Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
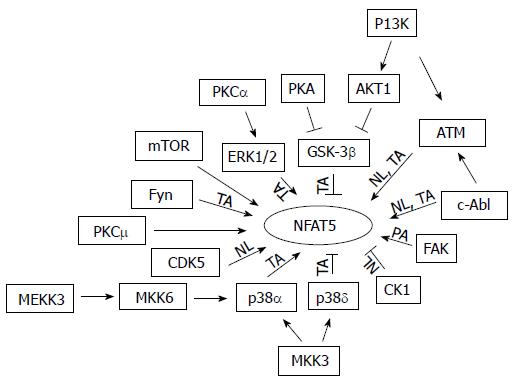
Figure 1 Summary of kinases known to regulate tonicity-dependent activation/inactivation of NFAT5 through an increase/decrease of its transactivating activity, nuclear localization and/or protein abundance.
If none of these three steps appears with an arrow, this means that the mechanism is unknown. mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; TA: Transactivating activity; NL: Nuclear localization; PA: Protein abundance; PKA: Protein kinase A; PKC: Protein kinase C; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; CDK: Cyclin dependent kinase.
- Citation: Zhou X. How do kinases contribute to tonicity-dependent regulation of the transcription factor NFAT5? World J Nephrol 2016; 5(1): 20-32
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v5/i1/20.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v5.i1.20