Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
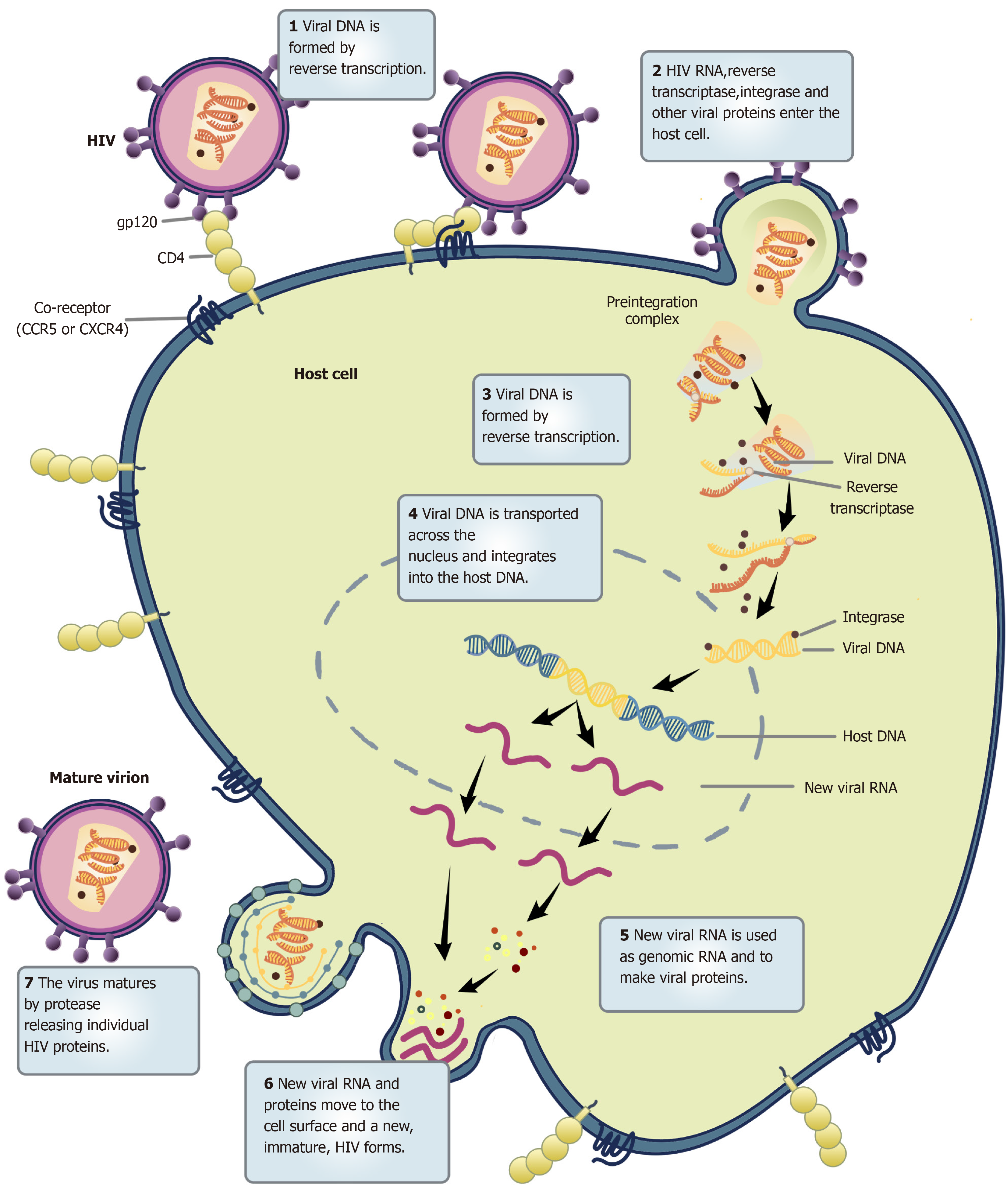
Figure 1 The mechanism by which human immunodeficiency virus attacks a target cell.
HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
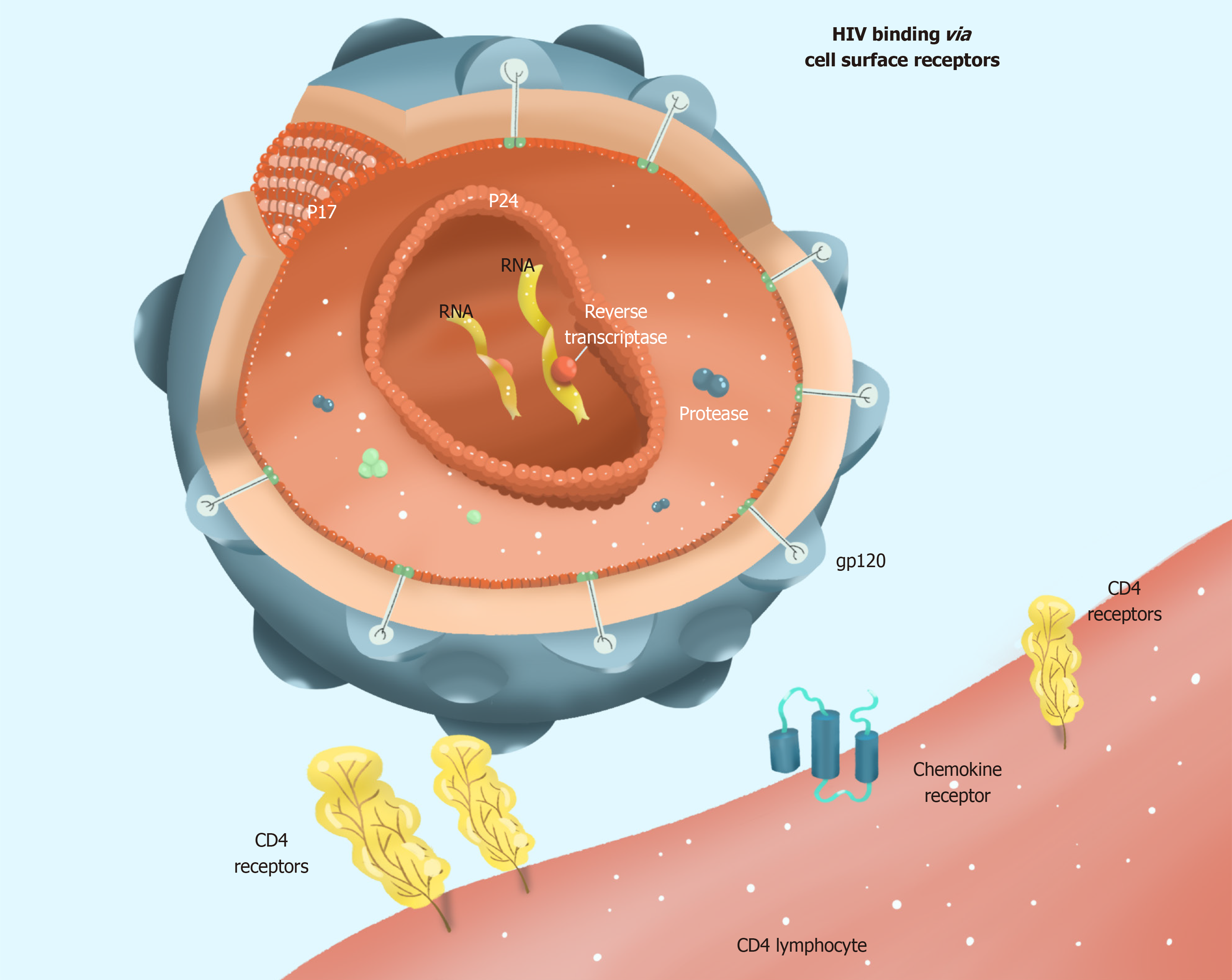
Figure 2 Human immunodeficiency virus recognizes and binds a CD4 lymphocyte.
HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
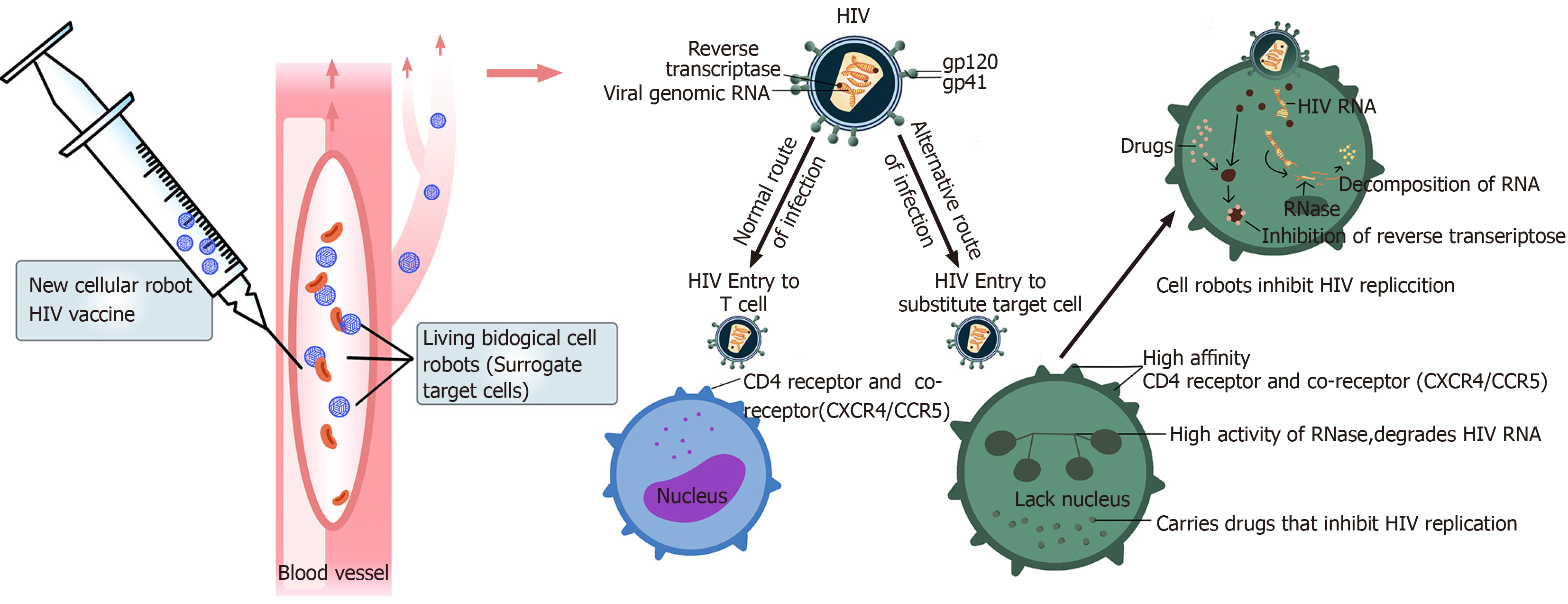
Figure 3 Functions of a living biological cell robot.
