Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2013; 1(3): 108-110
Published online Jun 16, 2013. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v1.i3.108
Published online Jun 16, 2013. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v1.i3.108
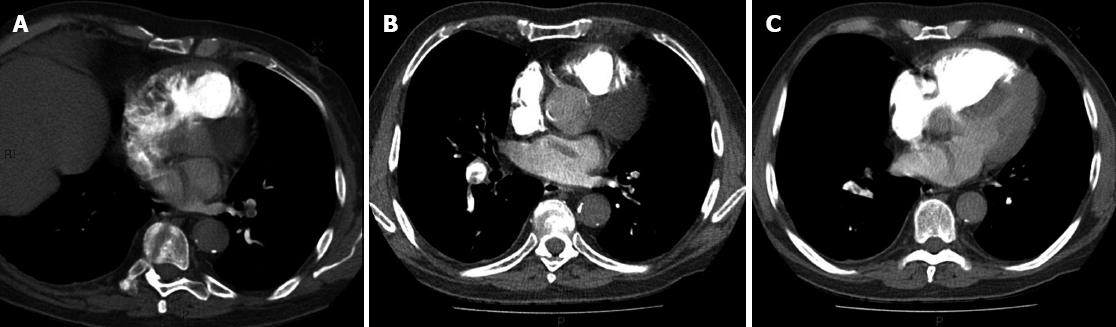
Figure 1 Findings at computed tomographic pulmonary angiography.
A: Computer tomography pulmonary angiogram (CDPA) demonstrating a serpiginous low attenuation filling defect in the left atrium which extends across into the right atrium through a patent foramen ovale representing a paradoxical embolus (oblique axial view). There are also filling defects in the left lower lobe pulmonary artery due to pulmonary emboli; B: Demonstrating a filling defect in the left atrium filling defects in the right lower lobe pulmonary artery due to pulmonary emboli (axial view); C: CDPA demonstrating a filling defect in the left atrium, abutting the intra-atrial septum and bowing of the intra-ventricular septum due to raised right heart pressure (axial view).
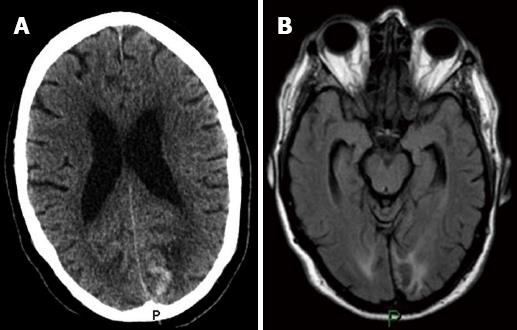
Figure 2 Neurological imaging.
A: Unenhanced computer tomography brain examination (axial view) demonstrating left occipital high attenuation with surrounding low attenuation; B: Magnetic resonance imaging brain examination (axial view, FLAIR sequence) demonstrating left occipital lobe infarct with haemorrhagic transformation.
- Citation: Cormack L, Murchison JT. Paradoxical embolus straddling patent foramen ovale demonstrated by computed tomographic pulmonary angiography. World J Clin Cases 2013; 1(3): 108-110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v1/i3/108.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v1.i3.108