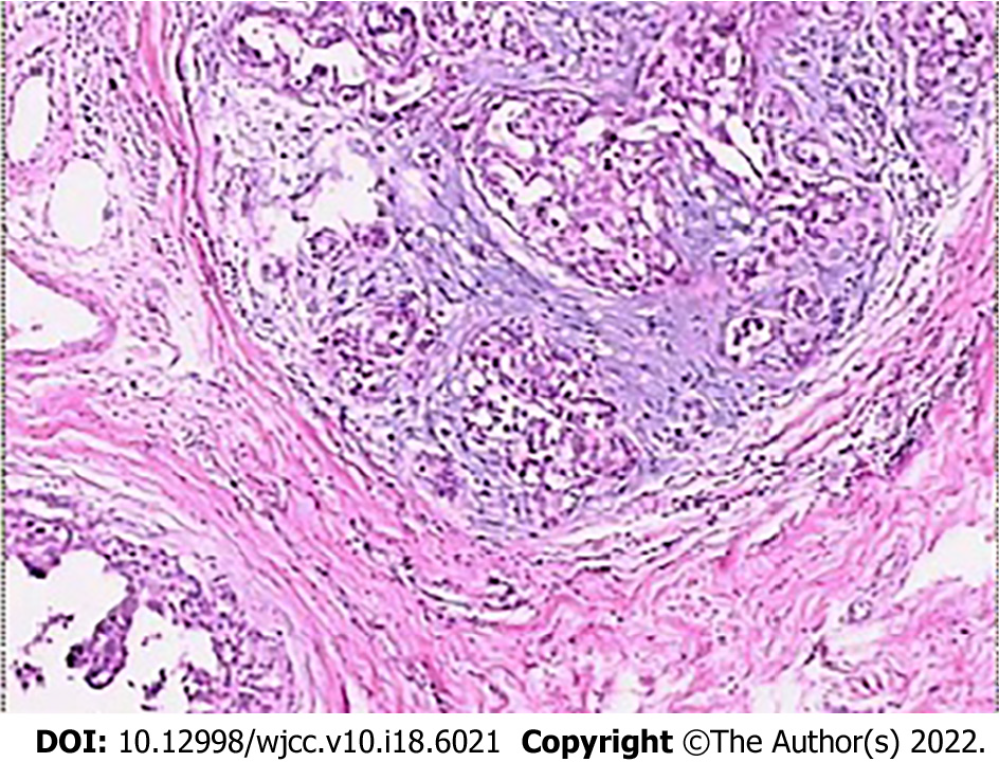
Figure 3 Histopathological examination showing moderate nuclear grade ductal carcinoma in situ, with stove shape II invasive ductal carcinoma (HE × 100).
- Citation: Zhang H, Zhang XY, Wang Y. Value of magnetic resonance diffusion combined with perfusion imaging techniques for diagnosing potentially malignant breast lesions. World J Clin Cases 2022; 10(18): 6021-6031
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v10/i18/6021.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6021