After entering the body, the living cell robot mediates human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection by the high-affinity receptor expressed on the cell surface, and HIV is killed by drugs or RNase carried by the cell. HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
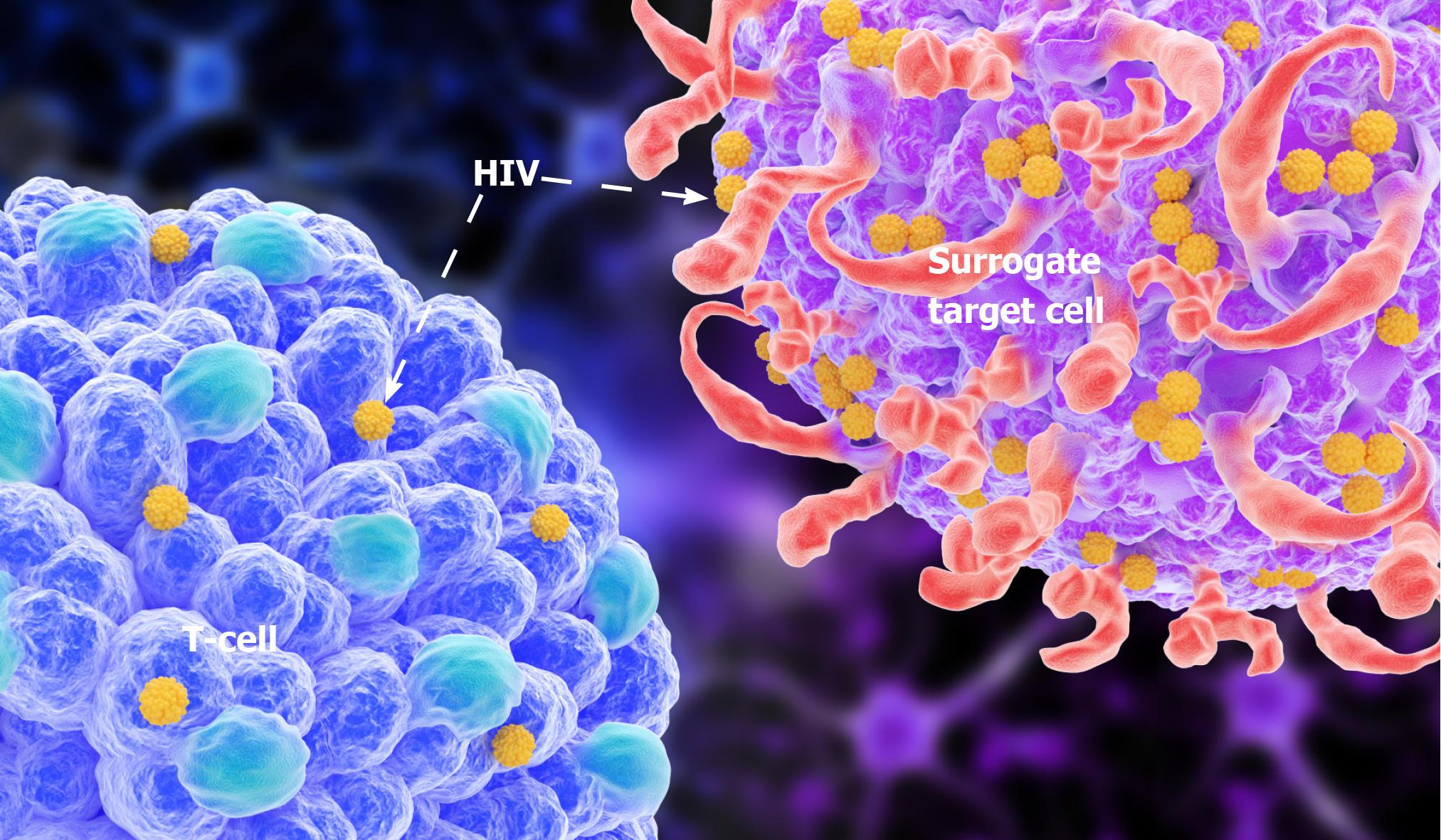
Figure 4 A simulation of human immunodeficiency virus infecting a surrogate target cell by the alternative infection.
By blocking the receptor on the T cell surface with the blocking antibody, the probability of human immunodeficiency virus infection surrogate target cell will increase. HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
- Citation: Xie YY, Yang F, Liao XY. Hypothesis of design of biological cell robot as human immunodeficiency virus vaccine. World J Virol 2020; 9(3): 19-26
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v9/i3/19.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v9.i3.19