Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Nephrol. Sep 6, 2016; 5(5): 482-488
Published online Sep 6, 2016. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v5.i5.482
Published online Sep 6, 2016. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v5.i5.482
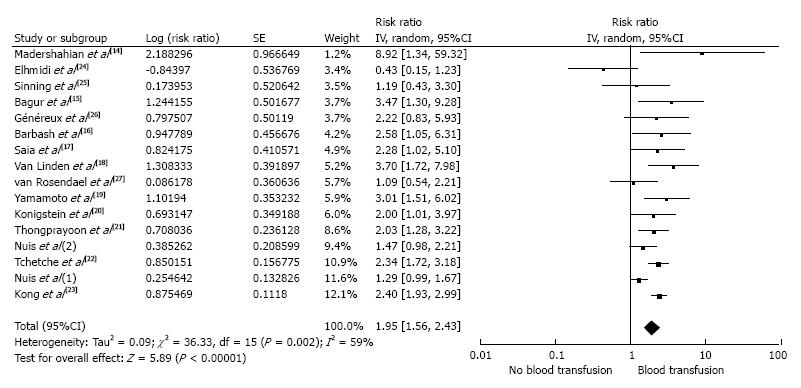
Figure 1 Forest plot of comparing the risk of acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement in patients who received red blood cell transfusion and those who did not.
Square data markers represent risk ratios (RRs); horizontal lines, the 95%CIs with marker size reflecting the statistical weight of the study using random-effects meta-analysis. A diamond data marker represents the overall RR and 95%CI for the outcome of interest.
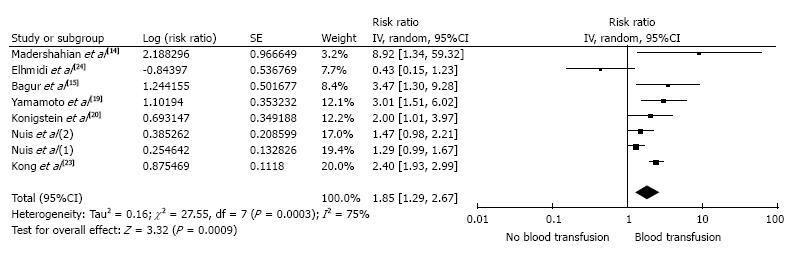
Figure 2 Forest plot of the adjusted analysis comparing the risk of acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement in patients who received red blood cell transfusion and those who did not.
The square data markers represent represent risk ratios (RRs); horizontal lines, the 95%CIs with marker size reflecting the statistical weight of the study using random-effects meta-analysis. A diamond data marker represents the overall RR and 95%CI for the outcome of interest.
- Citation: Thongprayoon C, Cheungpasitporn W, Gillaspie EA, Greason KL, Kashani KB. Association of blood transfusion with acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A meta-analysis. World J Nephrol 2016; 5(5): 482-488
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v5/i5/482.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v5.i5.482